
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:C Clever | Portal
9 Schoology
A bpsma.schoology.com/common-assessment-delivery/start/5320576770?action=onresume&submissionld=633086718
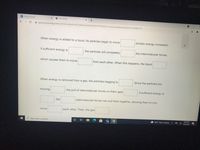
When energy is added to a liquid, its particles begin to move
(kinetic energy increases).
If sufficient energy is:
the particles will completely
the intermolecular forces,
which causes them to move
from each other. When this happens, the liquid;
When energy is removed from a gas, the particles begging to;
Since the particles are
moving
the pull of intermolecular forces on them gets
If sufficient energy is
the
intermolecular forces can pull them together, allowing them to only
move
each other. Then, the gas
4:39 PM
58°F Rain coming
10/4/2021
O Type here to search
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I have answered all of the numbers except number 2. I could really use some help for number 2, I don't get it at all. thanks!arrow_forwardExplainarrow_forwardHow much energy in units of J, is required to heat 71.7g of solid acetone from -156.3°C to -96.6°C. H(fusion)= 7.27 kJ mol-1 Cliq= 2.16 J g-1°C-1 Cgas= 1.29 J g-1°C-1 Csol= 1.65 J g-1°C-1 Tmelting= -95.0°Carrow_forward
- Consider the Sublimation of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide). The value of deltaHsub for CO2 is 25.2kj/mol 1) write the balanced chemical equation for the sublimation of CO2 2) Is this reaction "breaking bonds" (intramolecular) or "breaking intermolecular forces" (intermolecular)? What's the difference between the two?arrow_forwardUnit Name: Thermodynamic Chemistry When there is going to be a frost in Florida, farmers will spray their crops with water before the frost hits thereby preventing the fruit from freezing. Using concepts from this unit, explain why this helps to save the fruitarrow_forwardIce at -4.80oC is added to 220g of water at 26.60oC. What is the mass of ice needed to cool the water to an equilibrium temperature of 22.2oC?arrow_forward
- Which change does heat energy cause? greater energy differences between molecules reduced energy transfer more collisions between molecules slower molecule movementarrow_forwardConsider the following phase change equilibrium: CHCl3(s)= CHCl3(l) If delta H* is 9.74 kJ/mol and delta S* is 40.00 J/mol K, determine the melting point of CHCl3 in K?arrow_forwardWhat is the total enthalpy change during the process in which 100.0 g of water at 50.0 °C is cooled to ice at -30.0 °C ? (Assume P = 1.0 atm). Note: COOLING is an EXOTHERMIC PROCESS!!! AH WILL BE NEGATIVE! Solution S.H. water = 4.18 J/g °C Temperature AHfus = 6.01 kJ/mol 50.0 °C 0.0 °C 1 -30.0 °C 2 3 S.H. ice = 2.03 J/g °C 100.0 g H₂O = 5.552 mol H₂O 18.01 g/mol ΔΗ, = SH x Υ x ΔΤ AH₁ = (4.18 J/g °C)(100.0 g)(0.0 - 50.0 °C) == - 20900 J - 20.9 kJ Energy (J) Thus the total enthalpy change is: AH₂ = -AHfus XY AH₂ = -(6.01 kJ/mol)(5.552 mol) = -33.4 kJ ΔΗ, = SH x Υ x ΔΤ AH3 = (2.03 J/g °C)(100.0 g)(- 30.0 - 0.00 °C) = 6090 J = - 6.09 kJ -20.9 kJ-33.4 kJ - 6.09 kJ = - 60.4 kJarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY