
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
We can see from the payoff matrix that there are no pure strategy Nash equilibrium in this game because at least one firm would always have an incentive to change its behavior. From Nash's theorem, we know there must be at least one Nash equilibrium so there must be a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium for this game.
Find the mixed strategy Nash equilibrium by first deleting all dominated strategies in the game
What's the expected payoff to Firm 1 in the equilibrium?
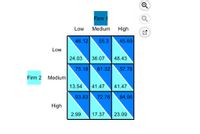
Transcribed Image Text:Firm 1
Low
Medium
High
46.12
55.3
45.69
Low
24.03
36.07
48.43
75.18
61.32
57.78
Firm 2
Medium
13.54
41.47
41.47
93.83
72.76
84.06
High
2.99
17.37
23.09
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Evaluate this statement All Nash equilibra are dominant strategy equilibria but not all dominant strategy equilibria are Nash Equilibriaarrow_forwardPlayer 2 Left P1: $40 Player 1 Up P2: $0 P1: $44 Down P2:$44 In the game shown above, list all of the EFFICIENT Nash Equilibrium (please check ALL that apply) (up, left) (up, right) (down, left) (down, right) No efficient Nash Equilibrium Right P1:$1 P2: $1 P1: $0 P2: $40arrow_forwardWe can see from the payoff matrix that there are no pure strategy Nash equilibrium in this game because at least one firm would always have an incentive to change its behavior. From Nash's theorem, we know there must be at least one Nash equilibrium so there must be a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium for this game. Find the mixed strategy Nash equilibrium by first deleting all dominated strategies in the game What's the expected payoff to Firm 2 in the equilibrium?arrow_forward
- What is game theory? How does it relate to strategic decision making? What do the phrases dominant strategy and Nash Equilibrium mean as they apply to game theory?arrow_forwardO Cell A O Cell C O Cell E O Cell I None of the abovearrow_forwardConsider the game in the table below. Find the Nash Equilibrium of the game. Add the payoffs of both players at the Nash Equilibrum and enter that number. Firm A Left Right Up Firm B 9,11 5,6 own 5,10 6,5 20arrow_forward
- What is meant by dominant strategy?arrow_forwardTwo rival companies competing in the same market need to decide their plans for future expansion of their stores. The Table below shows the possible outcomes of their mutually interdependent actions (payoffs are profits in £m) Giga Company Titanic Conglomerate No Change Refurbishment of existing stores Large Expansion No Change 30, 40 25, 35 15, 24 Refurbishment of existing stores 35, 30 28, 32 18, 33 Large Expansion 12, 22 18, 20 20, 25 The Nash equilibrium: (A) does not exist. (B) occurs when both firms choose Refurbishment of existing stores. (C) occurs when both firms choose Large Expansion. (D) occurs when both firms choose No Change.arrow_forwardConsider the two period Repeated Prisoner's Dilemma Game where each player is interested in the SUM of the payoffs she gets in each period. Players see the outcome after the play in each period. (The period payoffs are 10,5,1,0.) (i) Write out this game in its strategic form. (ii) Find all Nash equilibria and all Subgame Perfect Nash Equilibria.arrow_forward
- QUESTION 2 In the game above, what is/are the sub-game perfect Nash equilibrium? (up, up) (up, down) ( down, up) (down, down) No equilibrium exists QUESTION 2 Up Down Player 1 No equilibrium exists Up In the game above, what is/are the sub-game perfect Nash equilibrium? (up,up) (up,down) (down, up) □ (down, down) Down Up Down Player 2 P1 gets $45 P2 gets $155 P1 gets $100 P2 gets $10 P1 gets $85 P2 gets $85 P1 gets $95 P2 gets $95arrow_forwardConsider the game given. The top number is player 1’s payoff and the bottom number is player 2’s payoff.a. Find the SPNE.b. Find a Nash equilibrium that is not an SPNE.arrow_forwardWhile game theory predicts non-cooperative behavior for a one-shot Prisoner's dilemma. By repeating the game, say 20 rounds, it becomes possible to adopt more complex strategies that allow cooperative play as a Nash Equilibrium in at least some rounds of the game. True Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education