
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
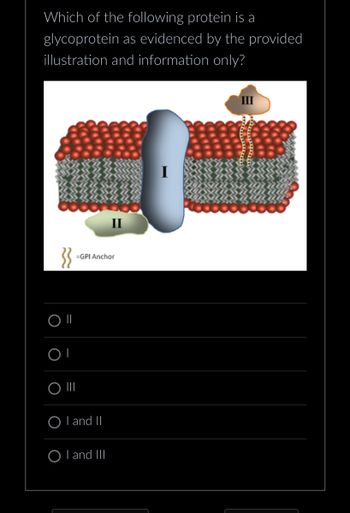
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following protein is a
glycoprotein as evidenced by the provided
illustration and information only?
}}
OI
O
O III
=GPI Anchor
OI and II
II
OI and III
III
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Introduce about the plasma membrane
Plasma membrane of the cells is the selective barrier and is made up of phospholipid bilayers. The bilayer structure is formed due to the hydrophobic interactions of phospholipid tails. In the plasma membrane proteins, cholesterol and carbohydrates are also present.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Changing one amino acid within a protein sequence from a tryptophan to a stop codon would be best classified as Amino acids groups Group Characteristics Names Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Pro, Phe Trp, Met Ala: A Leu: L non-polar hydrophobic Arg: R Asn: N Lys: K Met: M Asp: D Cys: C Gly: G polar hydrophilic (non-charged) Gly , Ser, Thr, Cys, Tyr, Asn Gln Phe: F Pro: P Ser: S acidic negatively charged Asp, Glu Glu: E Gln: Q Thr: T His: H lle: I Trp: W Туr: Y Val: V basic positively charged Lys, Arg, His A) Conservative missense O B) Nonsense O C) Neutral O D) Non-conservative missensearrow_forwardMatch each of the statements below with the fibrous protein that mostly fits the description. Coiled-coil of alpha helices V [ Choose] Collagen Silk fibroin Keratin Triple helical arrangement of polypeptide chains Extended anti-parallel beta sheets [ Choose ] Characterized by a predominant (GSGAGA)n repeat in the primary seguence [ Choose] Found in hair, feathers, scales, and nails [ Choose ] Is produced by insects and spiders [ Choose ] The sequence Gly-Pro-Hyp occurs frequently in this fibrous protein [ Choose ] Is characterized by the heptad pseudo- [ Choose ] repeat Major component of skin, tendons, ligaments and teeth [ Choose ] Characterized by regular inter-sheet spacing [ Choose ] of 0.35 and 0.57 nmarrow_forwardplease let it be for the three letter amino acid sequencearrow_forward
- i. ii. i.v. 22. Using the figure below, answer the following questions. Identify 2 independent helices domains Identify a disordered region In the structure, box the cofactor and name it (abbreviation accepted) Using the figure, draw the structure of the cofactor bound to this proteinarrow_forwardProteins can be separated into 9 general classifications based on the role they play in a cell. List or briefly describe two of these functional classifications and provide an example of a protein that falls into each of those two categories.arrow_forwardAmino Acid 3-Letter 1-Letter Second letter Code Code Alanine Cysteine Aspartic acid or aspartate Glutamic acid or glutamate | Phenylalanine Glycine Histidine Ala Cys Asp Glu UCU Phe UGU cys UGC UUUT UAU Tyr UAC D UUC UC Ser UUA UAA Stop UGA Stop UAG Stop UGG Trp G UCA Phe Leu UUG UCG Gly G H. His Ile CUU CCU CAU CGU U His CAC CÚC Leu CUA CGC CGA Isoleucine Lysine Leucine Pro Arg Lys K CAA Gin CAG CCA Leu L. CUG CCG CG Methionine Met M AUU AUC le ACU) ACC AAU1 AAC AGU Asn Asparagine Proline Glutamine Arginine Serine Asn Ser AGC AGA Arg Pro P. Thr AAA Gln Arg Ser AUA ACA AUG Met ACG AAG Lys AGG R GUU) GCU) GAU1 GGU GGC Gly Threonine Valine Tryptophan Tyrosine Thr GUC Val GUA GCC Ala GCA Val V GAA GAG GGA W Trp Тут Glu GUG GCG GGG Y Apply all that you have learned to solve the following: If you have the following DNA sequence: 5-ATGGCIOTOGTATTAAATAG-3 1. What is the sequence of the bases in the complementary DNA strand in a 3' to 5 direction ?( NB" Just type the letter for the bases) 2.…arrow_forward
- α-Keratin is an intermediate filament with a basic structural unit of two a helices in a coiled coil. Each helix has a seven-residue repeating unit (heptad repeat). A representation of the a helices of a coiled coil dimer is shown. Each letter represents a different amino acid residue. f g d e Review the table of amino acids. a d g f Identify the three true statements about the structure of keratin. ☐ The a helix of the coiled coil is wound less tightly than predicted for an α helix. ☐ Each polypeptide in the dimer has 3.6 residues per turn, and a nonpolar group occurs every 3.5 residues, resulting in a slight winding, or twist, around the other polypeptide, forming a coiled coil. Arg-Ala-His-Glu-His-Thr-Asp is a likely repeat in the a helix of keratin. ☐ Val-Thr-Asp-Ala-Glu-Arg-His is a likely repeat in the a helix of keratin. ☐ The residues at positions b and c are less likely to be polar or charged because they are in contact with the solvent. ☐ Keratin molecules are very strong due…arrow_forwardoligosaccharides are attached to proteins for a variety of reasons. They’re attached to the newly synthesized proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus to assign them destination labels, misfolded protein labels, and quality control labels. How does the polarity and charge of these oligosaccharides affect the protein they are bound to?arrow_forwardNon covalent bonds are very important in cell biology, could you explain why and provide an example that illustrates their importance ( do not chose protein folding as an example) What are the different levels of protein structure and what are the different parameters (sequence, type of bonds, etc...) that influence protein folding at these different levels?arrow_forward
- A tetradecapeptide (14 amino acid residues) gives the following peptide fragments on partial hydrolysis. From this information, deduce the primary structure of this polypep- tide. Fragments are grouped according to size. Pentapeptide Fragments Tetrapeptide Fragments Phe-Val-Asn-Gln-His Gln-His-Leu-Cys His-Leu-Cys-Gly-Ser His-Leu-Val-Glu Gly-Ser-His-Leu-Val Leu-Val-Glu-Alaarrow_forwardWhich of the following amino acids are more likely to be on the interior of the protein? And which are more likely to be exposed to the surface? L I D E W A V K H M Q Yarrow_forwardDisulfide linkages are uncommon in cytoplasmic proteins, whereas they are common in extracellular proteins. Why?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education