
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Refer to Figure 5.2. A square foundation measuring 1.5 m x 1.5 m is supported by a saturated clay layer of limited depth underlain by a rock layer. Given that Df = 1 m, H = 0.7 m, cu = 115 kN/m2, and γ = 18.5 kN/m3, estimate the ultimate bearing capacity of the foundation.
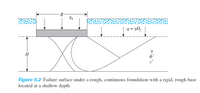
Transcribed Image Text:В
q = yD;
H
Figure 5.2 Failure surface under a rough, continuous foundation with a rigid, rough base
located at a shallow depth
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A square foundation is shown in Figure 4.30, with e = 0.3 m and eg = 0.15 m. Assume two-way eccentricity, and determine the ultimate load, Q %3D Sảnd 18 kN/m 30 1.5 m x 1.5 m R= 0.15 m 15 m EL 0.3 m Figure 4.30 An eccentrically loaded foundation 1.5 marrow_forwardThis is Civil Engineering. Specifically Foundation Engineering. Please post thorough answers and work. Any plot needs to be computer generated. Thank youarrow_forwardA sandstone bed with RQD = 70% and y = 26.0 kN/m³ lies beneath 1.5 m of overburden soil. A 2.0 m X 2.0 m square foundation is to be placed on top of the sandstone rock (i.e., at a 1.5 depth below the ground level) to carry a column load. The unit weight of the soil is 18.0 kN/m³. Assuming the rock strength parameters from Problem 7.17,arrow_forward
- Example 12.6 A square foundation is shown in Figure 12.9. Assume that the load eccentricity e 0.5 ft. Determine the ultimate load, Qut Sand y = 115 lb/ft d' = 30° 5ft X5ft c' 0 Figure 12.9arrow_forwardA 2.0 m wide continuous foundation is placed at 1.5 m depth in a saturated clay where cu = 40 kN/m2 and γ = 17 kN/m3. At 2.0 m below the ground level, this clay layer is underlain by a stiffer clay where cu = 60 kN/m2 and γ = 18 kN/m3. What would be the maximum wall load allowed with FS = 4?arrow_forward4. A flexible foundation is shown below, determine the immediate settlement below the center of the foundation. Assume the thickness of the soil below the foundation is 20 meters. Following is the variation of the modulus of the soil below the foundation. Es (kN/m²) Depth below the foundation(m) 0-4 4-8 8-20 >20 1.2m 10000 8000 12000 ∞ 90 = BXL = 2m x 2m Us = 0.3 150kPaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning