
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133949640
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Using the information below, calculate how much energy (in kJ) is released when 12.0 g of water vapor at 113.0 ºC is cooled to 100 ºC and then condensed, GFM = 18.016 g/mol. Show all work and report you final answers to the correct units and significant figures.
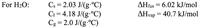
Transcribed Image Text:Cs = 2.03 J/(g.°C)
Ci = 4.18 J/(g-°C)
Cg = 2.0 J/(g.°C)
For H2O:
AHfus = 6.02 kJ/mol
AHvap = 40.7 kJ/mol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9.83 A student performing a calorimetry experiment combined 100.0 mL of 0.50 M HCl and 100.0 mL of 0.50 M NaOH in a coffee cup calorimeter. Both solutions were initially at 20.0°C, but when the two were mixed, the temperature rose to 23.2°C. (a) Suppose the experiment is repeated in the same calorimeter but this time using 200 mL of 0.50 M HCl and 200.0 mL of 0.50 M NaOH. Will the T observed he greater than, less than, or equal to that in the first experiment, and why? (b) Suppose that the experiment is repeated once again in the same calorimeter, this time using 100 mL of 1.00 M HCl and 100.0 mL of 1.00 M NaOH. Will the T observed he greater than, less than, or equal to that in the first experiment, and why?arrow_forwardPrinciples of Heat Flow Titanium is a metal used in jet engines. Its specific heat is 0.523 J/g C. If S.SS g of titanium absorb 4.78 J, what is the change in temperature?arrow_forwardA wad of steel wool (specific heat=0.45J/gC) at 25C is misplaced in a microwave oven, which later is accidentally turned on high. The oven generates microwaves of 13.5 cm wavelength at the rate of 925 moles of those photons per second. All of the photons are converted to high-heat energy, raising the temperature of the steel wool. Steel wool reacts explosively with the oxygen in the oven when the steel wool reaches 400.0C. If the steel wool explodes after 1.55 seconds, how many grams of steel wool were accidentally put into the oven?arrow_forward
- At 298 K, the standard enthalpies of formation for C2H2(g) and C6H6(l) are 227 kJ/mol and 49 kJ/mol, respectively. a. Calculate H for C6H6(l)3C2H2(g) b. Both acetylene (C2H2) and benzene (C6H6) can be used as fuels. Which compound would liberate more energy per gram when combusted in air?arrow_forwardGiven the following data 2O3(g) 3O2(g)H = 427 kJ O2(g) 2O(g)H = 495 kJ NO(g) + O3(g) NO2(g) + O2(g)H = 199 kJ Calculate H for the reaction NO(g) + O(g) NO2(g)arrow_forwardA student performing a calorimetry experiment combined 100.0 ml. of 0.50 M HCI and 100.0 ml. of 0.50 M NaOH in a StyrofoamTM cup calorimeter. Both solutions were initially at 20.0 C, but when the two were mixed, the temperature rose to 23.2 C (a) Suppose the experiment is repeated in the same calorimeter but this time using 200 mL of 0.50 M HCl and 200.0 ml of 0.50 M NaOH. WIII the AT observed be greater than, less than, or equal to that in the first experiment, and why? (b) Suppose that the experiment is repeated once again in the same calorimeter, this time using 100 mL of 1.00 M HCI and 100.0 ml. of 1.00 M NaOH. Will the T observed be greater than, less than, or equal to that in the first experiment, and why?arrow_forward
- 9.38 The energy densities of various types of coal are listed below: Anthracite 35 kJ/g Subbituminous 31 kJ/g Bituminous 28 kJ/g Lignite 26 kJ/g An unknown sample of one of these coals is burned in an apparatus with a calorimeter constant of 1.3 kJ/°C. When a 0.367-g sample is used, the temperature change is 8.75°C. Which type of coal is the sample?arrow_forwardExplain in your own words what is meant by the term entropy. Explain how both matter spread and energy spread are related to the concept of entropy.arrow_forwardThe overall reaction that occurs when sugar is metabolized is C12H22O11(s)+12O2(g)12CO2(g)+11H2O(l) For this reaction, H° is -5650 kJ and G° is -5790 kJ at 25°C. (a) If 25% of the free energy change is actually converted to useful work, how many kilojoules of work are obtained when one gram of sugar is metabolized at body temperature, 37°C? (b) How many grams of sugar would a 120-lb woman have to eat to get the energy to climb the Jungfrau in the Alps, which is 4158 m high? ( w=9.79103mh, where w= work in kilojoules, m is body mass in kilograms, and h is height in meters.)arrow_forward
- The decomposition of ozone, O3, to oxygen, O2, is an exothermic reaction. What is the sign of q? If you were to touch a flask in which ozone is decomposing to oxygen, would you expect the flask to feel warm or cool?arrow_forwardWould the amount of heat absorbed by the dissolution in Example 5.6 appear greater, lesser, or remain the same if the heat capacity of the calorimeter were taken into account? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardIn earlier times, ethyl ether was commonly used as an anesthetic. It is, however, highly flammable. When five milliliters of ethyl ether, C4H10O(l)(d=0.714g/mL), are burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature rises from 23.5C to 39.7C. The calorimeter contains 1.200 kg of water and has a heat capacity of 5.32 kJ/C. (a) What is qH2o? (b) What is qcal? (c) What is q for the combustion of 5.00 mL of ethyl ether? (d) What is q for the combustion of one mole of ethyl ether?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning