
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
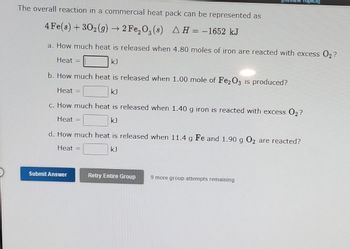
Transcribed Image Text:The overall reaction in a commercial heat pack can be represented as
4 Fe(s) + 30₂(g) → 2 Fe₂O₂ (s) AH = -1652 kJ
a. How much heat is released when 4.80 moles of iron are reacted with excess O₂?
Heat =
kJ
b. How much heat is released when 1.00 mole of Fe2O3 is produced?
Heat =
kJ
c. How much heat is released when 1.40 g iron is reacted with excess O₂?
Heat =
kJ
d. How much heat is released when 11.4 g Fe and 1.90 g O₂ are reacted?
Heat =
kJ
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In a constant-pressure calorimeter, 55.0 mL of 0.350 M Ba(OH), was added to 55.0 mL of 0.700 M HCI. The reaction caused the temperature of the solution to rise from 23.81 °C to 28.58 °C. If the solution has the same density and specific heat as water (1.00 g/mL and 4.184J/g °C.) respectively), what is AH for this reaction (per mole H₂O produced)? Assume that the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes. AH= kJ/mol H₂Oarrow_forwardConsider the reaction: 4A + B= 2C. Δ H=-443.6Kj/mol what reaction corresponds to a H of Δ221.8 Kj/molarrow_forwardHow much heat is produced when 57.4 g of NO2 react? 4NO2(g) + O2(g) → 2N2O5(g) heat of reaction = –110.2 kJarrow_forward
- Which of the following reactions is exothermic? C2H4(g) + O2(g) → 2C(s) + 2H2O(g) AH = 469.2 kJ O N204(g) + 57.6 kJ → 2NO2(g) C2H4(g) + 302(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) > AH = 1322.9 kJ PCI3(g) + Cl2(g)→ PCI5(g) + 92.5 kJarrow_forward3arrow_forwardThe flame in a torch used to cut metal is produced by burning acetylene (C2H2)(26.04 g/mol) in pure oxygen. Assuming the combustion of 1 mole of acetylene releases 1251 kJ of heat, what mass of acetylene is needed to cut through a piece of steel if the process requires 22.5 × 104 kJ of heat? 2 C2H2(g) + 5 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) ΔH = –2502 kJarrow_forward
- When 3.8 g A are reacted with 8.5 g D, according to the balanced chemical equation below, 33 kJ of energy are released. Please calculate the enthalpy for this reaction when 3 moles of G are produced. 2A + 3D = 2Z + 3G given molar masses: A = 141.8 g/mole D = 63.996 g/ mole Z = 4.032 g/ mole G = 56.028 g/ molearrow_forwardIn a constant-pressure calorimeter, 65.0 mL of 0.910 M H₂SO, was added to 65.0 mL of 0.300 M NaOH. The reaction caused the temperature of the solution to rise from 24.00 °C to 26.04 *C. If the solution has the same density and specific heat as water (1.00 g/mL and 4.184 J/g °C), respectively), what is AH for this reaction (per mole of H₂O produced)? Assume that the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes. AH = V 5 R B 6 MacBook Air N 39 8 M command P option kJ/mol H₂Oarrow_forwardHow much heat is produced when 33.9 g of NO2 react? 4NO2(g) + O2(g) → 2N2O5(g) heat of reaction = –110.2 kJarrow_forward
- For the reaction: 2 CH3OH) +3 02(g) (1) → 2 CO2 + 4 H20u) + 4 H200 + 347 kcal Calculate the amount of heat in kcal & kJ released when 25.4 g of CH,OH reacts.arrow_forwardThe overall reaction in commercial heat packs can be represented as 4Fe(s) + 302(g) →2Fe₂O3 (8) AH = -1652 kJ a. How much heat is released when 2.20 mol iron is reacted with excess O₂? kl released b. How much heat is released when 1.83 mol Fe2O3 is produced? kJ released c. How much heat is released when 2.20 g iron is reacted with excess O₂? kJ released d. How much heat is released when 11.8 g Fe and 2.61 g O2 are reacted? Submit Answer [Review Topics] kl released Retry Entire Group [References] 8 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY