
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
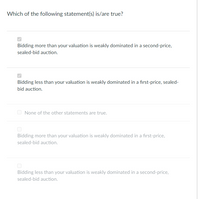
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
Bidding more than your valuation is weakly dominated in a second-price,
sealed-bid auction.
Bidding less than your valuation is weakly dominated in a first-price, sealed-
bid auction.
O None of the other statements are true.
Bidding more than your valuation is weakly dominated in a first-price,
sealed-bid auction.
Bidding less than your valuation is weakly dominated in a second-price,
sealed-bid auction.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4. An auctioneer holds a second-price auction for two bidders, Ann (A) and Bonnie (B), who have independent private values of the good 0, and 0g If a bidder wins, her payoff is her value 0 minus the price she pays, and if she loses, her payoff is 0. The values are independently and identically distributed, but otherwise you don't need to know the specific distributions to solve the problem. Ann and Bonnie's respective strategies are to bid some value b0), that is, bid given their privately-known value (type). e. Suppose the good had one true value for both bidders equal to the average of 0, and e, (signals that are still i.i.d.); hence, the good's true value has a common component. Suppose Ann knows Bonnie is going to bid her own evaluation 0, no matter what, but like normal, Ann doesn't know 0g. Explain why bidding 0, is now a strictly dominated strategy for Ann.arrow_forwardTwo competing firms are each planning to introduce a new product. Each will decide whether to produce Product A, Product B, or Product C. They will make their choices at the same time. The resulting payoffs are shown to the right. Are there any Nash equilibria in pure strategies? If so, then what are they? O A. The Nash equilibria are for both firms to introduce Product B and for both firms to introduce Product A. O B. The Nash equilibria are for Firm 1 to introduce Product B and Firm 2 to introduce Product C and for Firm 1 to introduce Product C and Firm 2 to introduce Product B. O C. The Nash equilibria are for Firm 1 to introduce Product A and Firm 2 to introduce Product B and for Firm 1 to introduce Product B and Firm 2 to introduce Product A. O D. The Nash equilibria are for Firm 1 to introduce Product A and Firm 2 to introduce Product C and for Firm 1 to introduce Product C and Firm 2 to introduce Product A. There are no Nash equilibria. O E. If both firms use maximin strategies,…arrow_forward1arrow_forward
- PLEASE CHECK THIS HOW TO SOLVEarrow_forwardP1| P2 Left Middle Right Left 4,2 3,3 1,2 Middle 3,3 5,5 2,6 Right 2,1 6,2 3,3 Consider the simultaneous move game represented by this payoff matrix. Suppose that the game is repeated for two periods and the players know that the game will end at the end of two periods. They observe the first period outcome before they move to the second period. Assume that there is no discounting, i.e. 2nd period payoffs are not discounted, or the discount factor is equal to 1. Which of the following outcomes could occur in some subgame perfect equilibrium (SPE) of this repeated game? Choose True if you think the outcome can be a SPE, otherwise choose False. a) (Left, Left) is played in both periods. b) (Right, Right) is played in both periods. c) (Middle, Middle) is played in both periods. d) (Middle, Middle) is played in the first period, followed by (Left, Left). e) (Middle, Middle) is played in the first period, followed by (Right, Right).arrow_forwardWhich one of the following descriptions is CORRECT?arrow_forward
- You should show that the best response map gives a fixed-point in symmetric strategies help pleasearrow_forwardThere are 4 bidders with valuations that are independently and uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. In equilibrium, what is the probability that the highest bid is less than 0.2 in a first-price auction? Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardConsider the following matrix Firm A Firm B Low Price High Price Low Price 6,5 High Price 4,11 10,3 8,9 Which of the following statements is true regarding the players' secure strategies? Both firms have a secure strategy to play low price. O Neither firm has a secure strategy to play low price. Ⓒ Only Firm A has a secure strategy to play low price. O Only Firm B has a secure strategy to play low price.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education