
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
When standardizing two liters of a potassium permanganate solution, approximately 0.0100 M, with a primary standard solution of sodium oxalate, it was planned to use between 30.00 and 45.00 ml of the titrated reagent. In which mass range (in grams) the primary standard should be weighed?
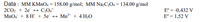
Transcribed Image Text:Data : MM KMNO4 = 158.00 g/mol; MM NazC2O4 = 134.00 g/mol
2CO2 + 2e + C204
MnO, + 8 H* + 5e + Mn²+ + 4 H20
E° = -0,432 V
E° = 1,52 V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 0.8159 g sample of HCl was placed into a 50 mL volumetric flask and the sample was thoroughly dissolved in water to make 50 mL of solution. It required 22.07 mL of NaOH to reach the endpoint in the titration. What is the molarity of the NaOH solution? I mg IHE/ 2.022 4 mol 0.81599 Hcl 36.4bg.arrow_forwardThe following solutions are needed to be prepared for the titration procedure:1. 20 mL of 2 M HCl2. 20 mL of 0.05 M KOHYou went through the titration process wherein 1.0867 grams of Fe(OH)n was mixed with the 20 mL of 2 M HCl that you initially prepared. This solution was diluted to 200 mL and was labeled as solution A. 20.0 mL aliquot of solution A was taken and titrated with 20.0 mL of 0.05 M KOH.Submit a detailed procedure of what you had done the above titration (include all the laboratory apparatus that you used).arrow_forwardIn a lab, you diluted a sample of bleach to 1/10 concentration in a 250 volumetric flask. Then quantitatively transferred 25 ml of the 1/10 concentration diluted bleach into a beaker and titrated it with a standard sodium thiosulfate solution that has a molarity of 0.1215M. You repeated this 3 times. The data below is the amount of sodium thiosulfate that was titrated in the 3 runs. Calculate the molarity in each run of the diluted bleach and the concentration of undiluted bleach sample. Titration 1: 45.55 ml Titration 2: 45.67 ml Titration 6: 45.58 mlarrow_forward
- A 185.0 mL sample of 1.200 M Pb(NO₃)₂ is mixed with 52.50 mL of 1.500 M NaCl, and the PbCl₂ precipitate is filtered from the solution. Then 200.0 mL of 3.000 M NaBr is added to the remaining solution, and the PbBr₂ precipitate is also collected and dried. What is the mass (in grams) of the PbBr₂ precipitate, assuming the yield in each precipitation step is 100%?arrow_forwardA 21.25 g of a mixture of the solid salts, sodium chloride and lead II nitrate, is added to distilled water and stirred. The precipitate that is formed is filtered and dried. Its mass was determined to be 11.06 g. Analysis of the remaining solution shoed that the following ions were present: Pb2+, Na+ and NO3". Determine the percent (by mass) of lead (II) nitrate in the mixture. Assume 100 % yield.arrow_forwardSonomic acid is a monoprotic acid developed in the chemistry department of Sacramento state University. The storeroom staff successfully obtained a sample of sonomic acid and made a solution. They made the solution by adding 302.4 g of sonomic acid and diluting it to a volume of 10.00 L with water. Unfortunately, the stockroom attendant, Steven , does not know the molar mass of sonomic acid so he could not calculate the molarity of the solution he prepared. It would be great if you could help him.arrow_forward
- A sample with a mass of 1.340 g was dissolved in water, releasing chlorine ions. The aqueous solution was treated with access AgNO3(aq), the AgCl precipitate collected and weighted. Its mass was 2.709 g. What percentage by mass was the original sample? Make sure to use the correct number of significant figures in your answer.arrow_forwardThe antacid found in Tums™ has the active ingredient calcium carbonate, which undergoes a reaction when mixed with hydrochloric acid to produce water, calcium chloride and carbon dioxide. A tablet of this antacid had a mass of 1.774g and was dissolved completely in an excess of 30.0mL of 0.794M HCl. The resulting solution was then titrated with 0.995M NaOH. The initial buret reading was 11.05mL and the final buret reading was 28.52mL. The listed mass of active ingredient on the bottle is 325mg. a. What is the calculated mass of active ingredient in this tablet? b. What is the percent error from the listed mass? c. What percent of the tablet is inert (non-active) ingredients? explain in detailarrow_forwardThe iodine contained in every one mL of the 0.010 M iodine solution in the buret will react with 1.76 mg of vitamin C. (In other words, every mL of iodine solution needed for the titration indicates the presence of 1.76 mg of vitamin C in the juice sample.) If your titration used 5.86 mL of iodine solution, what mass of vitamin C is in your fruit juice sample (in milligrams, mg)?arrow_forward
- 5.00 mL of acetic acid required 37.28 mL of 0.0999 M NaOH to be neutralized in a titration. Calculate the molarity of vinegar.arrow_forwardA solution of NaOH(aq) was standardized by titration using oxalic acid (H₂C₂O4) as the primary standard. The following data was collected: Mass of H₂C₂O4(s) used = 1.02 g Volume of NaOH(aq) used = 40.6 ml. Calculate the concentration of the NaOH(aq)arrow_forward2.0 g of a mixture containing unknown amounts of sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and a neutral component were titrated according to the experimental procedure. Answer the questions that follow related to the individual steps of the titration. Calculate the number of moles of sodium bicarbonate titrated in the second step of the titration if 13.7 ml of 1.0 M HCl were used to titrate the resulting mixture from the first step of the titration with methyl orange as the indicator. Enter your numerical answer below in units of moles with the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY