
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
This is Civil Engineering. Specifically Foundation Engineering. Please post thorough answers and work. Any plot needs to be computer generated. Thank you
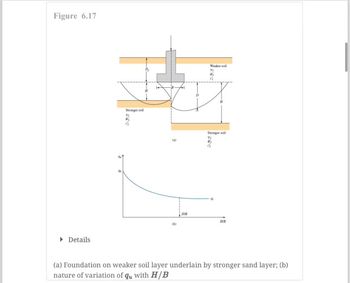
Transcribed Image Text:**Figure 6.17**
**Diagram (a):** Represents a foundation on a weaker soil layer underlain by a stronger sand layer. The diagram shows the structure's placement on two soil layers: the upper layer (weaker soil) and the lower layer (stronger soil). Key dimensions in the diagram are labeled, such as:
- \(D_1\): Depth of weaker soil
- \(D_2\): Depth of stronger soil
- \(B\): Width of the foundation
- \(H\): Height of the weaker soil layer
- \(\phi_1\): Angle of friction of the weaker soil
- \(\phi_2\): Angle of friction of the stronger soil
- \(\gamma_1\): Unit weight of the weaker soil
**Graph (b):** Illustrates the nature of variation of \(q_u\) with \(H/B\). The graph displays a curve that shows how the ultimate bearing capacity (\(q_u\)) changes as the ratio of the height of the weaker soil layer (\(H\)) to the width of the foundation (\(B\)) varies. Initially, the \(q_u\) value is relatively high when \(H/B\) is small, and it gradually decreases as \(H/B\) increases, showing an inverse relationship between \(q_u\) and \(H/B\).

Transcribed Image Text:### Problem 6.12
Refer to Figure 6.17. For a continuous foundation on layered clay, the following parameters are given:
- **Foundation Dimensions and Depth:**
- Width (\( B \)) = 1.5 m
- Depth of foundation (\( D_f \)) = 1 m
- Thickness of clay layer (\( H \)) = 0.8 m
- **Layer 1 Properties:**
- Unit weight (\( \gamma_1 \)) = 16.5 kN/m³
- Cohesion (\( c_1 = c_{u(1)} \)) = 48 kN/m²
- Angle of internal friction (\( \phi_1 \)) = 0
- **Layer 2 Properties:**
- Unit weight (\( \gamma_2 \)) = 17.5 kN/m³
- Cohesion (\( c_2 = c_{u(2)} \)) = 96 kN/m²
- Angle of internal friction (\( \phi_2 \)) = 0
Using Equation (6.46), determine the gross ultimate bearing capacity.
### Explanation:
The problem involves calculating the bearing capacity of a foundation resting on a two-layered clay system. The necessary parameters like width, depth, unit weights, cohesion values, and angles of internal friction for each layer are specified. Since the angles of internal friction are zero, the soil behaves as a purely cohesive material.
### Diagram Explanation:
The diagram (Figure 6.17) typically illustrates a cross-section of the layered foundation system, showing the different layers of clay with their respective properties, including the thickness (\( H \)), depth (\( D_f \)), and width (\( B \)). Each layer is labeled with its specific unit weight and cohesion.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning