
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
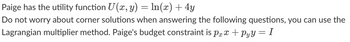
Transcribed Image Text:Paige has the utility function \( U(x, y) = \ln(x) + 4y \).
Do not worry about corner solutions when answering the following questions; you can use the Lagrangian multiplier method. Paige's budget constraint is \( p_x x + p_y y = I \).
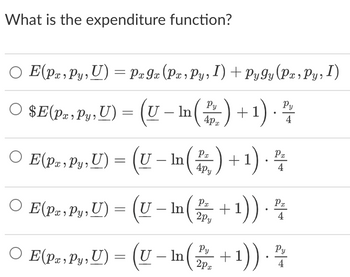
Transcribed Image Text:### What is the expenditure function?
#### Options:
1. **\(E(p_x, p_y, U) = p_x g_x(p_x, p_y, I) + p_y g_y(p_x, p_y, I)\)**
2. **\(E(p_x, p_y, U) = \left(U - \ln\left(\frac{p_y}{4p_x}\right) + 1\right) \cdot \frac{p_y}{4}\)**
3. **\(E(p_x, p_y, U) = \left(U - \ln\left(\frac{p_x}{4p_y}\right) + 1\right) \cdot \frac{p_x}{4}\)**
4. **\(E(p_x, p_y, U) = \left(U - \ln\left(\frac{p_x}{2p_y}\right) + 1\right) \cdot \frac{p_x}{4}\)**
5. **\(E(p_x, p_y, U) = \left(U - \ln\left(\frac{p_y}{2p_x}\right) + 1\right) \cdot \frac{p_y}{4}\)**
**Note:**
- \( E(p_x, p_y, U) \) denotes the expenditure function.
- \( p_x \) and \( p_y \) represent the prices of goods x and y, respectively.
- \( U \) is the utility level.
- \( \ln \) denotes the natural logarithm function.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Sub : EconomicsPls answer very fast.I ll upvote correct answer. Thank Youarrow_forwardSuppose that firm uses 3 units of labor (L) with 4 units of capital (K) in fixed proportion. Which of the following is correct? The law of diminishing MRTSLK holds and thus Lagrange multiplier method is applicable MRTSL,K is not well defined and thus Lagrange multiplier method is applicable The law of diminishing MRTSLK holds and capital and labor are perfect complements. O MRTSLK is not well defined and thus Lagrange multiplier method is not applicablearrow_forwarda) Write an expression for 8(t) (aka: force of interest) such that its accumulation function is the same as a 2% rate of simple interest. b) What is 8(8)?arrow_forward
- 2. Compute Ay = f(x + dx) – f(x) and the differential dy = f'(x)dx for the following: %3D (a) f(x) = when x= 3, dx =-D (b) ƒ(x)= ln x when x= 1, dæ =arrow_forwardIf Michelle's income is reduced to zero after she loses her job, her consumption will be and her saving will be O greater than zero; greater than zero O less than zero; greater than zero O greater than zero; less than zero O less than zero; less than zeroarrow_forwardTim lives in Vancouver and runs a business that sells pianos. In an average year, he receives $733,000 from selling pianos. Of this sales revenue, he must pay the manufacturer a wholesale cost of $433,000; he also pays wages and utility bills totalling $257,000. He owns his show room; if he chooses to rent it out, he will receive $13,000 in rent per year. Assume that the value of this show room does not depreciate over the year. Also, if Tim does not operate this piano business, he can work as a paralegal, receive an annual salary of $23,000 with no additional monetary costs, and rent out his show room at the $13,000 per year rate. No other costs are incurred in running this piano business.arrow_forward
- Only typed answer and don't use chat gptarrow_forwardKenji lives in Mississauga and runs a business that sells pianos. In an average year, he receives $723,000 from selling pianos. Of this sales revenue, he must pay the manufacturer a wholesale cost of $423,000; he also pays wages and utility bills totalling $267,000. He owns his show room; if he chooses to rent it out, he will receive $2,000 in rent per year. Assume that the value of this show room does not depreciate over the year. Also, if Kenji does not operate this piano business, he can work as a financial advisor, receive an annual salary of $20,000 with no additional monetary costs, and rent out his show room at the $2,000 per year rate. No other costs are incurred in running this piano business. Identify each of Kenji's costs in the following table as either an implicit cost or an explicit cost of selling pianos. Implicit Cost The wages and utility bills that Kenji pays The salary Kenji could earn if he worked as a financial advisor The rental income Kenji could receive if he…arrow_forwardNote:- Please don't simply copy and paste content from other AI tools or bots, or else I may have to downvote your actions. Do not provide the handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism.Answer completely.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education