
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
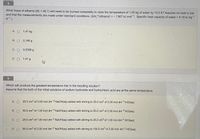
Transcribed Image Text:What mass of ethanol (M, = 46.1) will need to be burned completely to raise the temperature of 1.00 kg of water by 10.0 K? Assume no heat is lost
and that the measurements are made under standard conditions. (AH, (ethanol) = – 1367 kJ mol-1; Specific heat capacity of water = 4.18 kJ kg1
K-1.)
A. O 1.41 kg
В. О 0.146 g
C. O 0.0306 g
D. O 1.41 g
9.
Which will produce the greatest temperature rise in the resulting solution?
Assume that the both of the initial solutions of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid are at the same temperature.
A. O 25.0 cm³ of 2.00 mol dm3 NaOH(aq) added with stirring to 25.0 cm³ of 2.00 mol dm 3 HCI(aq).
B. O 50.0 cm³ of 1.00 mol dm NaOH(aq) added with stirring to 50.0 cm° of 2.00 mol dm 3 HCI(aq).
C. O 25.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol dm3 NaOH(aq) added with stirring to 25.0 cm³ of 1.00 mol dm-3 HCI(aq).
D. O
50.0 cm³ of 2.00 mol dm3 NaOH(aq) added with stirring to 100.0 cm³ of 2.00 mol dm-3 HCl(aq).
身
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9) The following thermochemical equation is for the reaction of ammonia(g) with oxygen(g) to form nitrogen monoxide(g) and water(g): 4 NH3(g) + 5 O₂(g) → 4 NO(g) + 6 H₂O(g) 8100.0 25228 AH = -905 kJ 2730.0 How many grams of NH3(g) would have to react with excess O₂(g) to produce 58.6 kJ of energy?arrow_forwardPotassium nitrate, KNO,, has a molar mass of 101.1 g/mol. In a constant-pressure calorimeter, 19.3 g of KNO, is dissolved in 249 g of water at 23.00 °C. O'H K*(aq) + NO, (aq) - (s)*ON The temperature of the resulting solution decreases to 21.00 °C. Assume that the resulting solution has the same specific heat as water, 4.184 J/(g °C), and that there is negligible heat loss to the surroundings. How much heat was released by the solution? Isoln = What is the enthalpy of the reaction? AH, = ux HV rxn kJ/mol 114arrow_forwardA chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 4.70 kg of water at 37.5C. During the reaction 92.8kJ of heat flows out of the flask and into the bath. Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. Heat capacity of water is 4.18J.g-1.K-1. Round your answer to 3arrow_forward
- ator%=Dassignment-take Not syncing The combustion of 0.1557 g benzoic acid increases the temperature of a bomb calorimeter by 2.50°C. Calculate the heat capacity of this calorimeter. (The energy released by combustion of benzoic acid is 26.42 kJ/g.) [References) Heat capacity = kJ/°C A 0.2155-g sample of vanillin (Cg Hg O3) is then burned in the same calorimeter, and the temperature increases by 3.20°C. What is the energy of combustion per gram of vanillin? Energy = kJ/g Per mole of vanillin? Energy = kJ/mol Submit Answer Try Another Version 5 item attempts remaining (Previous Next Save and Exit Email Instructor Technical Supportarrow_forwardThe overall reaction in a commercial heat pack can be represented as 4 Fe(s) + 30₂(g) → 2 Fe₂O₂ (s) AH = -1652 kJ a. How much heat is released when 4.80 moles of iron are reacted with excess O₂? Heat = kJ b. How much heat is released when 1.00 mole of Fe2O3 is produced? Heat = kJ c. How much heat is released when 1.40 g iron is reacted with excess O₂? Heat = kJ d. How much heat is released when 11.4 g Fe and 1.90 g O₂ are reacted? Heat = kJ Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardab The enthalpy of solution (AH) of NaNO3 is 20.4 kJ/mol. If 8.50 g NaNO3 is dissolved in enough water to make a 100.0 mL solution, what is the change in temperature (°C) of the solution? (The specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.184 J/g °C and the density of the solution is 1.02 g/mL). Tap here or pull up for additional resources 1 Q @ 2 W # 3 E $ 4 R % 5 T Question 1 of 10 6 Y & 7 U 8 1 9 1 4 7 +/- 0arrow_forward
- the formation of table salt from chlorine gas and sodium metal is highly exothermic 2Na + Cl2=NaCl H=-787kJ/mol if I react 35g of sodium, approximately how much heat will e gernerate a). 2400 kJ b).600kJ c). 1200 d). 300 e). 14000arrow_forwardAluminum mass of metal 50.820g temp of boiling water 98.1 C volume of water in cup 50mL temp of water in cup 21.4 C final temp of system 35.3 C *4.18 J/gK specific heat capacity *Ccal = 16.1 J/C approx. 1. Calculate heat gained by water in calorimeter (qwater) after adding aluminum. 2. Calculate heat gained by calorimeter (qcalorimeter) after adding aluminum. 3. From 1 and 2, calculate heat lost by aluminum (qmetal). 4. Calculate specific heat capacity of aluminum in (J/gK)arrow_forward2. a. Determine the standard heat of formation, AH for the following reaction using the Data from the Table. C3H12 ) + 802(g) → 5CO2 + 6H₂O b. State whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic. Explain. c. Rewrite the equation as thermochemical equations in two different ways to include the heat calculated in (2a). d. Draw a detail Energy Diagram representing the thermochemical equation in Ⓒ illustrating the the reactants and products and their positions.arrow_forward
- A food product containing 82% moisture content is being frozen. Predict the specific heat of the product at -8 ° C when 82% of the air is frozen. The specific heat of the dry product is 2.5 kJ / (kg ° C). It is assumed that the specific heat of water at -10 ° C is the same as that of water at 0 ° C, and that the specific heat of ice follows the function Cp ice = 0.0062 T frozen + 2.0649. Cp of frozen product = answer J / kg ° C.arrow_forward||| O THERMOCHEMISTRY Calculating the heat of reaction from molar reaction enthalpy a... V A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: 2 H₂O(l) → 2 H₂(g) + O₂(g) Use the information to answer the following questions. This reaction is... Suppose 91.7 g of H₂O react. Will any heat be released or absorbed? If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. esc Explanation ← Check ΔΗ= 572. kJ → endothermic. exothermic. Yes, absorbed. O Yes, released. No. E kJ x10 X MacBook Pro Search or type URL 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Farrow_forward4. What mass of propane must be burned to supply 700. kJ as heat? The thermochemical equation for the combustion of propane is: C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4H₂O(1) AH°-2220. kJarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY