
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Determine the magnitude and sense of the forces in bars A and B of the figure below. Use the Algebraic method then graph the results.
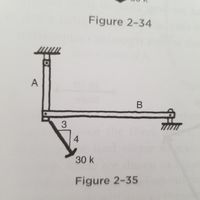
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 2-34
A
B
4
30 k
Figure 2-35
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Determine the X and Y -components of the forces shown in the figure.arrow_forwardPart Farrow_forwardIn the structures shown below all members have the same Young's Modulus, E, second moment of area, I, and cross sectional area, A. (a) Calculate the vertical deflection of the point load in the structure shown below. L A L (b) Using the principle of virtual work, calculate the internal forces in all the members in the structure shown below L A в (c) State all the assumptions. Barrow_forward
- 2. Solve the following problem of bars in axial load using the finite element method, finding a) displacements at the nodes, b) reactions at supports, c) forces and stresses in each element. Consider E1=E2=E3=200GPa, A1= 20x10-4 m2, A2= 10x10-4 m2, A3= 8x10-4 m2 for the bars. F2= 40kN, F3= 50kNarrow_forwardThere are two segments to the beam: (1) Point A to Point C, and (2) Point C to Point B. Establish a coordinate system such that x = 0 at Point A. (a) Draw a Free Body that extends from Point A for a distance x such that x1.5 m. Solve for the internal forces V(x) and M(x) as functions of x. Use the F.B. and Equations of Equilibrium to find these functions. (c) Draw a 3rd Free Body from a point x (x>1.5) to Point B. In other words draw a free body of the right hand portion of the beam. This segment should have length = 3m – x. Use this F.B. and equations of equilibrium to solve for internal force V(x) and M(x) as functions of x. Prove to yourself that the V(x) and M(x) functions found in Part II.(c) are equal to those found in Part II.(b). 8 kN/m 4 kN/m В 1.5 m 1.5 marrow_forwardI'm quite confused whether we're going to consider the friction at C going to the left or going to the right since by inspection, the object has the tendency to slip to the right so we'll have friction on the opposite direction. On the other hand, we can have friction to the right since there is force P acting on member BC. How do you solve this?arrow_forward
- 2. Resolve the vector force into its components in the Figure shown. * Z 2m F=80 kN 5m 3marrow_forwardSolve the problem by the moment-area method. The beam has constant flexural rigidity EI. A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P at the positions shown in the figure. B C 4. 4 A support C at the midpoint of the beam is positioned at distance d below the beam before the loads are applied. Assuming that d = 12 mm, L = 5.4 m, E = 200 GPa, and I = 193 x 10° mm, calculate the magnitude of the loads P (in kN) so that the beam just touches the support at C. 163.87 x kNarrow_forwardIn the system shown, the rigid bar ABC is subjected to a load w = 0.5 kip/in. Bars 1, 2 and 3 are made of steel and are hinged at both ends. a) State whether the system is statically determinate or indeterminate and the degree of indeterminacy. b) Determine the force in steel bars 1, 2, and 3 (indicating whether they are in tension or compression). c) Determine the displacement of point A. All steel bars have area A=1.25 in^2 L= 6 in Eac = 29×10^3 ksiarrow_forward
- Determine the force in members BC, GA, and BG of the truss shown in the figure below. Let P = 175 kN. NOTE: If your answer is a compressive force then just put a negative sign. If your answer is a tensile force then just type the answer directly. (ALSO, DON'T FORGET THE UNITS) 2P 2P 30 60V60° 60°V60° C 30 D 3P 4m 4m 4m Solve the force in member BC. Solve the force in member GA. Solve the force in member BG.arrow_forwardProblem 2: For the beam given below: (a) Calculate all support reactions. (b) Draw the shear diagram. Show all important values of shear. Show the sign convention within each region. (c) Draw the moment diagram. Show all important values of moment. Show the sign conventions within each region (concavity: smiley face, sad face, etc.) (d) Sketch the deflected shape. Show supports in your sketch. For your solution, let w = 2 kips/ft and L = 20 ft. A L 22 B L W Carrow_forwardThe beam section given in the figure is under the influence of M = 5 kN.m bending moment. Section C and B ' Calculate the normal stresses that will occur at the points. E = 200 GPa. (N-A axis weight passes through the center.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning