
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Water enters a two-armed lawn sprinkler along the vertical axis at a rate of 150 L/s, and leaves the sprinkler nozzles as 2cm diameter jets at an angle of u from the tangential direction. The length of each sprinkler arm is 0.52 m. Disregarding any frictional effects, determine (a) Angular momentum and (b) the rate of rotation n of the sprinkler in rev/min
For ϴ = 0° .
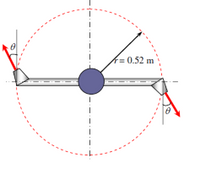
Transcribed Image Text:kD0.52 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 3: A rocket with a fixed mass flow rate will continue to increase its velocity (accelerate) while it is expelling mass. A cart, on a frictionless surface with a vertical flat plate being pushed by a horizontal steady jet of water from a fixed nozzle, will accelerate to some fixed velocity. Explain why the rockets velocity is not fixed, but the carts velocity is. Problem 4 Problem 3arrow_forwardCan someone please help me to solve the following question showing all work. R-in = 5cm R-out = 15cmarrow_forwardWater enters a two-armed lawn sprinkler along a vertical axis at a rate of 60 L/s and leaves the sprinkler nozzles as 2-cm diameter jets at a 30°angle, determine the rotational speed in RPM of the sprinkler.arrow_forward
- Express the unsteady angular momentum equation in vector form for a control volume that has a constant moment of inertia I, no external moments applied, one outgoing uniform flow stream of velocity V→, and mass flow rate m. .arrow_forwardA single-stage axial flow pump with outer radius r2 = 0.240 m and inner radius r1=0.120 m is given. At a radius of r =0.090 m, absolute flow flows in from the axial direction just before the impeller inlet and relative flow flows out in the axial direction just after the impeller outlet. Assuming a flow rate Q = 0.265 m^3/s, a water density p = 1.000 x 103 kg/m^3, a rotation speed n = 2.4 x 10^3 rpm, and a gravitational acceleration g = 9.81 m/s^2, and assuming that the theoretical head Hth = W/g (W: specific work) derived from Euler's law is constant at all impeller radii, answer the following questions. (1) Looking at the following image, find all values of the velocity triangle just before the impeller inlet and just after the impeller outlet at radius r =0.09 m. impeller Figure 37.1 A propeller of an axial flow pump a₁ w1 U₁ Outlet guide vane B₁ Impeller α₂ Vw2 U₂=U₂=Uarrow_forwardA jet airplane moving at 900 km/hr takes 700 N/s of air into is engine, burns 15 N/s of fuel, and discharges the exhaust gasses at atmospheric pressure. If the thrust of the engine is 40,000 N, what is the absolute velocity of the gases in meters per seconds?arrow_forward
- Q6) A water jet hits horizontally a 50-kg block with a velocity of (20 m/s), see the figure. The friction coefficient between the block and the ground is (0.9). What is the minimum diameter (d) of the water jet required for the block to slide to the left?arrow_forwardA single-stage axial flow pump with outer radius r2 =0.240 m and inner radius r1 =0.120 m is given. At a radius of r =0.090 m, absolute flow flows in from the axial direction just before the impeller inlet and relative flow flows out in the axial direction just after the impeller outlet. Assuming a flow rate Q = 0.265 m^3/s, a water density ρ = 1.000 × 103 kg/m^3, a rotation speed n = 2.4 × 10^3 rpm, and a gravitational acceleration g = 9.81 m/s^2 , and assuming that the theoretical head Hth = W/g (W: specific work) derived from Euler's law is constant at all impeller radii, answer the following questions. (1) Find the velocity triangles just before the impeller inlet and just after the impeller outlet at a radius of r =0.09 m.arrow_forwardFluids Question Water flows steadily from a tank mounted on a cart as shown, after the water jet leaves the nozzle of the tank, it falls and strikes a vane attached to another cart. The cart's wheels are frictionless, and the fluid is inviscid. (a) Determine the speed of the water leaving the tank, V1, and the water leaving the cart, V2. (b) Determine the tension in rope A, (c) Determine the tension in rope B.arrow_forward
- Prob6 conveyor belt discharges gravel into a barge as shown at a rate of 40 m³/min. If the gravel specific weight 18860 N/m³ 120 lbf, what is the tension in the hawser that secures the barge to the dock? Conveyor belt F-10 ft/s Hawser, Dock Gravel Barge Gravel 20⁰ +arrow_forward. Indiana Jones needs to ascend a high-rise building. There is a large hose filled with pressurized water hanging down from the building top. He builds a square platform and mounts four 4-cm-diamter nozzles pointing down at each corner. By connecting hose branches, a water jet can be produced from each nozzle. Jones, the platform, and the nozzles have a combined mass of 150 kg. Determine the minimum water jet velocity needed to raise the system.arrow_forwardA water jet with velocity of 15 m/sec leaving the 10 cm diameter nozzle strike to the plate in normal direction. Upon impact with the plate, the water is equally divided into two parts, i.e. one half leaves at 60° with respect to horizontal and the other half in a straight vertical direction. The density of water is 1000 kg/m3. Find the velocity at outlet neglecting change in elevation between inlet and outlet, gravity and friction between water and plate. Show your control volumearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY