
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
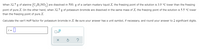
Transcribed Image Text:When 32.7 g of alanine (C3H,NO,)
are dissolved in 500. g of a certain mystery liquid X, the freezing point of the solution is 3.9 °C lower than the freezing
point of pure X. On the other hand, when 32.7 g of potassium bromide are dissolved in the same mass of X, the freezing point of the solution is 5.5 °C lower
than the freezing point of pure X.
Calculate the van't Hoff factor for potassium bromide in X. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round your answer to 2 significant digits.
i = |
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When 225. of urea (CH,N,0) are dissolved in 1200. g Oof a certain mystery g liquid x, the freezing point of the solution is 8.4 °c lower than the freezing point of pure x. On the other hand, when 225. g of sodium chloride are dissolved in the same mass of x, the freezing point of the solution is 14.5 °C lower than the freezing point of pure x. olo Ar Calculate the van't Hoff factor for sodium chloride in x. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. i = |arrow_forward6. Ethylene glycol [CH₂(OH)CH₂(OH)] is a common automobile antifreeze. It is water soluble and fairly nonvolatile (b.p. 197°C). Calculate (a) the freezing point and (b) the boiling point of a solution containing 268 g of ethylene glycol in 1015 g of water.arrow_forwardThe normal freezing point of a certain liquid X is 0.60°C, but when 0.14 kg of barium hydroxide (BaOH2) are dissolved in 900.g of X the solution freezes at −1.6°C instead. Use this information to calculate the molal freezing point depression constant Kf of X. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- When 224. mg of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 45.0 g of cyclohexane (C6H₁2), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 6.5 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on cyclohexane, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to 1 significant digit.arrow_forwardWhen 2.85 g of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 85. g of dibenzyl ether ((CH₂CH₂)₂O), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 2 -1.2 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on dibenzyl ether, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. X x10 Śarrow_forwardWhen 4.18 g of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 45.0 g of benzene (C6H6), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 4.9 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on benzene, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. □□ 品 5arrow_forward
- The molal boiling point elevation constant K = 1.15 °C·kg⋅mol the solution boils at 145.4 °C. Calculate the boiling point of pure X. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. °C x10 1 for a certain substance X. When 14.4 g of urea Ś ((NH,),CO) (NH₂) CO) are dissolved in 150. g of X,arrow_forward1.613 g sample of an unknown nonionizing molecular compound is added to 250.0 g of benzene(C6H6, MW = 78.11 g/mol). The normal freezing point of the solution is 0.17 C lower than the normalfreezing point of pure benzene. Based on this information, find the molecular weight of the unknowncompound. benzene = Kf = 5.12 kg x Degrees C/mol.arrow_forwardWhen 14.4 g14.4 g of an organic compound known to be 55.81% C55.81% C, 7.0% H7.0% H, and 37.17% O37.17% O by mass is dissolved in 825.8 g825.8 g of benzene, the freezing point is 4.80 ∘C4.80 ∘C. The normal freezing point of benzene is 5.49 ∘C5.49 ∘C. What is the molecular formula for the organic compound? Assume that the organic compound is a molecular solid and does not ionize in water. ?fKf values for various solvents are given in the colligative constants table. molecular formula: CHOarrow_forward
- When 911. mg of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 35.0 g of benzene (C,H6), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 2.5 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on benzene, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Ox10 미□arrow_forwardWhen 60.1 mg of a certain molecular compound X are dissolved in 70.0 g of benzene (CH), the freezing point of the solution is measured to be 5.4 °C. Calculate the molar mass of X. If you need any additional information on benzene, use only what you find in the ALEKS Data resource. Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to 1 significant digit. 0 ☐ X x10 Śarrow_forwardWhen 98.9 g of glycine (C₂H5NO₂) are dissolved in 900. g of a certain mystery liquid X, the freezing point of the solution is 4.7 °C lower than the freezing point of pure X. On the other hand, when 98.9 g of iron(III) nitrate = (Fe(NO3)3): are dissolved in the same mass of X, the freezing point of the solution is 5.4 °C lower than the freezing point of pure X. Calculate the van't Hoff factor for iron(III) nitrate in X. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round your answer to 2 significant digits. i= 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY