
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
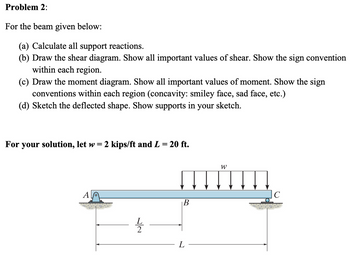
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2:
For the beam given below:
(a) Calculate all support reactions.
(b) Draw the shear diagram. Show all important values of shear. Show the sign convention
within each region.
(c) Draw the moment diagram. Show all important values of moment. Show the sign
conventions within each region (concavity: smiley face, sad face, etc.)
(d) Sketch the deflected shape. Show supports in your sketch.
For your solution, let w
=
2 kips/ft and L = 20 ft.
A
L
22
B
L
W
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Question: Determine the internal loading in the hook shown below at the point R, 8. A free body diagram of the hook's end is provided. The hook may be analysed as a 2 dimensional body. Given: R = 0.2 m 0 = 30 deg F-3 KN 1) Find the normal force N. 2) Find the shear force V. 3) Find the bending moment M. Narrow_forward90 MPa 55 MPa 70 MPa y I 70 MPa ➜X 55 MPa →90 MPa 65°arrow_forward9 Consider the plane truss with load Pas shown in the figure. Let the horizontal and vertical reactions at the joint B be Hg and V, respectively and Vc be vertical reaction at the joint C. 2 exhoM S SLO 60° - II B A 60° D L 60° F 60° KLA G P с Which one of the following sets gives the correct values of VB, HB and V? (a) VB = 0; HB = 0; Vc = P (b) VB P/2; HB = 0; Vc = P/2 (c) VB = P/2; HB = P (sin60°); Vc = P/2 (d) VB = P; HB = P (cos(60°); Vc = 0 [2016arrow_forward
- The horizontal beam is supported by a pin at A and the pin-connected link BC. It has a uniformly distributed loading w = 7.0 kN/m as shown in the figure. All the pins are in double shear and have a diameter of 20 mm. Determine the max shear stress in the pin at A. Input your answer as a value only in MPa to one decimal place without +/- sign. W 1.5 m 2 m B 1 marrow_forwardThe two bars are made of polystyrene, which has the stress-strain diagram shown. If the cross-sectional area of bar AB is 975 mm² and BC is 2600 mm², determine the largest force P that can be supported before any member ruptures. Assume that buckling does not occur. Include complete steps with explanations and FBD. 1m baxilno σ (MPa) 175 140 105 70 A 35ptension 0 0.20 -1.2 m P 0.40 compression B 0.60 0.80 € (mm/mm)arrow_forwardThe shear strain at corner A of the following rectangle with respect to Y-axis is 350 300 All dimensions are in mmarrow_forward
- Calculate the forces in all members using equilibrium of joint, ALso check weather the member is in tension or in compression. only HANDWRITTEN answer needed ( NOT TYPED)arrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point in a member is shown on the element. Determine the principal normal stresses and their orientation and the maximum in-plane shear stress and their orientation. Draw Mohr’'s circle and Show results on properly oriented elements. -60 30 -50 40 -40 T-30 30 30 -20 40 30 -10 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 30 40 50 10 20 бо 10 20 30 40 50 60arrow_forwardI need help with this exercise from my homework. I have no idea about how to solve it. I need an step by step solving and explanation, please.arrow_forward
- Identify the equation for the deflection at point C.arrow_forwardQuestion stated in the picture. Detailed answer is neededarrow_forwardThe beam cross section shown below has been proposed for a short pedestrian bridge. The cross section will consist of two pipes that are welded to a rectangular web plate. Dimensions of the cross section are: h = 470 mm tw = 14 mm d = 120 mm t = 9.6 mm Additionally: • The area of each pipe is A = 3330 mm2. • The moment of inertia of the entire beam cross section about the z centroidal axis is IZ = 428040000 mm4. If the beam will be subjected to a shear force of V = 225 kN, determine the shear stress at point H, located at yH = 110 mm above the z centroidal axis.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning