
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
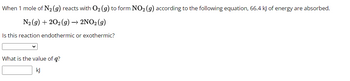
Transcribed Image Text:When 1 mole of N₂ (g) reacts with O₂ (g) to form NO₂ (g) according to the following equation, 66.4 kJ of energy are absorbed.
N₂(g) +202(g) → 2NO2 (9)
Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic?
What is the value of q?
kJ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When CO(g) reacts with NO(g) according to the following reaction, 373 kJ of energy are evolved for each mole of CO(g) that reacts. Complete the following thermochemical equation. 2CO(g) + 2NO(g)- →2CO₂(g) + N₂(g) ΔΗ = kJarrow_forwardAccording to the equation below, do the products have stronger or weaker bonds than the reactants? C (s) + 2H (g) → CH4 (g), ΔHrxn = -74.86 kJ/molarrow_forwardThe following thermochemical equation is for the reaction of hydrogen chloride(g) with ammonia(g) to form ammonium chloride(s). HCl(g) + NH3(g) --> NH4Cl(s) ΔH = -176kJ How many grams of HCl(g) would have to react to produce 45.2 kJ of energy? _______ gramsarrow_forward
- Nitrogen oxide (NO) has been found to be a key component in many biological processes. It also can react with oxygen to give the brown gas NO2. When one mole of NO reacts with oxygen, 57.0 kJ of heat are evolved. How many grams of nitrogen oxide must react with an excess of oxygen to liberate 20 kJ of heat? NO(g) + ½O2(g) → NO2(g) ΔH = –57.0 kJ ___________ garrow_forwardHow much energy is required to decompose 1970 g of PCl3, according to the reaction below? 4 PCl3(g) → P4(s) + 6 Cl2(g) ΔH°RXN = +1207 kJarrow_forwardCharcoal is primarily carbon. What mass of CO2 is produced if you burn enough carbon (in the form of charcoal) to produce 4.80 x 10² kJ of heat? The balanced chemical equation is as follows: C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g), Express the mass in grams to three significant figures. VE ΑΣΦ m = ? g AHxn=-393.5 kJarrow_forward
- In the following reaction, how much heat is generated when 3.21 moles of CH4 are burned? CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O(g) AH° = -802 kJ/molarrow_forwardA chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: 2 H₂O(l) → 2 H₂(g) + O₂(g) ΔΗ= 572. kJ Use the information to answer the following questions. This reaction is... Suppose 64.5 g of H₂O react. Will any heat be released or absorbed? If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. O endothermic. O exothermic. O Yes, absorbed. O Yes, released. O No. 0 kJ x10 Start overarrow_forwardDetermine the amount of heat released when 180.00 g AsBr5(g) reacts according to the following equation: As4O10(g) + 6 AsBr5(g) → 10 Br3AsO(g) Additional equations that may be useful: 1/4 As4(s) + 3/2 Br2(g) → AsBr3(g) ΔH = -336.4 kJ/mol As4(s) + 5 O2(g) → As4O10(g) ΔH = -2967.3 kJ/mol AsBr3(g) + Br2(g) → AsBr5(g) ΔH = -84.2 kJ/mol AsBr3(g) + 1/2 O2(g) → Br3AsO(g) ΔH = -295.7 kJ/molarrow_forward
- Consider these reactions: Reaction 1: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HC1(g) AH = -184.6 kJ Reaction 2: 20F2 (9) → 02 (9) + 2 F2 (9) AH= -49.4 kJ Reaction 3: N2 (g) + 202(g) → 2NO2(g) AH=+66.4 kJ Use Reaction 2. How much energy (in kJ) is released when 61.0 g of oxygen difluoride decomposes? Answer: - kJ (enter a positive value)arrow_forwardA 7.37 g sample of an unknown salt (MM = 116.82 g/mol) is dissolved in 150.00 g water in a coffee cup calorimeter. Before placing the sample in the water, the temperature of the salt and water is 23.72°C. After the salt has completely dissolved, the temperature of the solution is 28.54°C. What quantity in moles of the unknown salt were used in the reaction?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY