
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Hi! This question has 8 subparts. I need the last two G through H. Thank you!
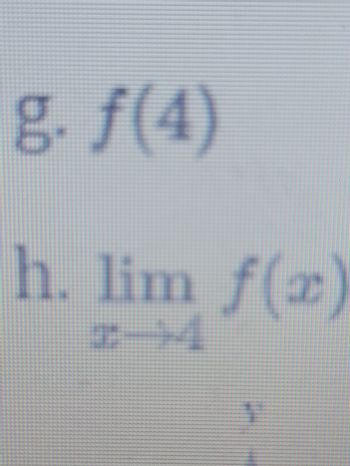
Transcribed Image Text:Here is the transcription of the image content, formatted for an educational website:
---
## Mathematical Problems
g. \( f(4) \)
h. \( \lim_{{x \to 4}} f(x) \)
---
### Explanation:
The problems presented involve two fundamental concepts in calculus and function analysis:
1. **Function Evaluation (g)**:
- The expression \( f(4) \) represents the value of the function \( f \) when the input \( x \) is 4. To solve this, one would substitute the value 4 into the function \( f \) and calculate the result.
2. **Limit of a Function (h)**:
- \( \lim_{{x \to 4}} f(x) \): This notation represents the limit of the function \( f(x) \) as \( x \) approaches 4. It involves analyzing the behavior of the function \( f \) in the vicinity of \( x = 4 \), but not necessarily at \( x = 4 \).
---
Understanding these concepts is crucial for mastering higher-level mathematics, including calculus and analysis. Further explanations and examples can be found in the resources provided on this site.
Transcribed Image Text:**Graph Analysis:**
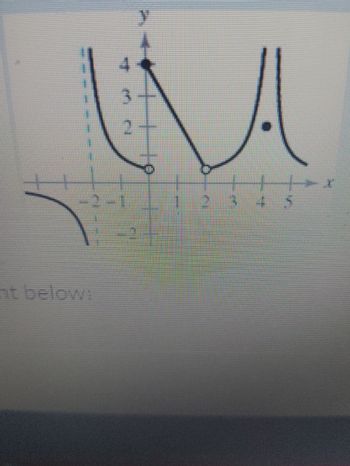
In this diagram, we observe the graphical representation of a mathematical function, featuring key points and characteristics. The x-axis and y-axis both span from -6 to 6, encompassing a portion of the Cartesian plane. The graph comprises various curves and distinct markers representing critical points.
### Key Features of the Graph:
1. **Axes:**
- The x-axis is labeled from -6 to 6.
- The y-axis is also labeled from -6 to 6.
2. **Curves:**
- The graph displays a function that appears to be broken into multiple segments, each of which exhibits unique behaviors.
3. **Points:**
- There are several significant points marked on the graph:
- The point (1, 4) is solid, indicating it is included in the function.
- There are points at (2, 3) and (3, 3) marked with circles, representing points excluded from the function.
- The point (3, 1) is solid, indicating it is included in the function.
- An additional point is located at (4, 4). This point is solid, indicating inclusion in the function.
### Detailed Function Behavior:
- As x approaches 2, there is an open circle indicating a discontinuity at y = 3.
- Moving along the x-axis, there is another open circle at (3, 3), followed by a solid point at (3, 1), suggesting a function shift or jump.
- Another segment proceeds from x = 3 onwards, with a solid increasing curve towards x = 4, where y reaches 4, represented by another solid point.
This graph could represent a piecewise function with specific inclusions and exclusions at marked points, highlighting important discontinuities. This is useful in understanding advanced mathematical concepts such as limits, continuity, and piecewise functions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning