
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
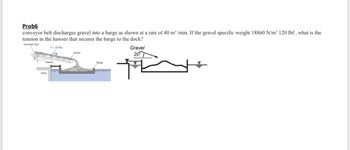
Transcribed Image Text:Prob6
conveyor belt discharges gravel into a barge as shown at a rate of 40 m³/min. If the gravel specific weight 18860 N/m³ 120 lbf, what is the
tension in the hawser that secures the barge to the dock?
Conveyor belt
F-10 ft/s
Hawser,
Dock
Gravel
Barge
Gravel
20⁰
+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A circular tank of diameter 3 m contains water up to a height of 4 m. The tank is provided with an orifice of diameter of 0.4 m at the bottom. Find the time taken by water to fall from 4 m to 2m. Take Cd= 0.60include your free body diagrama.84.7 seconds b.47.8 seconds c.24.8 seconds d.43.8 secondsarrow_forward3. A pump is located 4.5 m to one side of, and 3.5 m above a reservoir. The pump is designed for a flow rate of 6 L/s. For satisfactory operation, the static pressure at the pump inlet must not be lower than 26 m of water gage. Determine the smallest standard commercial steel pipe that will give the required performance. 4.5 mm- Pump -Q = 6 L/s 90°- elbows 3.5 m Water 5°Carrow_forwardAn engineering student has been given the assignment of designing a hydraulic holding system for a hay-baling system. The system has four cylinders with 120 mm diameter pistons with a stroke of 0.320 m. The lines connecting the system are 1 cm id (inside diameter). There are 15.5 m of lines in the system. For proper design, the reserve tank should hold a minimum of 50 percent more than the amount of hydraulic fluid in the system. If the diameter of the reserve tank is 30.48 cm, what is the shortest height it should be?arrow_forward
- A projectile is launched at an angle of 45 degrees from the top of a 100 m tall cliff at 50 m/s. How high does the projectile fly above the bottom of the cliff? Use g = -10 m/s/s.arrow_forwardA train has a weight of 100 tons (2,000lbf) is stopped from 4 mph in 1 ft by a hydraulic cushion.If rolling friction is 0.05 of the car weight, Find: • The stopping force using the gs method • The stopping force using the energy methodarrow_forwardA69 A typical escalator in the London Under- ground rises at an angle of 30° to the horizontal. It lifts people through a vertical height of 15 m in 1.0 minute. Assuming all the passengers stand still whilst on the escalator, 75 people can step on at the bottom and off at the top in each minute. Take the average mass of a passenger to be 75 kg. (a) Find the power needed to lift the passen- gers when the escalator is fully laden. For this calculation assume that any kinetic energy given to the passengers by the escalator is negligible. (b) The frictional force in the escalator system is 1.4 x 10*N when the escalator is fully laden. Calculate the power needed to overcome the friction. Hence find the power input for the motor driving the fully laden escalator, given that the motor is only 70% efficient. (c) When the passengers walk up the moving escalator, is more or less power required by the motor to maintain the escalator at the same speed? Explain your answer. (0 & C, '90]arrow_forward
- Consider a train consisting of an engine of mass 55 tonne pulling 10 trucks, each of mass 13 tonne, travelling up an incline of 1 in 100 (sine). The rolling resistance to motion is 40 N/tonne, and the train's speed is increased from 20 km/h to 37 km/h over a distance of 600 m. Calculate: the total mass of the train: kg. the change in height of the train: metres. the change in potential energy of the train: MJ. the starting velocity of the train: m/s. the final velocity of the train: m/s. the change in kinetic energy of the train: MJ. the work done against the rolling resistance: MJ. the total work done by the engine: MJ.arrow_forwardb) Figure Q3 shows a vehicle uses water scooping to slow down. The scoop is 3-m wide. Draw the free body diagram of the scoop. Determine the amount of force exerted on the scoop. If the force exerted by the flow to the scoop is 460 kN, determine the velocity of the vehicle. The vehicle scoops off 10 cm of water.arrow_forwardA TRUCK is SHoleliNG LiquiD slusH (8 = 20 kg/m²) THE SUSH is THROWN FORWARD AT 0= 60° As SHOWN , THE BADE is 3m wiDE. I h= 0.5m a) calalatE THE HasS Fow RATE OF slusH REMOVED FROM THE ROAD b) MAKE A SCHEMATIC OF A CONTRd voluMe AROUND THE BlADE INDICATE FORCES AND MASS FOw RATES IN 2 QUT OF THE CV. c calculATE THE VERTICA FORCE THAT THE slusH EXERTS ON THE elADE (NEGATIVE OP (MAGNITUDE 8 DIRECTiON) THE REACTION FORCE d) dalolATE THE HORIZONTA) FOROE AT THE shSH ERERTS ON THE BLADE (HAGN ITUDE E DIRECTnioN) berRA "e) How is THE TRUCK ABle To PROJIDE SUCH HORizoNTAl FORCE ? *F) waulo A LARGER O (Sax e=90°) RESUT iN A LARGER OR SMAller HorizONnA) FORCEarrow_forward
- Fluid flows through the pipe out of a rigid tank in the shape of a cube. During that process, heat is transferred into the rigid tank. Show the correct final form of energy equation valve m_cv2*u_cv2-m_cv1*u_cv1=-m_out*h_out+Q_in m_cv2*u_cv2-m_cv1*u_cv1=-m_out*h_out+Q_in+W_in m_cv2*u_cv2-m_cv1*u_cv1=m_in*h_in+Q_in-W_out m_cv2*u_cv2-m_cv1*u_cv1=-m_out*h_out-Q_out O m_cv2*u_cv2-m_cv1*u_cv1=m_in*h_in+Q_inarrow_forwardAn open cylinder tank, D= 1.0m, h=1.5m, contain water at depth 1.0m. If this tank rotate about its central vertical axis. Its the angular velocity without falling water from its open end * 8 rad/sec 8 rev/min 5 rad/sec 4.5 rad/min none of these=..arrow_forwardYou are designing a hydraulic lift for an automobile garage. It will consist of two oil-filled cylindrical pipes of different diameters. A worker pushes down on a piston at one end (d = 25cm), raising the car on a platform at the other end (d=?). To handle a full range of jobs, you must be able to lift cars up to 3000 kg, plus the 700 kg platform on which they are parked. To avoid injury to your workers, the maximum amount of force a worker should need to exert is 100 N. What should be the diameter of the pipe under the platform? If the worker pushes down with a stroke 50 cm long, by how much will he raise the car at the other end?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY