
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
![### Boiling Point Elevation Problem
**Problem Statement:**
What is the boiling point of a solution composed of 21.0 g of urea, \( (NH_2)_2CO \), in 0.800 kg of water?
- \( K_{bp} \) for \( H_2O \) is \( +0.5121 \,^\circ C/m \).
**Input Fields:**
- **Boiling Point:** [ ]
**Interface Options:**
- **Submit Answer** button
- **Try Another Version** button
**Attempts Remaining:**
- 2 item attempts remaining
### Explanation:
This exercise involves calculating the boiling point elevation of a solution using the formula:
\[
\Delta T_b = i \cdot K_{bp} \cdot m
\]
Where:
- \( \Delta T_b \) is the boiling point elevation.
- \( i \) is the van 't Hoff factor (1 for urea since it does not ionize).
- \( K_{bp} \) is the ebullioscopic constant (\( 0.5121 \,^\circ C/m \) for water).
- \( m \) is the molality of the solution, calculated by dividing moles of solute by kilograms of solvent.
To solve this problem:
1. Calculate the moles of urea from its given mass.
2. Determine the molality of the solution.
3. Use the boiling point elevation formula to calculate the new boiling point of water.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/61a624e8-9805-4882-bd7c-8b439f9ba0a9/5c34e2a0-1b28-4328-a508-73efbecf10ed/i7f3re_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:### Boiling Point Elevation Problem
**Problem Statement:**
What is the boiling point of a solution composed of 21.0 g of urea, \( (NH_2)_2CO \), in 0.800 kg of water?
- \( K_{bp} \) for \( H_2O \) is \( +0.5121 \,^\circ C/m \).
**Input Fields:**
- **Boiling Point:** [ ]
**Interface Options:**
- **Submit Answer** button
- **Try Another Version** button
**Attempts Remaining:**
- 2 item attempts remaining
### Explanation:
This exercise involves calculating the boiling point elevation of a solution using the formula:
\[
\Delta T_b = i \cdot K_{bp} \cdot m
\]
Where:
- \( \Delta T_b \) is the boiling point elevation.
- \( i \) is the van 't Hoff factor (1 for urea since it does not ionize).
- \( K_{bp} \) is the ebullioscopic constant (\( 0.5121 \,^\circ C/m \) for water).
- \( m \) is the molality of the solution, calculated by dividing moles of solute by kilograms of solvent.
To solve this problem:
1. Calculate the moles of urea from its given mass.
2. Determine the molality of the solution.
3. Use the boiling point elevation formula to calculate the new boiling point of water.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
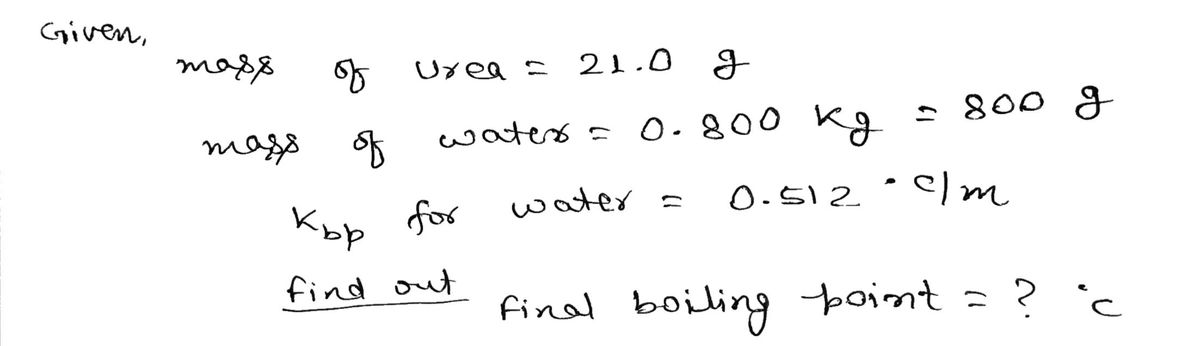
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- DA-LITE In-class Exercise 1: Osmotic Pressure Consider a solution of glucose on one side of a membrane that is impermeable to the transport of glucose. The temperature of the glucose solution is 20°C. What is the osmotic pressure on the glucose side of the membrane to stop the flow of water into the glucose solution? Assume the glucose concentration is 1 mg/ mL and that the molecular weight of glucose is 180 g/mol. What would the osmotic pressure be if the solution also contained 0.1 mg/ml of sodium chloride?arrow_forwardThe boiling point of 20.0 g of Ca(NO3)2 dissolved in 500.0 g of water would be? kp = 0.512 °C/m %3D A 0.125 レ 100.13 Correct answer X 6.08 Your answer D 102.4arrow_forwardAn aqueous solution is 10.0 % by mass hydrochloric acid, HCI, and has a density of 1.05 g/mL. The molarity of hydrochloric acid in the solution is M. Submit Answer Try Another Version 8 item attempts remainingarrow_forward
- The vapor pressure of water is 23.76 mm Hg at 25°C.How many grams of urea, CH4N2O, a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte (MW = 60.10 g/mol), must be added to 247.9 grams of water to reduce the vapor pressure to 23.28 mm Hg ?water = H2O = 18.02 g/mol.answer=_____ g ureaarrow_forwardWhat would be the freezing point, in degree Celsius, of a 3.8 m aqueous solution of Sc(CIO4)3? kç = 1.86 °C/m 28.3 X 7.07 Your answer -28.3 Correct answer D 7.07 AIarrow_forwardAnswer part A,B and Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY