
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
explain step by step
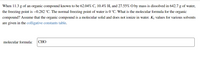
Transcribed Image Text:When 11.3 g of an organic compound known to be 62.04% C, 10.4% H, and 27.55% O by mass is dissolved in 642.7 g of water,
the freezing point is –0.282 °C. The normal freezing point of water is 0 °C. What is the molecular formula for the organic
compound? Assume that the organic compound is a molecular solid and does not ionize in water. Kf values for various solvents
are given in the colligative constants table.
molecular formula:
СНО
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 10-mm cube of copper metal is placed in 250 mL of 12 M nitric acid at 25°C and the reaction below occurs: Cu(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2NO3(aq) → Cu2+(aq) +2NO2(g) + 2H20(I) At a particular instant in time, nitrogen dioxide is being produced at the rate of 2.3 × 10^-4 M/min. AT this same instant, what is the rate at which hydrogen ions are being consumed in M/min? Report you answer with 5 places past the decimalarrow_forwardAccording to the following reaction, disappearance rate of oxygen is 5.75 x 10-2 mol L-1 s-1. Determine formation rate of dinitrogen pentaoxide (g)? 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 N2O5(g) a. 0.0225 mol L-1 s-1 b. 0.1150 mol L-1 s-1 c. 0.0575 mol L-1 s-1 d. 0.0450 mol L-1 s-1 e. 0.180 mol L-1 s-1arrow_forwardThe rate of a reaction is how quickly the reaction goes to completion. If two reactions have the same amount of reactant, increasing the rate does not increase the amount of product produced, it simply reduces the time that it takes to make the product. Using the internet, research the Reactant concentration factor below that affect the rate of a chemical reaction. 1. Reactant concentration (be very detailed add graphs to explain your details it should be 300 words) Your work should be written in complete sentences, and assume your audience is grade 11 chemistry students who do not understand this unit. Make sure all research is put into your own words!arrow_forward
- Time (min) Concentration of Phenyl Acetate (M) 0 0.55 0.25 0.42 0.50 0.31 0.75 0.23 1.00 0.17 1.25 0.12 1.50 0.082 what is the difference between concentration vs. time, 1/concentration vs. time, and ln concentration vs. time in terms of graphing?arrow_forward13. The production of nitric oxide is governed by the following reaction: 4NH3(g) +502(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g). produced? If the rate at which NO is produced is 6.35 x 10-2 mol/ L*s, at what rate is H₂O a. 8.29 x 10-3 mol/L✶ s b. 9.53 x 10-2 mol/L*s c. 6.35 x 10-2 mol/L*s d. 7.94 x 10-2 mol/L*s 14. Sulfur trioxide production follows the reaction: 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) consumed? If the rate at which SO3 is produced is 4.28 x 10 mol L-'s-', at what rate is O2 a. 4.28 × 10-4 mol L-'s-1 b. 1.08 x 10-3 mol L-'s-1 c. 1.07 × 10-4 mol L-'s-1 d. 2.14 x 104 mol L-'s-1 15. Consider the following reaction: 2A+B→ C. A kinetics study on this reaction yielded the following data: [A] mol/L [B] mol/L Rate=mol/L/s 0.0450 0.0250 5.03 x 10-3 0.0450 0.0500 2.01 x 10-2 0.0900 0.0250 5.03 x 10-3 What is the order of the reaction with respect to ([A], [B])? a. 1, 2 b. 2, 1 c. 2, 0 d. 0, 2arrow_forwardSome measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. [N] 0.815M1.56M N,|H||initial rate of reaction 185. M/s 141.M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. 口 rate = 0 ロ || = 1 Explanation Check D2022 McGrny Hl LLC. Al Rights Reserved. Terms of N 回 至 五arrow_forward
- T = Chemical reactions produce one or more product substances from one or more reactant substances. If x molecules of reactant X combine with y molecules of reactant Y to produce z molecules of product Z, we write xX+yY→ ZZ. The reaction rater is the rate of change of concentration of 1 dz 1 dX one of the products over time; for this example, r = 1 dy z dt x dt dY dt dX dt Nitrogen gas N₂ and hydrogen gas H₂ combine to produce ammonia NH3 according to dY dX dt 1N₂ + 3H₂ → 2NH3. Find r, and if ammonia is being produced at a rate of 5 moles dt per liter per hour. = esc T M Question Help: Message instructor Submit Question K 8366-SUMMER2023 / June 5- June 11 / Practice: Derivative mol Lh mol Lh → # C - $ y dt M % O Ollarrow_forwardA certain reaction has the following general form: aA → bB At a particular temperature and = 2.40 x 10-2 M, concentration versus time data were collected for this reaction, and a plot of [A]o In[A] versus time resulted in a straight line with a slope value of -4.39 x 10-2 min a Determine the rate law for this reaction. Rate = Determine the integrated rate law for this reaction. In[A] = Determine the value of the rate constant for this reaction. Rate constant = min-1arrow_forwardA substance containing dye decomposes very quickly. The graphs below were constructed with data pertaining to changes in [dye] over time. The initial concentration of dye was 1.0 M. After 20 seconds passed the concentration of dye was measured to be 0.13 M. [Dye] (mM) 10 00 0.9 -0.5 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 In([Dye]) In(mM) 6 -1 -1.5 1/[Dye] (1/mM) m 0.3 -2 2 0.2 0.1 -2.5 0 10 20 0 10 20 10 20 time (sec) time (sec) time (sec) 1. What is the order for the overall reaction? Justify your answer. Your answer *arrow_forward
- 0.003 ? 0.00218 0.002 - M 0.001 5 10 15 20 25 30 seconds created x10 Is H,0, being created or destroyed by the chemical destroyed reaction? neither created nor destroyed If f H,O, is being created or destroyed, what is the rate at which it is being created or destroyed 7 seconds after the reaction starts? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. If H,O, is being created or destroyed, what is the average rate at which it is being created or destroyed during the first 7 seconds of the reaction? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. 미arrow_forwardCalculating the reaction rate of one reactant from that of another Nitric acid is a key industrial chemical, largely used to make fertilizers and explosives. The first step in its synthesis is the oxidation of ammonia. In this reaction, gaseous ammonia reacts with dioxygen gas to produce nitrogen monoxide gas and water. Suppose a chemical engineer studying a new catalyst for the oxidation of ammonia reaction finds that 687. liters per second of dioxygen are consumed when the reaction is run at 158. °C and the dioxygen is supplied at 0.90 atm. Calculate the rate at which nitrogen monoxide is being produced. Give your answer in kilograms per second. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. kg S x10 ☑ ك Undoarrow_forwardThe rate of a reaction is how quickly the reaction goes to completion. If two reactions have the same amount of reactant, increasing the rate does not increase the amount of product produced, it simply reduces the time that it takes to make the product. Using the internet, research the Reactant concentration factor below that affect the rate of a chemical reaction. 1. Reactant concentration (be very detailed add graphs to explain your details it should be 300 words) Your work should be written in complete sentences, and assume your audience is grade 11 chemistry students who do not understand this unit. Make sure all research is put into your own words!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY