
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
13. bubbled is the wrong answer
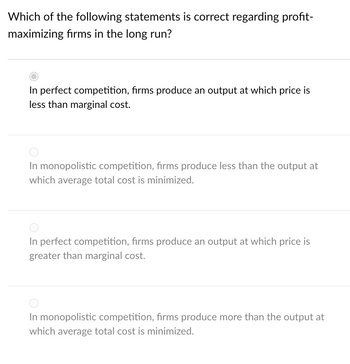
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following statements is correct regarding profit-
maximizing firms in the long run?
In perfect competition, firms produce an output at which price is
less than marginal cost.
In monopolistic competition, firms produce less than the output at
which average total cost is minimized.
In perfect competition, firms produce an output at which price is
greater than marginal cost.
In monopolistic competition, firms produce more than the output at
which average total cost is minimized.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- N=2 video broadcasting websites, You and Twi, must decide the number of minutes of ads to be displayed for every video that the user elects to watch. Let tY be the number of ad-minutes per video set by You, and tT the number of ad-minutes per video set by Twi. Streaming one video costs You cY=0.02, while it costs Twi cT=0.03. There are 100 million potential users, and each watches videos according to the following demand curves: qY((tY,tT) =10-2tY+tT=10-2tT+tY a- What is the cross-price elasticity between You and Twi? b- Suppose, for now, that You and Twi enter an (illegal) agreement by which they set tY=tT=t Derive the total number of users in the market as a function of t. Derive the profits for each website as a function of t. c- Now let the two platforms compete by each setting their number of ad-minutes: i. What is the best reply of You? What is the best reply of Twi? ii. Find the Nash Equilibrium of the game. iii. How many total users choose You and how many total users choose…arrow_forward21) Games Galore has a new video game that it hopes will increase its sales. It is offering coupons and a sweepstake to get people to buy the game. These are all examples of A) personal selling. B) direct retail. C) publicity. D) sales promotion. E) advertising. 21)arrow_forward5. To advertise or not to advertise Suppose that two firms, Hatte Latte and Bean Bruuer, are the only sellers of espresso in some hypothetical market. The following payoff matrix gives the profit (in millions of dollars) earned by each company depending on whether or not it chooses to advertise: Hatte Latte Advertise Doesn't Advertise Advertise 10, 10 Bean Bruuer 2,18 Doesn't Advertise 18, 2 11, 11 For example, the lower left cell of the matrix shows that if Bean Bruuer advertises and Hatte Latte does not advertise, Bean Bruuer will make a profit of $18 million, and Hatte Latte will make a profit of $2 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Hatte Latte and Bean Bruuer are both profit-maximizing firms. If Hatte Latte chooses to advertise, it will earn a profit of $ does not advertise. If Hatte Latte chooses not to advertise, it will earn a profit of $ Bruuer does not advertise. million if Bean Bruuer advertises and a profit of $ million if Bean Bruuer advertises and a…arrow_forward
- 9. Find all of the Nash equilibria for the three-player game here. Player 1 a b Player 3: A Player 2 X y Z 1,1,0 2,0,0 2,0,0 3,2,1 1,2,3 0,1,2 2,0,0 0,2,3 3,1,1 Player 1 a b C Player 1 Player 3: C X Player 2 y 2,0,0 0,1,2 0,1,1 1,2,1 3,1,2 0,1,2 a b C Player 3: B Player 2 X 2,0,0 1,2,0 0,1,2 Z 0,1,2 0,1,2 1,1,2 y 0,0,1 1,2,1 2,2,1 Z 2,1,2 1,2,1 2,1,0arrow_forwardQUESTION 38 What are the two routes that we use to process information, according to the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM)? O central & minor O central & peripheral O fundamental & peripheral O dominant & central QUESTION 39 Which statement best explains the Extended Parallel Processing Model's take-home message? O Fear appeals are most effective when they get the attention of their audience but are not so intense as to induce too high levels of fear. The more intense a fear appeal, the less successful it will be at enacting behavior change. Fear appeals are more successful if they are more intense. O Fear appeals simply do not work in changing behaviors.arrow_forwardSub : EconomicsPls answer very fast.I ll upvote. Thank You In each of the following games, how many pure strategies (complete plans of action) are available to each player? List all of the pure strategies for each player.arrow_forward
- 4. Finding Nash equilibria in sequential games Hubert and Larry are trying to decide what movie to see together. There are two theaters in town, each playing one movie. Hubert would prefer to see one movie (call it movie H) and Larry would prefer to see the other movie (movie L), but both would prefer to see one of the movies together rather than their preferred movies separately. As they are discussing where to meet, Larry's cell phone loses power, cutting the conversation short. Both movies start in 10 minutes; therefore, each person must decide which movie to see without being able to communicate with the other. The following payoff matrix represents the game they are playing. Hubert Movie H Movie L Hubert Larry Movie H 45, 30 0,0 Suppose Larry is near home and quickly starts charging his phone. At home, however, he gets terrible phone service but a strong wireless signal. Therefore, instead of calling Hubert, he uses a smartphone app to observe Hubert's location using GPS. Because…arrow_forward8. Solving for dominant strategies and the Nash equilibrium Suppose Tim and Alyssa are playing a game in which both must simultaneously choose the action Left or Right. The payoff matrix that follows shows the payoff each person will earn as a function of both of their choices. For example, the lower-right cell shows that if Tim chooses Right and Alyssa chooses Right, Tim will receive a payoff of 3 and Alyssa will receive a payoff of 6. Tim Left Left 5, 6 Right 4, 2 Alyssa Right 5,5 3,6 The only dominant strategy in this game is for to choose The outcome reflecting the unique Nash equilibrium in this game is as follows: Tim chooses and Alyssa choosesarrow_forward6. Eventually, Aron and Nora who we met in the previous problem were able to get together and have now been an item for some time. So long, in fact, that there are issues. Aron is a little insecure, which makes him jealous. Nora is none too pleased about it. When she arranges a girls' night out with some of her friends, Aron is very upset and threatens to break up. So Nora has to decide to go out with her friends or stay home with Aron. If she stays home, she gets a payoff of 0, whereas Aron gets what he wants and a payoff of 2 (perhaps he should be a little more concerned with Nora's happiness). On the other hand, if Nora decides to go out, then Aron must make a choice between breaking up or not. If he breaks up, both he and Nora are miserable and each receives a payoff of -1. If he does not, he gets a payoff of 1 while Nora gets what she wants and a payoff of 2. a) Draw the extensive form of this game. b) Find all Nash equilibria. Explain your answer carefully. c) Find the backward…arrow_forward
- Potential Entrant Enter Stay Out Incumbent (100, 800) High Prices Low Prices (300, 500) (-100, 400) 11. Consider the entry-deterrence game above. In this game the Incumbent Firm has a. an incentive to threaten high prices, which would be credible. b. an incentive to threaten low prices, which would be credible. an incentive to threaten high prices, which would be an empty threat. d. an incentive to threaten low prices, which would be an empty threat. no incentive to make a threat. с. е.arrow_forward5.q1arrow_forward7. Solving for dominant strategies and the Nash equilibrium Suppose Russell and Aaliyah are playing a game that requires both to simultaneously choose an action: Up or Down. The payoff matrix that follows shows the earnings of each person as a function of both of their choices. For example, the upper-right cell shows that if Russell chooses Up and Aaliyah chooses Down, Russell will receive a payoff of 6 and Aaliyah will receive a payoff of 4. Russell Up Down Aaliyah Up 6,3 3,3 Down 6,4 7,4 In this game, the only dominant strategy is for to choose The outcome reflecting the unique Nash equilibrium in this game is as follows: Russell chooses and Aaliyah choosesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education