
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
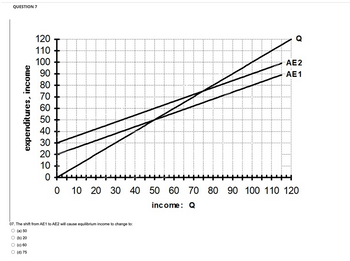
Transcribed Image Text:### Question 7
This graph represents the relationship between expenditures and income.
#### Graph Explanation
- **Axes**:
- The vertical axis represents "expenditures, income" ranging from 0 to 120.
- The horizontal axis represents "income: Q" ranging from 0 to 120.
- **Lines**:
- The line labeled **Q** represents actual expenditures and income.
- The line labeled **AE1** and **AE2** are aggregate expenditure lines, showing different levels of planned expenditures.
#### Question
07. The shift from AE1 to AE2 will cause equilibrium income to change to:
- (a) 50
- (b) 20
- (c) 60
- (d) 75
The diagram illustrates how changes in planned expenditures can affect equilibrium income. To find the new equilibrium, observe the intersection of AE2 with the income line **Q**.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Define aggregate expenditure.
Aggregate expenditure is the sum of consumption, investment, government spending and net export.
The equilibrium is where the aggregate expenditure curve intersects the 45° income curve.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A4arrow_forwardYou are choosing between two goods, X and Y, and your marginal utility from each is shown in the following table. Units of X MUx Units of Y MUy 1 10 1 8 2 8 2 7 3 6 3 6 4 4 4 5 5 3 5 4 6 2 6 3 a. If your income is $9 and the prices of X and Y are $2 and $1, respectively, what quantities of each will you purchase to maximize utility? ______units of X and ______units of Y b. What total utility will you realize? ______utils c. Assume that, other things remaining unchanged, the price of X falls to $1. What quantities of X and Y will you now purchase? _____units of X and ______units of Y d. Using the two prices and quantities for X, complete the table to derive the demand schedule (a table showing prices and quantities demanded) for X. Instructions: Start with the highest price first Price of X Quantity Demanded of X $ $arrow_forwardQUESTION 39 48 44 40 36 32 28 24 20 16 12 O 8 4 E.Q a) 12 b) 20 c) 24 d) 30 0 8 16 24 39. The shift from AE1 to AE2 will cause equilibrium income to change to: 32 40 Q AE2 AE1arrow_forward
- typing clear pls i will give upvotesarrow_forwardHandwritten solution not required correct answer will get instant upvote.arrow_forwardA consumer's ordinary demand curve for x1* (p1, p2, 1) = [² p1². How will a 2% increase in income affect this consumer's consumption of x1? O 1% 2% 3% 4% 5%arrow_forward
- Given f(x,y) = 2x2 - 6xy + 9y2, and Px= 7, Py= 5 and income, I = 175. Construct the budget contraint and Lagrange function and solve for the equilibrium values of x and y. (a) What is the equilibrium value of x? (Give your answer to two decimal places, if required) (b) What is the equilibrium value of y? (Give your answer to two decimal places, if required) (c) What is the value of the determinant of the bordered Hessian matrix? (Give your answer to two decimal places, if required) unanswered d. Based on the value of the Bordered Hessian, comment whether the objective function is maximized or minimized. Answer in one word.arrow_forwardSuppose the consumer's utility function is given by U(x,y) = X3/5y2/5, and the exogenous variables are given by M = 500, Px = 5, and Py = 4. Price of y changes to Py = 2. What is the income effect ony?O A.-14.53O B. +14.53O C. +24.21O D. +25.79O E. None of the above Note:- Please avoid using ChatGPT and refrain from providing handwritten solutions; otherwise, I will definitely give a downvote. Also, be mindful of plagiarism. Answer completely and accurate answer. Rest assured, you will receive an upvote if the answer is accurate.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education