
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Two cars, both of mass m, collide and stick together. Prior to the collision, one car had been traveling north at speed 2v, while the second was travelling at speed v at an angle theta south of east (as indicated in the figure). After the collision, the two car system travels at a speed vfinal at an angle phi east of north. Express your answers in terms of known quantities.
Find the magnitude of the speed vfinal in terms of v and theta.
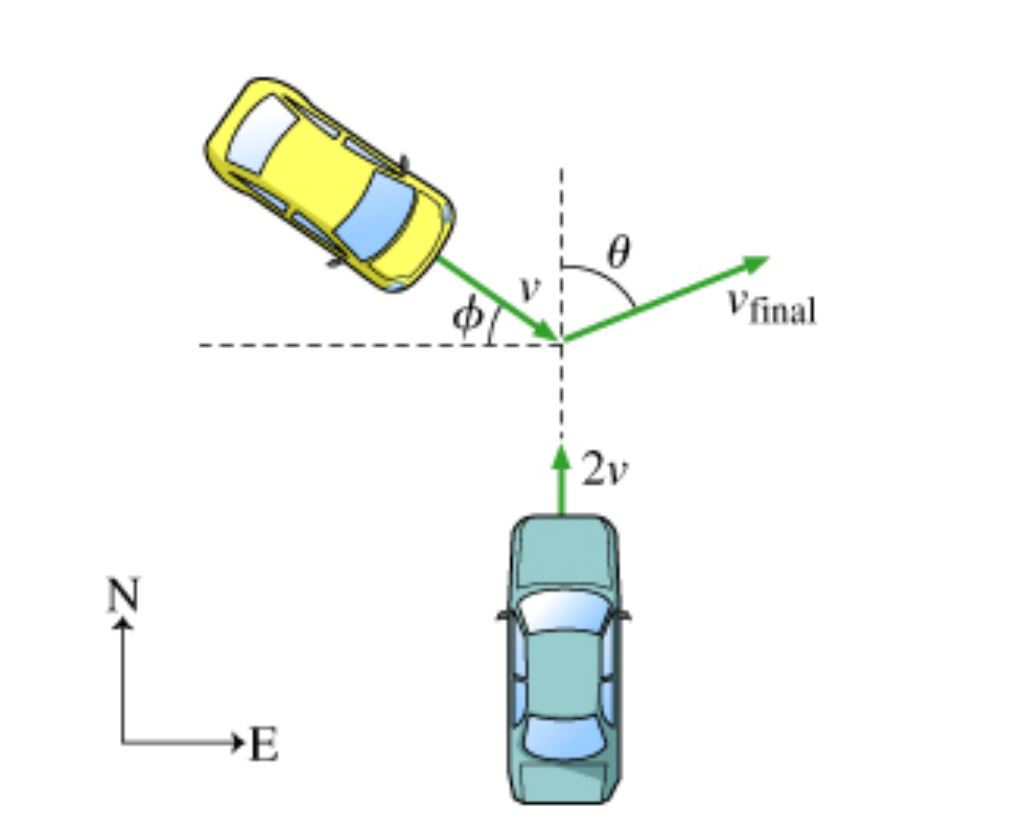
Transcribed Image Text:Vfinal
2v
→E
Z+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Now let's consider the impulse associated with kicking a soccer ball (Figure 1). The ball has mass 0.40 kg . Initially it moves horizontally to the left at 20 m/s, but then it is kicked and given a velocity with magnitude 30 m/s and direction φ=45∘ upward and to the right. Find the impulse of the force and the average force on the ball, assuming a collision time Δt=0.010s a) Suppose the ball is moving at 30 ∘ downward from the horizontal before it is kicked. If all the numerical values are the same as before, find the magnitude of the average force on the ball. b)Find the direction of the average force on the ball found in Part A.arrow_forwardTrain cars are coupled together by being bumped into one another. Suppose two loaded train cars are moving toward one another, the first having a mass of 170,000 kg and a velocity of 0.300 m/s, and the second having a mass of 105,000 kg and a velocity of -0.120 m/s. (The minus indicates direction of motion.) What is their final velocity (in m/s)? 38400 X m/s Additional Materials O Readingarrow_forward6.3 PQ1 Newton's second law can be stated that the force is equal to the rate of change of momentum, F = d(mv)/dt. Tak- ing the derivative by parts yields F = m(dv) / (dt) + v(dm) / (dt). This does not correspond to F = ma. What is the source of the discrepancy? %3Darrow_forward
- A 1200 kg car driving due north at 15 m/s collides with a 2300 kg truck traveling east at aspeed of 10 m/s. After the collision, they lock bumpers traveling together. What is the final velocityvector of the combined car/truck after the collision? Give in unit vector notation and compute amagnitude and direction.arrow_forwardA firework explodes into three pieces as shown in the diagram below. Now that you have set up the equation for the x and y components of the final momentum of the firework, let's do some physics! Given: The initial firework had a mass of 9.0 kg and was launched at vi = 110 m/s vertically straight up. The firework explodes into three pieces of equal mass 3.0 kg. The angles θ1 = θ3 = 20 ∘. Speed v1 = 100 m/s. What is the speed v2? Note: the angles shown for mass m1 and mass m3 are relative to the horizontal x axis. Mass m2 is moving straight up (y axis).arrow_forwardDon't use chat gptarrow_forward
- Consider the collision of a karate expert's hand with a concrete block. Based on the graphs in the figure below, the initial downward velocity of the fist with mass 0.50 kg is about −12.5 m/s and the collision time is approximately 25 ms. Find the impulse (in kg · m/s) and the average force (in N) exerted on the block by the fist during the collision. (Indicate the direction with the signs of your answers.) impulse...... kg · m/s average force....... Narrow_forwardIn order to answer this question, follow the steps provided and remember that the total initial momentum of the system must equal the total final momentum. Also, remember that momentum and velocity are vector quantities so you must specify a negative sign if the motion is to the left. A green truck of mass 2500 kg travels to the right with a velocity vig = 3.7 m/s. The green truck approaches a red truck with mass 1460 kg that is traveling to the left with a velocity of vir = -3 m/s. The trucks collide and stick together after the collision. What is the final velocity, vf of the green-red truck system after the collision. (look at the figure/picture)(a) What was the initial momentum of the green truck before the collision?pgi = 9250 kg m/s(b) What was the initial momentum of the red truck before the collision?pri = -4380 kg m/s(c) What was the total initial momentum of the system of trucks?pTf = 4870 kg m/s (d) What must be the total final momentum of the system after the collision if…arrow_forwardA and B pleasearrow_forward
- A ball of mass m moving with velocity v⃗ i strikes a vertical wall as shown in (Figure 1). The angle between the ball's initial velocity vector and the wall is θi as shown on the diagram, which depicts the situation as seen from above. The duration of the collision between the ball and the wall is Δt , and this collision is completely elastic. Friction is negligible, so the ball does not start spinning. In this idealized collision, the force exerted on the ball by the wall is parallel to the x axis.What is the magnitude F of the average force exerted on the ball by the wall?arrow_forwardA billiard ball moving at 5.95 m/s strikes a stationary ball of the same mass. After the collision, the first ball moves at 4.93 m/s, at an angle of 34° with respect to the original line of motion. (a) Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the second ball after collision. (Enter the direction with respect to the original line of motion. Include the sign of your answer. Consider the sign of the first ball's angle.) m/s (b) was the collision inelastic or elastic? O inelastic O elasticarrow_forwardUSING THE UAM FORMULA, SOLVE: A constant force of 3.5 N acts on a 7 kg block, initially at rest, for 7.0 s. Find the(a) acceleration of the block, (b) speed of the block at the end of 7.0 s, (c) change in momentum of the block, and (d) impulse produced by the force.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON