V = 36 V Refer to the figure at the right. iz What is the potential of point a with respect to point b when switch S is open? 3 0 What is the current through switch S S When it is closed? What is the equivalent resistance of this combination of resistors when S is closed?

The given circuit diagram is shown below:
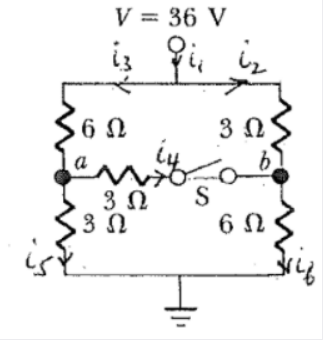
(a)
The circuit diagram when the switch S is open can be drawn as shown below:
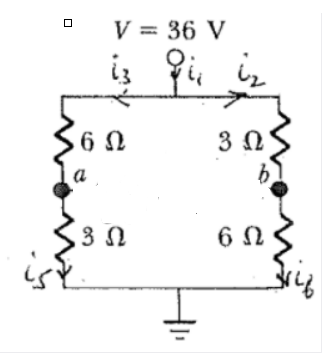
The equivalent resistance if the resistance which are in series on the left-hand side and right-hand side of the circuit is:
Similarly,
Thus, these equivalent resistances will be in parallel combination. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the complete circuit is:
From ohm's law:
Since the resistance on the left-hand side of the circuit is the same as the resistance on the right-hand side of the circuit. Thus, the current flowing through them will be the same:
Thus, the potential at point 'a' can be calculated as:
And, the potential at point 'a' can be calculated as:
Therefore, the required potential is:
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images









