
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A balanced Δ load having a 20 Ω resistance in each leg is connected to a three-phase, three-wire, Y-connected generator having a line voltage of 208V. Calculate the magnitude of the following. Express in Eng notation
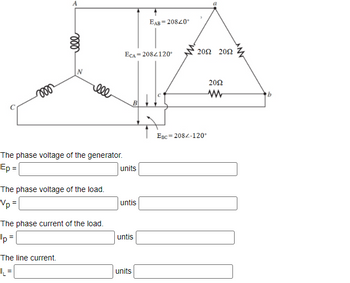
Transcribed Image Text:### Transcription for Educational Use
#### Diagram Explanation:
The image depicts a balanced three-phase system with a delta-connected load. The system consists of a Y-connected (wye-connected) generator and a delta-connected load.
**Generator:**
- Points A, B, and C represent the generator terminals.
- The phase voltages of the generator are:
- \( E_{AB} = 208 \angle 40^\circ \)
- \( E_{CA} = 208 \angle 120^\circ \)
- \( E_{BC} = 208 \angle -120^\circ \)
**Load:**
- Points a, b, and c represent the terminals of the delta-connected load.
- Each component of the delta load has a resistance of 20Ω.
#### Fields for Completion:
1. **The phase voltage of the generator:**
- \( E_P = \_\_\_\_ \) units \(\_\_\_\_\).
2. **The phase voltage of the load:**
- \( V_P = \_\_\_\_ \) units.
3. **The phase current of the load:**
- \( I_P = \_\_\_\_ \) units.
4. **The line current:**
- \( I_L = \_\_\_\_ \) units.
Each field is to be filled in with appropriate calculations based on the given physical properties and relationships in a balanced system, using principles such as Ohm’s Law and the relationships between line and phase voltages/currents in delta and wye configurations.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The shaft of a three-phase synchronous generator is rotating at 3000 RPM synchronous speed. This generator is supplying a load of 40 KW, 0.8 PF lagging, with an efficiency of 75 %. The copper losses are neglected. Calculate the sum PF&W + Pcore + Pstray Answer: The sum PF&W + Pcore + Pstray is: A 2300 V, 400 HP, 50 Hz, eight-pole, 0.85 Leading PF, Y-connected synchronous motor is having a negligible armature resistance, and a synchronous reactance of 15 2. This motor is operating at EA = 1841 Volts, and 8 = -25°. If the flux is increased by 10 % while the power is kept constant, find the new armature current and the new power factor of the motor. Answers: Magnitude of IA = PF = KW. Amp. ENarrow_forwardThree parallel three-phase loads are supplied from a 207.85-V rms, 60-Hz three-phase supply. The loads are as follows: Load 1: A 15 HP motor operating at full-load, 93.25 percent efficiency, and 0.6 lagging power factor. Load 2: A balanced resistive load that draws a total of 6 kW. Load 3: A Y-connected capacitor bank with a total rating of 16 kvar. (a) Draw the three-phase circuit. (b) What is the total system kW, kvar, power factor, and the supply current per phase? Please show formulas and work. (c) What is the system power factor and the supply current per phase when the resistive load and induction motor are operating but the capacitor bank is switched off? Please show formulas and work.arrow_forwardA three-phase, 3-wire, 120V, 60Hz, delta connected AC generator is applied to abalanced load having a resistance of 5Ω and 530.5µF in parallel. Find the phasecurrents.arrow_forward
- The single-line diagram of a three-phase power system is shown below. Bus 2 Q+01 10+Q T₁ T₂ Y Bus 1 Device Generator G₁: Generator G₂: Transformer T1: Transformer T2: Transformer T3: Line 2 Line 1 toot Load T3 S₁ 48 MVA 25 MVA 50 MVA 30 MVA 50 MVA Line 3 Bus 3 Figure 1 The manufacturer's nominal ratings are given as follows: Bus 4 (L-L)n 20 kV 13.8 kV 20/110 kV 13.8/110 kV 11/110 kV X₁ 20% 15% 8% 6% 10% (Note: Of course, the Xn in each row is the per-unit value impedance of that equipment when using on the Sn (Capacity of that equipment) and the U(L-L)n (Line-to-line voltage of that equipment) of that row as the MVA base and the voltage base.) The balanced three-phase load at bus 4 absorbs 60 MVA at 0.75 power factor (lagging), and lines 1, 2, and 3 have the reactance of 400, 32 Q, and 300, respectively. (a) Using the common base Sb = 50 MVA, draw the impedance diagram in per unit including the load impedance. (b) Now there is a solid balanced three-phase short-circuit fault at Bus 4,…arrow_forwardGlasses For the shown Crank diagram, if the voltage at the load is equal to ER=35 Volt and the characteristic impedance Z0-50 Ohm, then the Current scale for this diagram is equal exactly to 3A/8 d3 d=0=x/2 do 7.68 13.14 C. 10 4. 13.11 7.71 d2 1/4 1/8 35.5 mA/cm 53.3 mA/cm 90.8 mA/cm O 50 mA/cm 19arrow_forwardA three-phase, Y-connected, synchronous generator supplies a rated load of 12 MW at a power factor of 0.8 lagging. The synchronous impedance is 0.2 + j2 2/phase. If the terminal (line) voltage is 11 kV, calculate the no load line voltage. What is the voltage regulation? Vline (no load)=Eline=13 kV VR(%) 18.19%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,