
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
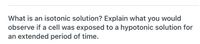
Transcribed Image Text:What is an isotonic solution? Explain what you would
observe if a cell was exposed to a hypotonic solution for
an extended period of time.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You have a beaker filled with a solution containing 2M glucose, 4M urea and 1M salt.Suspended in the solution is a cell that containing a solution of 1M glucose, 8M urea and 3Msalt. The membrane of the cell is permeable to glucose and salt but not urea. Answer each of thefollowing questions:a. Where will water move?b. Where will urea move?c. Where will glucose move?d. Where will salt move?e. What will happen to the volume of fluid inside the cell?f. What will happen to the osmolarity of the fluid inside the cell?arrow_forwardA concentration gradient affects the direction that solutes diffuse. Describe how molecules move with respect to concentration.arrow_forwardRebuild the cell above that is hypertonic to the solution outside. By hitting the red button, add 20 solutes (green) to the inside of the cell and add 5 water (blue) to the inside of the cell. Also, add 20 water (blue) to the outside of the cell and 5 solutes (green) to the outside of the cell. Add blue gated channels to the membrane. Q: What happens to the water molecules in this situation? Q: Which of the above situations is closer to a living membrane system?arrow_forward
- Can you assist me in answerig questions a, b, and c with the given data and graph provided, please?arrow_forwardRegarding ISOTONIC solutions, which of the following are TRUE? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY A. Water movement between the ICF and EFC is equal B. Solvent concentration inside the cell and outside the cell are equal. C. Solute concentration inside the cell and outside the cell are equal. D. Solute concentraion inside the cell is equal to solvent concentration outside the cell.arrow_forwardWhen a cell is surronded by hyptonic solution, which of the following will occur? A. The cell will swell up, as water goes into the cell. B. The cell will shrivel, as water leaves the cell. C. The cell will remain the same size.arrow_forward
- Suppose that you have a splinter that is embedded so deep in your foot that you cannot remove it with tweezers. How could you use what you learned in this unit as a first-aid remedy in this situation? Select one: O A. Use active transport to your advantage to draw water into your foot. O B. Use osmosis to your advantage by placing your foot in a hypotonic solution. C. Use osmosis to your advantage by placing your foot in a hypertonic solution. D. Use an artificial concentration gradient to draw water into your foot. E. Use osmosis to your advantage by placing your foot in an isotonic solution.arrow_forwardThe cell membrane is permeable to water but not to ions. Select all that apply. Question options: Beaker A is isotonic to the cell. Some water in cell A is moving in and out of the cell. There is a net movement of water into Cell B. Beaker C is hypotonic to Cell C.arrow_forwardA solution that is described by the term hypertonic means that it isarrow_forward
- The beaker is divided into two compartments (C and D) that has equal volumes of solution separated by an artificial membrane that has a pore size of 23 Å (Angstrom). Explain the movement of solute after eight hours if comparment C has 17 % sucrose while the compartment D has 2 % sucrose (diameter of sucrose molecule = 9 Å (Angstrom))arrow_forwardRegarding osmosis, be able to predict the movement of water molecules when cells are placed in solutions with various tonicities.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON