
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
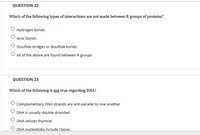
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 22
Which of the following types of interactions are not made between R groups of proteins?
Hydrogen bonds
lonic bonds
Disulfide bridges or disulfide bonds
O All of the above are found between R groups
QUESTION 23
Which of the following is not true regarding DNA?
Complementary DNA strands are anti-parallel to one another
DNA is usually double stranded
DNA utilizes thymine
DNA nucleotides include ribose
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 65 Which statement best explains why alcohols have a higher boiling point than Alcohols have weaker intermolecular forces than alkanes. Alcohols have London dispersion forces only and alkanes have dipole-dipole attracti None of the choices are correct. Alcohols have stronger London dispersion forces than alkanes. Alcohols have strong hydrogen bonding forces between molecules and alkanes have Question 66 Which statement concerning the double helix structure of DNA is FALSE? The helix completes one turn every 10 base pairs. The two strands of the double helix are called parallel strands. Base pairs in the double helix are attached by way of hydrogen bonding. The base pairs are directed in toward the middle of the double helix. In the double helix, adenine connects to thymine and cytosine connects to guanine. Darrow_forwardQUESTION 22 When double-stranded DNA is heated at neutral pH, which change does not occur? The N-glycosidic bond between the base and the pentose breaks The helical structure unwinds The absorption of ultraviolet (260 nm) light increases The viscosity of the solution decreases The hydrogen bonds between A and T breakarrow_forwardQUESTION 1 The relative amounts of each nucleotide base are tabulated below for four different viruses. Virus T CUG A 1 34 42 0 18 39 || III 0 24 35 27 17 0 12 9 12 9 IV 23 16 0 16 23 For each virus, indicate whether its genetic material is DNA vs. RNA and double-stranded vs. single-stranded by putting the correct letter in the box next to each virus. Every choice will be used once and only once. Virus I: Virus II: Virus III: Virus IV: a. Single-stranded DNA b. Double-stranded DNA c. Single-stranded RNA d. Double-stranded RNAarrow_forward
- Question 12 Which of the following best explains the relatively more complex folded structure that an RNA molecule assumes? A B с D RNA molecules do not contain a pentose sugar in their backbone, which allows them to be more structurally flexible. RNA molecules contain the nitrogenous base uracil, which can pair with several other ni- trogenous bases in the RNA molecule. RNA molecules contain negatively charged phosphate groups in their backbone, which allows the molecule to bend into complex shapes. RNA molecules are made of only four types of nucleotides, which allows their nitroge- nous base to pair more readily.arrow_forwardQUESTION 25 Phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, and ubiquitylation are all ways to: Regulate carbohydrates using small molecules O Turn on and off the activity of proteins O Remove amino acids from proteins O Join proteins togetherarrow_forwardQuestion 6 Which of the following are differences between DNA and RNA? (select all that apply) DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded DNA and RNA have different sugar molecules in their sugar-phosphate backbone DNA is found in the nucleus, RNA is only found in the cytoplasm DNA is a long-lasting molecule, RNA is destroyed very quickly Ouontiarrow_forward
- Question 3 (1 pt): Which positions in adenine and guanine have the potential to form hydrogen bondsbut are not involved in Watson-Crick base pairing? What might this be used for?1 of 2arrow_forwardQUESTION 10 Select all of the true statements regarding the molecule below: NH, -P-O NH G OH NH, О-Р-О- H,N N- A ОН -P-O `NH U ОН 0-P-O- N' ОН ОН This is RNA This is DNA This chain is a polymer. The backbone of these nucleotides is a ribose sugar This nucleic acid is the hereditary material for humans. This nucleic acid is the hereditary material for coronaviruses. This type of nucleic acid is never found in healthy human cells. This nucleic acid contains the nucleobase thymine.arrow_forwardQuestion 7 Which is best explanation of "Law of Base Paring?" O determines the type of protein produced O allows variable width of the double helix O adenine forms hydrogen bonds with thymine and cytosine forms hydrogen bonds with guanine O permits DNA bind to protein molecules during DNA replication determines the tertiary structure of a DNA molecule Question 8arrow_forward
- Question 4. Imagine the main chain of a protein bends back on itself so that two amino acid residues R1 and R2 come close to each other. In the table below are four possibilities for what R1 and R2 might be. In each case, decide whether a specific interaction could form between the residues. If a specific interaction could form, give the name of the interaction. R₁ cysteine tyrosine threonine arginine R₂ cysteine phenylalanine glutamine aspartate specific interaction? OO yes O yes O no no OO O yes no yes no name of specific interaction 0 П 0 0arrow_forwardQUESTION 27 Which of the following has (have) both a favorable hydrogen bonding pattern and o and W values that fall within the allowed Ramachandran conformational regions? alpha-helix collagen helix all of the above none of the above B sheet O O O O Oarrow_forwardQuestion 16 Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the comparison of the alpha-helix structure to the beta-sheet structure in proteins? O The peptide bond in each is planar and trans O Each is stabilized by inter-chain hydrogen bonds O All possible hydrogen bonds between the peptide carbonyl oxygen (C=O) and the amide hydrogen (N-H) are formed in each O Each may occur in typical globular proteins O Each is an example of secondary structurearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education