
An Illustrated Guide To Vet Med Term
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305465763
Author: ROMICH
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
1. What is the chromosomal mutation and meiotic stage for each sample?
2. How did these mutations formed?
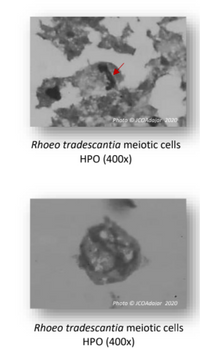
Transcribed Image Text:Photo JCOAdajar 2020
Rhoeo tradescantia meiotic cells
НРО (400х)
Photo © JCOAdajar 2020
Rhoeo tradescantia meiotic cells
НРО (400х)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Alternation of generations describes which of the following? The haploid form can be multicellular; the diploid form is unicellular The haploid form is unicellular; the diploid form can be multicellular Both the haploid and diploid forms can be multicellular Neither the haploid nor the diploid forms can be multicellular.arrow_forwardFigure 17.8 Do you think Dolly was a Finn-Dorset or a Scottish Blackface sheep?arrow_forward________ contributes to variation in traits among the offspring of sexual reproducers. a. Crossing over b. Random attachment of chromosomes to spindle poles c. Fertilization d. both a and b e. all are factorsarrow_forward
- Figure 23.25 Which of the following statements about Paramecium sexual reproduction is false? The macronuclei are derived from micronuclei. Both mitosis and meiosis occur during sexual reproduction. The conjugate pair swaps macronuclei. Each parent produces four daughter cellsarrow_forwardA cell has a diploid number of 6 (2n = 6). a. Draw the cell in metaphase of meiosis I. b. Draw the cell in metaphase of mitosis. c. How many chromosomes are present in a daughter cell after meiosis I? d. How many chromatids are present in a daughter cell after meiosis II? e. How many chromosomes are present in a daughter cell after mitosis? f. How many pairs of homologous chromosomes are visible in the cell in metaphase of meiosis I?arrow_forwardFigure 10.6 Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis? Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides. Cohesin proteins break down and the sister chromatids separate. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Cohesin proteins break down and the sister chromatids separate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides. The kinetochore becomes attached to the cohesin proteins. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. Cohesin proteins break down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides.arrow_forward
- BPA and Abnormal Meiosis In 1998, researchers at Case Western University were studying meiosis in mouse oocytes (germ cells) when they saw an unexpected and dramatic increase of abnormal events (FIGURE 12.6). Improper segregation of chromosomes during meiosis is one of the main causes or human genetic disorders. The spike in abnormal meiosis began right after the mouse facility started washing the animals' plastic cages and water bottles in a new, alkaline detergent. The detergent had damaged the plastic, which as a result was leaching bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is a synthetic chemical that mimics estrogen, the main female sex hormone in animals. Though it has since been banned for use in baby bottles, BPA is still widely used to manufacture other plastic items and epoxies (such as the coating on the inside of metal cans of food). BPA-free plastics are often manufactured with a related compound, bisphenol S (BPS), that has effects similar to BPA. FIGURE 12.6 Abnormalities in meiosis that occurred after exposure to BPA. Top, the most abnormal meiosis events occurred in mice that were housed in damaged plastic caging with damaged plastic bottles. Damaged plastic releases BPA. Bottom, fluorescent micrographs show the chromosomes (red) and spindle (green) in nuclei of mouse germ cells in metaphase I. A Normal metaphase; BD abnormal metaphase. Which group of mice had the most meiotic abnormalities in their oocytes?arrow_forwardBPA and Abnormal Meiosis In 1998, researchers at Case Western University were studying meiosis in mouse oocytes (germ cells) when they saw an unexpected and dramatic increase of abnormal events (FIGURE 12.6). Improper segregation of chromosomes during meiosis is one of the main causes or human genetic disorders. The spike in abnormal meiosis began right after the mouse facility started washing the animals' plastic cages and water bottles in a new, alkaline detergent. The detergent had damaged the plastic, which as a result was leaching bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is a synthetic chemical that mimics estrogen, the main female sex hormone in animals. Though it has since been banned for use in baby bottles, BPA is still widely used to manufacture other plastic items and epoxies (such as the coating on the inside of metal cans of food). BPA-free plastics are often manufactured with a related compound, bisphenol S (BPS), that has effects similar to BPA. FIGURE 12.6 Abnormalities in meiosis that occurred after exposure to BPA. Top, the most abnormal meiosis events occurred in mice that were housed in damaged plastic caging with damaged plastic bottles. Damaged plastic releases BPA. Bottom, fluorescent micrographs show the chromosomes (red) and spindle (green) in nuclei of mouse germ cells in metaphase I. A Normal metaphase; BD abnormal metaphase. What is abnormal about metaphase I as it is occurring in the oocytes shown in FIGURE 12.6B, C, and D?arrow_forwardFigure 24.14 Which of the following statements is true? A dikaryotic ascus that forms in the ascocarp undergoes karyogamy, meiosis, and mitosis to form eight ascospores. A diploid ascus that forms in the ascocarp undergoes karyogamy, meiosiis, and mitosis to form eight ascospores. A haploid zygote that forms in the ascocarp undergoes karyogamy, meiosiis, and mitosis to form eight ascospores. A dikaryotic ascus that forms in the ascocarp undergoes plasmogamy, meiosis, and mitosis to form eight ascospores.arrow_forward
- Figure 6.4 Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis? a. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore becomes attached to the initotic spindle. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. The sister chromatids separate. b. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The sister chromatids separate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. c. The kinetochore becomes attached to metaphase plate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. d. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks apart and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.arrow_forwardA cytology student believes he has identified an individual with monoploidy. The instructor views the dividing cells under the microscope and correctly dismisses the claim. Why was the claim dismissed? What types of cells were being viewed?arrow_forwardMatch the phase of cell division with the following diagrams. In these cells, 2n = 4. a. anaphase of meiosis I b. interphase of mitosis c. metaphase of mitosis d. metaphase of meiosis I e. metaphase of meiosis IIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning


Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning