
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
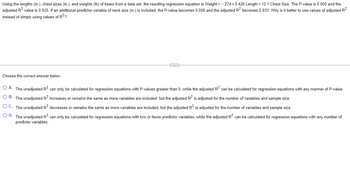
Transcribed Image Text:Using the lengths (in.), chest sizes (in.), and weights (lb) of bears from a data set, the resulting regression equation is Weight= -274 +0.426 Length + 12.1 Chest Size. The P-value is 0.000 and the
adjusted R² value is 0.925. If an additional predictor variable of neck size (in.) is included, the P-value becomes 0.000 and the adjusted R² becomes 0.933. Why is it better to use values of adjusted R²
instead of simply using values of R²?
Choose the correct answer below.
C
O A. The unadjusted R² can only be calculated for regression equations with P-values greater than 0, while the adjusted R² can be calculated for regression equations with any manner of P-value.
O B. The unadjusted R² increases or remains the same as more variables included, but the adjusted R² is adjusted for the number of variables and sample size.
OC. The unadjusted R² decreases or remains the same as more variables are included, but the adjusted R² is adjusted for the number of variables and sample size.
O D. The unadjusted R² can only be calculated for regression equations with two or fewer predictor variables, while the adjusted R² can be calculated for regression equations with any number of
predictor variables.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The data show the chest size and weight of several bears. Find the regression equation, letting chest size be the independent (x) variable. Then find the best predicted weight of a bear with a chest size of 39 inches. Is the result close to the actual weight of 236 pounds? Use a significance level of 0.05. Chest size (inches) 44 41 41 55 51 42 Weight (pounds) 213 206 176 309 300 178 Click the icon to view the critical values of the Pearson correlation coefficient r. What is the regression equation? y = x (Round to one decimal place as needed.) What is the best predicted weight of a bear with a chest size of 39 inches? The best predicted weight for a bear with a chest size of 39 inches is pounds. (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Is the result close to the actual weight of 236 pounds? A. This result is close to the actual weight of the bear. B. This result is exactly the same as the actual weight of the bear. O C. This result is not very close to the actual weight of the bear. O…arrow_forwardintents d Resource Listed below are foot lengths (mm) and heights (mm) of males. Find the regression equation, letting foot length be the predictor (x) variable. Find the best predicted height of a male with a foot length of 273.1 mm. How does the result compare to the actual height of 1776 mm? Foot Length 282.4 277.9 253.4 259.3 279.2 258.2 273.6 262:3 Height 1785.1 1770.9 1676.0 1646.1 1859.0 1710.1 1789.3 1736.9 The regression equation is y=+x. (Round the y-intercept to the nearest integer as needed. Round the slope to two decimal places as needed.) ype here to search Tutoring Help me solve this O i Get more help. C 3¹ ... 99+ 0 LA 6 3 Clear all Check answer 78°F ^®arrow_forwardThe relationship between the number of games won by a minor league baseball team and the average attendance at their home games is analyzed. A regression to predict the average attendance from the number of games won has an R2 = 25.6%. The residuals plot indicated that a linear model is appropriate. What is the correlation between the average attendance and the number of games won. A. 0.066 B. 0.863 C. 0.506 D. 0.744 E. 0.256arrow_forward
- Listed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (in mm Hg) obtained from the same woman. Find the regression equation, letting the right arm blood pressure be the predictor (x) variable. Find the best predicted systolic blood pressure in the left arm given that the systolic blood pressure in the right arm is 90 mm Hg. Use a significance level of 0.05. Right Arm 103 102 95 79 80 Left Arm 174 168 143 143 144 LOADING... Click the icon to view the critical values of the Pearson correlation coefficient r The regression equation is y=____?+____?x.arrow_forwardYou need to determine the slope of the regression line for a data set. The sums of the variables are given below. n = 14 Ex = 146.5 Ey = 993 Exy = 10,427 Ex2 = 1552 Ey? : = 70,510.5 Find the slope, only. Round the answer to the thousandths place.arrow_forwardFind the regression equation, letting the diameter be the predictor (x) variable. Find the best predicted circumference of a marble with a diameter of 1.8 cm. How does the result compare to the actual circumference of 5.7 cm? Use a significance level of 0.05. Baseball Basketball Golf Soccer Tennis Ping-Pong Volleyball 7.5 21.4 4.0 Diameter Circumference 23.6 23.9 75.1 4.3 22.1 13.5 69.4 7.1 22.3 12.6 67.2 Click the icon to view the critical values of the Pearson correlation coefficient r. The regression equation is y= 0 (Round to five decimal places as needed.) + X.arrow_forward
- The data show the chest size and weight of several bears. Find the regression equation, letting chest size be the independent (x) variable. Then find the best predicted w Click to copy table. a chest size of 58 inches. Is the result close to the actual weight of 632 pounds? Use a significance level of 0.05. Chest size (inches) Weight (pounds) 46 57 53 41 40 40 384 580 542 358 306 320 Click the icon to view the critical values of the Pearson correlation coefficient r. What is the regression equation? y = + x (Round to one decimal place as needed.) What is the best predicted weight of a bear with a chest size of 58 inches? The best predicted weight for a bear with a chest size of 58 inches is pounds. (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Is the result close to the actual weight of 632 pounds? A. This result is close to the actual weight of the bear. B. This result is very close to the actual weight of the bear. C. This result is exactly the same as the actual weight of the bear. D.…arrow_forwardUse the following data to estimate a regression with femur length as the x-variable and tibia length as the y-variable. Femur Length Tibia Length 18.7 14.2 20.5 15.9 16.2 13.1 15.0 12.4 19.0 16.2 21.3 15.8 21.0 16.2 14.3 12.1 15.8 13.0 14.3 13.8 18.8 18.7 Is the following statement true or false: "The intercept of the regression is equal to (approximately) 3.59" True Falsearrow_forwardA regression was run to determine if there is a relationship between hours of tv watched per day (x) and number of sit-ups a person can do (y)arrow_forward
- For the relationship between Calories and Carbs, here is the equation of the line of best fit: nts Regression Equation: Calories = 2.36 + 4.432 Carbs The range of Carb values in the dataset was between 17 and 47 Carbs. What wourd you say if asked to predict the number of Calories if a cereal had 60 Carbs? Type your response in the text box..arrow_forwardUsing the regression formula with a slope = .704 and an intercept = .719, what would the predicted college GPA be for a student whose current high school GPA = 3.2?arrow_forwardUse the value of the linear correlation coefficient r to find the coefficient of determination and the percentage of the total variation that can be explained by the linear relationship between the two variables. r=0.853arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman