
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
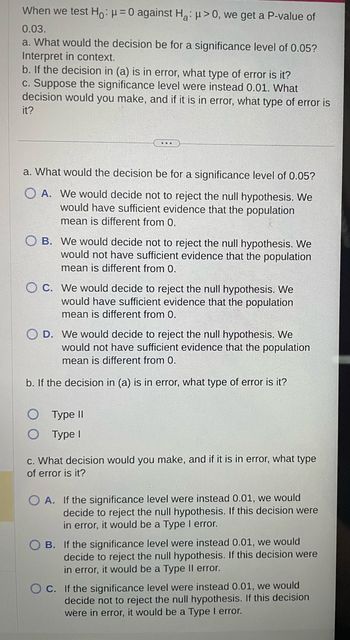
Transcribed Image Text:When we test Ho: μ = 0 against Ha: μ>0, we get a P-value of
0.03.
a. What would the decision be for a significance level of 0.05?
Interpret in context.
b. If the decision in (a) is in error, what type of error is it?
c. Suppose the significance level were instead 0.01. What
decision would you make, and if it is in error, what type of error is
it?
a. What would the decision be for a significance level of 0.05?
OA. We would decide not to reject the null hypothesis. We
would have sufficient evidence that the population
mean is different from 0.
B. We would decide not to reject the null hypothesis. We
would not have sufficient evidence that the population
mean is different from 0.
OC. We would decide to reject the null hypothesis. We
would have sufficient evidence that the population
mean is different from 0.
O D. We would decide to reject the null hypothesis. We
would not have sufficient evidence that the population
mean is different from 0.
b. If the decision in (a) is in error, what type of error is it?
Type II
Type I
c. What decision would you make, and if it is in error, what type
of error is it?
OA. If the significance level were instead 0.01, we would
decide to reject the null hypothesis. If this decision were
in error, it would be a Type I error.
B. If the significance level were instead 0.01, we would
decide to reject the null hypothesis. If this decision were
in error, it would be a Type II error.
OC. If the significance level were instead 0.01, we would
decide not to reject the null hypothesis. If this decision
were in error, it would be a Type I error.
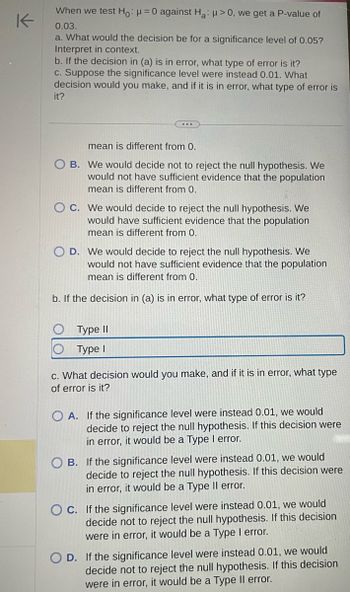
Transcribed Image Text:K
When we test Ho: μ = 0 against Ha: >0, we get a P-value of
0.03.
a. What would the decision be for a significance level of 0.05?
Interpret in context.
b. If the decision in (a) is in error, what type of error is it?
c. Suppose the significance level were instead 0.01. What
decision would you make, and if it is in error, what type of error is
it?
...
mean is different from 0.
OB. We would decide not to reject the null hypothesis. We
would not have sufficient evidence that the population
mean is different from 0.
OC. We would decide to reject the null hypothesis. We
would have sufficient evidence that the population
mean is different from 0.
D. We would decide to reject the null hypothesis. We
would not have sufficient evidence that the population
mean is different from 0.
b. If the decision in (a) is in error, what type of error is it?
Type II
Type I
c. What decision would you make, and if it is in error, what type
of error is it?
OA. If the significance level were instead 0.01, we would
decide to reject the null hypothesis. If this decision were
in error, it would be a Type I error.
B. If the significance level were instead 0.01, we would
decide to reject the null hypothesis. If this decision were
in error, it would be a Type II error.
OC. If the significance level were instead 0.01, we would
decide not to reject the null hypothesis. If this decision
were in error, it would be a Type I error.
D. If the significance level were instead 0.01, we would
decide not to reject the null hypothesis. If this decision
were in error, it would be a Type Il error.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A study was conducted to determine the proportion of people who dream in black and white instead of color. Among 285 people over the age of 55, 68 dream in black and white, and among 307 people under the age of 25, 14 dream in black and white. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the proportion of people over 55 who dream in black and white is greater than the proportion for those under 25. An explanation for the results is that those over the age of 55 grew up exposed to media that was displayed in black and white. Can these results be used to verify that explanation? A. Yes. The results can be used to verify the given explanation because the difference in proportions is practically significant. B. Yes. The results can be used to verify the given explanation because the difference in proportions is statistically significant. C. No. The results speak to a possible difference between the proportions of people over 55 and under 25 who dream in…arrow_forwardA case-control (or retrospective) study was conducted to investigate a relationship between the colors of helmets worn by motorcycle drivers and whether they are injured or killed in a crash. Results are given in the accompanying table. Using a 0.01 significance level, test the claim that injuries are independent of helmet color. D Black Color of Helmet Yellow 32 Blue White 331 Controls (not injured) Red 159 482 100 Cases (injured or 211 109 8 65 47 killed) Click here to view the chi-square distribution table. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Ho: Whether a crash occurs and helmet color are dependent H₁: Whether a crash occurs and helmet color are independent OB. Ho: Injuries and helmet color are dependent H₁: Injuries and helmet color are independent OC. Ho: Whether a crash occurs and helmet color are independent H₁: Whether a crash occurs and helmet color are dependent O D. Ho: Injuries and helmet color are independent H₁: Injuries…arrow_forwardA study was conducted to determine the proportion of people who dream in black and white instead of color. Among 300 people over the age of 55,80 dream in black and white, and among 287 people under the age of 25, 14 dreams in black and white. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the proportion of people over 55 who dream in black and white is greater than the proportion for those under 25. An explanation for the results is that those over the age of 55 grew up exposed to media that was displayed in black and white. Can these results be used to verify that explanation?arrow_forward
- A study was conducted to determine the proportion of people who dream in black and white instead of color. Among 285 people over the age of 55, 68 dream in black and white, and among 307 people under the age of 25, 14 dream in black and white. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the proportion of people over 55 who dream in black and white is greater than the proportion for those under 25. An explanation for the results is that those over the age of 55 grew up exposed to media that was displayed in black and white. Can these results be used to verify that explanation? OA. No. The results speak to a possible difference between the proportions of people over 55 and under 25 who dream in black and white, but the results cannot be used to verify the cause of such a difference. OB. No. The results speak to a possible difference between the proportions of people over 55 and under 25 who dream in black and white, but the results are not statistically significant enough to…arrow_forwardMitchell works in the produce section at a small local supermarket and would like to test whether the proportion of apples people purchase is the same for each season, using a significance level of 0.05. He analyzes the apple purchases each season for a year and records his findings in the following table. Season Spring Summer Fall Winter Total --------- --------- ------ ------ ------- # of apples purchased 896 934 934 971 3735 (a) In performing this statistical test, state the hypotheses. O Ho: the proportion of customers is the same each season vs. HA: the proportion of customers is not the same each season O Họ: the distribution of apples people purchased is not the same for each season vs. HẠ: the distribution of apples people purchased is the same for each season O Họ: the observed number of apples people purchased is the same for each season vs. Ha: the observed number of apples people purchased is not the same for each season O Họ; the distribution of apples people purchased is…arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the images.arrow_forward
- A case-control (or retrospective) study was conducted to investigate a relationship between the colors of helmets worn by motorcycle drivers and whether they are injured or killed in a crash. Results are given in the accompanying table. Using a 0.01 significance level, test the claim that injuries are independent of helmet color. Color of Helmet Black White Yellow Red Blue Controls (not injured) 494 343 27 168 99 Cases (injured or killed) 210 107 6 71 47arrow_forwardSeearrow_forwardProvide some details for the following examples using a significance value of .05 (using the sign, number, and significance): r = 0.3 (p > .05) r = .99 (p < .05) r = -.8 (p < .05)arrow_forward
- A poll was conducted to investigate opinions about global warming. The respondents who answered yes when asked if there is solid evidence that the earth is getting warmer were then asked to select a cause of global warming. The results are given in the accompanying data table. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the sex of the respondent is independent of the choice for the cause of global warming. Do men and women appear to agree, or is there a substantial difference? 9 Human activity Natural patterns Don't know 66 64 Male 288 307 130 155 Female Click here to view the chi-square distribution table. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H₂₁: Compute the test statistic. ▼and and (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the critical value(s). are ▼are (Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test? Ho. There sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim…arrow_forwardA researcher believe that increasing attention given to children will improve academic performance. He invites parents to volunteer during school to help the children with their activities. At the end of the school year he compares the academic performance of these children with the mean and standard deviation of historical rate on academic achievement. Which statistic test is appropriate for this study and why? (By using the decision tree). A. Z test B. Single sample t test C. Two independent samples t test D. Two related samples t test E. One way between subjects ANOVA F. Correlationarrow_forwardA statistician changes her level of significance from .001 to .05. What impact will this change have on her risk of making a Type I and Type II error? Is the change in the level of significance a good decision? Why or why not?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman