
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
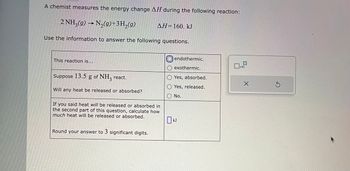
Transcribed Image Text:A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction:
2 NH3(g) → N₂(g)+3H₂(g)
Use the information to answer the following questions.
This reaction is...
Suppose 13.5 g of NH3 react.
Will any heat be released or absorbed?
ΔΗ= 160. kJ
If you said heat will be released or absorbed in
the second part of this question, calculate how
much heat will be released or absorbed.
Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
endothermic.
O exothermic.
Yes, absorbed.
Yes, released.
No.
0 KJ
x10
X
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: Cl₂(g) + H₂(g) → 2 HCl(g) Use the information to answer the following questions. This reaction is... Suppose 14.7 of Cl₂ react. g Will any heat be released or absorbed? ΔΗ = - 184. kJ If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. endothermic. O exothermic. O Yes, absorbed. Yes, released. O No. ០៤ kJ ☐x10 Xarrow_forwardFrom a molecular viewpoint, where does the energy absorbed in an endothermic chemical reaction go? Why does the reaction mixture undergo a decrease in temperature even though energy is absorbed?arrow_forwardThe following thermochemical equation is for the reaction of hydrogen chloride(g) with ammonia(g) to form ammonium chloride(s). HCl(g) + NH3(g) --> NH4Cl(s) ΔH = -176kJ How many grams of HCl(g) would have to react to produce 45.2 kJ of energy? _______ gramsarrow_forward
- #18arrow_forwardThe following thermochemical equation is for the reaction of carbon monoxide(g) with oxygen(g) to form carbon dioxide(g). 2CO(g) + O2(g)- →2CO2(g) AH=-566 kJ How many grams of CO(g) would have to react to produce 104 kJ of energy? gramsarrow_forwardA chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: 2 H₂O(l) → 2 H₂(g) + O₂(g) ΔΗ= 572. kJ Use the information to answer the following questions. This reaction is... Suppose 64.5 g of H₂O react. Will any heat be released or absorbed? If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. O endothermic. O exothermic. O Yes, absorbed. O Yes, released. O No. 0 kJ x10 Start overarrow_forward
- A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: Cl₂(g) + H₂(g) → 2 HC1 (g) AH=184. kJ Use the information to answer the following questions. endothermic. This reaction is... 0 exothermic. Suppose 28.0 g of Cl₂ react. Yes, absorbed. Yes, released. Will any heat be released or absorbed? No. If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ☐kJ x10 X ?arrow_forwardA chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: CH₂(g) +20₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(1) N Use the information to answer the following questions. This reaction is... Suppose 23.2 g of CH4 react. Will any heat be released or absorbed? If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ΔΗ= - 882. kJ endothermic. exothermic. OYes, absorbed. OYes, released. No. 0 kJ X 5arrow_forwardConsider the following formation reaction. Ni + 4C + 2O2 → Ni(CO)4 ΔH = -607kJ What mass of carbon reacts if 45.5 kJ of energy is released?arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction. N2 + 3 H2 -> 2 NH3 ΔH = -92 kJ/mol If 35 g of NH3 are produced, then what amount of heat energy is released?arrow_forwardneed help with this chemistryarrow_forward3. Suppose the 25.0 g of the following substances all initially at 27.0 °C absorb 2.35 kJ of energy. What is the final temperature of each? D) Water. You will need to look up specific heat values.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY