
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
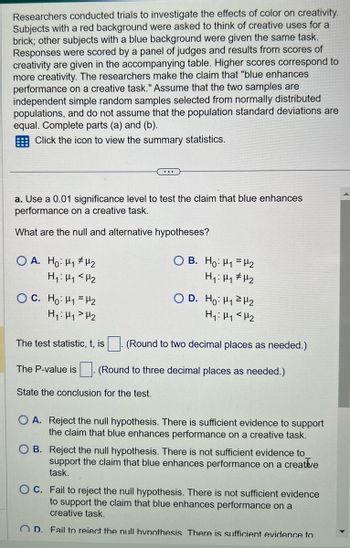
Transcribed Image Text:Researchers conducted trials to investigate the effects of color on creativity.
Subjects with a red background were asked to think of creative uses for a
brick; other subjects with a blue background were given the same task.
Responses were scored by a panel of judges and results from scores of
creativity are given in the accompanying table. Higher scores correspond to
more creativity. The researchers make the claim that "blue enhances
performance on a creative task." Assume that the two samples are
independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed
populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are
equal. Complete parts (a) and (b).
Click the icon to view the summary statistics.
a. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that blue enhances
performance a creative task.
What are the null and alternative hypotheses?
OA. Ho: H₁ H₂
H₁ H₁ <H₂
C. Ho: ₁ = ₂
H₁ H₁ H₂
H₂
H₁ H₁ H₂
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the conclusion for the test.
OB. Ho: H1 H₂
H₁: H₁ H₂
The test statistic, t, is
D. Ho: H₁
A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support
the claim that blue enhances performance on a creative task.
OB. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to
support the claim that blue enhances performance on a creative
task.
OC. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence
to support the claim that blue enhances performance on a
creative task.
OD. Fail to reiect the null hypothesis There is sufficient evidence to
Transcribed Image Text:→
O
O
O
о
о
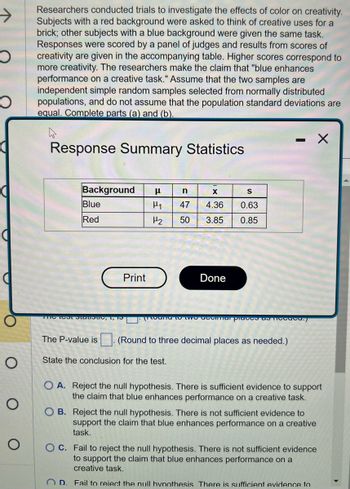
Researchers conducted trials to investigate the effects of color on creativity.
Subjects with a red background were asked to think of creative uses for a
brick; other subjects with a blue background were given the same task.
Responses were scored by a panel of judges and results from scores of
creativity are given in the accompanying table. Higher scores correspond to
more creativity. The researchers make the claim that "blue enhances
performance on a creative task." Assume that the two samples are
independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed
populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are
equal. Complete parts (a) and (b).
Response Summary Statistics
Background μl
Blue
Red
The Lost Statistic
The P-value is
Print
n
X
H₁ 47 4.36
H₂
50
3.85
Done
S
0.63
0.85
hd to the commar places as they
State the conclusion for the test.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
X
O A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support
the claim that blue enhances performance on a creative task.
OB. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to
support the claim that blue enhances performance on a creative
task.
OC. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence
to support the claim that blue enhances performance on a
creative task.
OD. Fail to reiect the null hypothesis There is sufficient evidence to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- MY NOTES Bags of a certain brand of tortilla chips claim to have a net weight of 12.5 oz. A representative of a consumer advocate group wishes to see if there is any evidence that the mean net weight is less than advertised and so intends to test the hypotheses H0: μ = 12.5, HA: μ < 12.5. To do this, he selects 24 bags of tortilla chips of this brand at random and determines the net weight of each. Data reveals a bell-shaped histogram, a sample mean of 12.31 ounces, and a standard deviation of 0.48 ounces.(a) What type of test is this? Two-sided, one-sample test Two-sided, two-sample test One-sided, two-sample test One-sided, one-sample test (b) Given the test statistic = -1.94 and α = 0.05, which of the following statements is the decision? Reject H0; conclude the bags are underweight. Fail to reject H0; do not conclude the bags are underweight. Fail to reject H0; conclude the the bags are underweight. Reject H0; conclude the bags are overweight.arrow_forwardAnswer all part A B and Carrow_forward#14 Thanksarrow_forward
- Need help with #30arrow_forwardhelp solve attached, and following parts pertaining to attached image, all parts please. find test statisitic t find p value State the conclusion for the test. A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda. Your answer is not correct. B.Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda. C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda. D.Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda. b. Construct a confidence…arrow_forwardNeed help on the last partarrow_forward
- Ho at the 0.02 level of significance? Do you reject or fail to reject and H,: u=25, H,:4#25 P = 0.028 25, H: u +25 Given O Not sufficient information to decide Ho Reject reject H 4. Fail to rejectarrow_forwardDescribe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the indicated claim. A furniture store claims that at least 40% of its new customers will return to buy their next piece of furniture. Describe the type I error. Choose the correct answer below. OA. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece of furniture is at least 0.40, but you fail to reject Ho: p20.40. OB. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece furniture is at least 0.40, but you reject Ho: p20.40. OC. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece of furniture is no more than 0.40, but you reject Ho: p ≤ 0.40. OD. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of new customers who return to buy their next piece f furniture is no more than 0.40, but you fail to reject Ho: p ≤0.40. Describe the type II error. Choose the correct answer…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman