
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
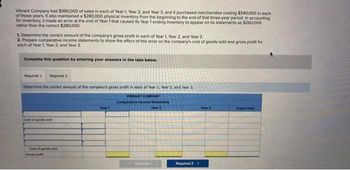
Transcribed Image Text:Vibrant Company had $980,000 of sales in each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3, and it purchased merchandise costing $540,000 in each
of those years. It also maintained a $280,000 physical inventory from the beginning to the end of that three-year period. In accounting
for inventory, it made an error at the end of Year 1 that caused its Year 1 ending inventory to appear on its statements as $260,000
rather than the correct $280,000.
1. Determine the correct amount of the company's gross profit in each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3.
2. Prepare comparative income statements to show the effect of this error on the company's cost of goods sold and gross profit for
each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1 Required 2
Determine the correct amount of the company's gross profit in each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3.
VIBRANT COMPANY
Cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold
Year 1
Comparative Income Statement
Year 2
Required 2 >
Year 3
3-year total
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Wildhorse Company took a physical inventory on December 31 and determined that goods costing $676,000 were on hand. Not included in the physical count were $9,000 of goods purchased from Sandhill Corporation, f.o.b. shipping point, and $29,000 of goods sold to Ro-Ro Company for $37,000, f.o.b. destination. Both the Sandhill purchase and the Ro-Ro sale were in transit at year-end. What amount should Wildhorse report as its December 31 inventory? December 31 Inventory $ %24arrow_forwardAt the beginning of the year Candle Co. has an inventory balance of $32,000. The company has net income for the year of $56,000. Later, the accountant discovers an error that caused the beginning invenotory to be understated by $6,000. a. Assuming no other changes, what is the correct net income for the year? b. If the error was discovered after year-end, what was the effect of the error on the balance sheet? Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardDuring the taking of its physical inventory on December 31, 20Y3, Zula Company incorrectly counted its inventory as $116,985 instead of the correct amount of $131,025. Indicate the effect of the misstatement on Zula's December 31, 20Y3, balance sheet or income statement for the year ended December 31, 20Y3. For each, select if the amount is overstated or understated. Then, input the over or under amount, entered as a positive value. Line Item Description Financial Statement Understated or Overstated Amount Current assets $fill in the blank 3 Gross profit $fill in the blank 6 Inventory $fill in the blank 9 Net income $fill in the blank 12 Stockholders' equity $fill in the blank 15 Total assets $fill in the blank 18arrow_forward
- Alphabet Company, which uses the periodic inventory method, purchases different letters for resale. Alphabet had no beginning inventory. It purchased A thru G in January at $5.00 per letter. In February, it purchased H thru L at $7.00 per letter. It purchased M thru R in March at $8.00 per letter. It sold A, D, E, H, J and N in October. There were no additional purchases or sales during the remainder of the year. If Alphabet Company uses the specific identification method, what is the cost of its ending inventory? Multiple Choice O O $81 $118 $36 $91arrow_forwardVibrant Company had $1,040,000 of sales in each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3, and it purchased merchandise costing $570,000 in each of those years. It also maintained a $340,000 physical inventory from the beginning to the end of that three-year period. In accounting for inventory, it made an error at the end of Year 1 that caused its Year 1 ending inventory to appear on its statements as $320,000 rather than the correct $340,000. 1. Determine the correct amount of the company's gross profit in each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3. 2. Prepare comparative income statements to show the effect of this error on the company's cost of goods sold and gross profit for each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Determine the correct amount of the company's gross profit in each of Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3. Cost of goods sold Cost of goods sold Gross profit Year 1 0 $ VIBRANT COMPANY Comparative Income Statements…arrow_forwardDengerarrow_forward
- Nord Store’s perpetual accounting system indicated ending inventory of $20,000, cost of goodssold of $100,000, and net sales of $150,000. A year-end inventory count determined that goodscosting $15,000 were actually on hand. Calculate (a) the cost of shrinkage, (b) an adjusted costof goods sold (assuming shrinkage is charged to cost of goods sold), (c) gross profit percentagebefore shrinkage, and (d) gross profit percentage after shrinkage. Round gross profit percentagesto one decimal placearrow_forwardNavajo Company's year-end financial statements show the following. The company recently discovered that in making physical counts of inventory, it had made the following errors: Year 1 ending inventory is understated by $60,000 and Year 2 ending inventory is overstated by $30,000. Year 2 965,000 $ 285,000 1,370,000 1,590,000 Year 3 800,000 260,000 1,240,000 1,255,000 For Year Ended December 31 Year 1 (a) Cost of goods sold (b) Net income (c) Total current assets (d) Total equity 24 735,000 $ 278,000 1,257,000 1,397,000 Required: 1. For each key financial statement figure-(a), (b), (C), and (d) above-prepare a table to show the adjustments necessary to correct the reported amounts. 2. What is the total error in combined net income for the three-year period resulting from the inventory errors? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 For each key financial statement figure-(a), (b), (c), and (d) above-prepare a table to show the adjustments…arrow_forwardIf Soda Popinski's Company's ending inventory was actually $86,000 but was adjusted at year end to a balance of $68,000 in error, what would be the impact on the presentation of the balance sheet and income statement for the year that the error occurred, if any?arrow_forward
- Stanley Flooring Company’s perpetual inventory records indicate that $1,129,000 of mer-chandise should be on hand on December 31, 20Y1. The physical inventory indicates that $1,109,300 of merchandise is actually on hand. Journalize the adjusting entry for the inventory shrinkage for Stanley Flooring Company for the year ended December 31, 20Y1. Assume that the inventory shrinkage is a normal amount.arrow_forwardFalkenberg Company uses the periodic method. They had the following inventory transactions throughout the period. (Assume these are the only transactions for the period). Additionally, Falkenberg had $13,200 of Operating Expenses, $4,500 of Interest Revenue and $3,300 of Interest Expense for the period. March 3: Purchased $160,000 of merchandise from Lin Company under terms 2/10, n/30. March 4: Paid $900 in freight charges to ship goods from Lin Company. March 7: Returned $10,000 of goods to Lin Company that were deemed defective. March 13: Paid the balance due to Lin Company. March 20: Sold goods costing $120,000 to Renner company for $156,000 under terms 1/15, n/30. March 25: Renner returned $14,300 of goods to Falkenberg. The goods cost Falkenberg $11,000. April 4 – Renner paid Falkenberg the balance due. 1.What is Falkenberg’s Net Purchases? What is Falkenberg’s Cost of Goods Purchased? What is Falkenberg’s Cost of Goods Available for sale, assuming that beginning inventory is…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education