
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
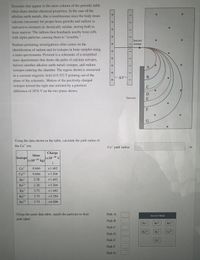
Transcribed Image Text:Elements that appear in the same column of the periodic table
oflen share sinmilar chemical properties, In the case of the
alkaline earth metals, this is troublesome since the body treats
calcium (necessary for proper bone growth) and radium (a
radioactive element) as chemically similar, storing both in
bone marrow, The radium then bombards nearby bone cells
with alpha particles, causing them to "crumble."
lonized
Radium poisoning investigations often center on the
identification of radium and its isotopes in bone samples using
isotope
a mass spectrometer. Pictured is a schematic of a simplified
mass spectrometer that shows the paths of calcium isotopes,
barium (another alkaline earth metal) isotopes, and radium
isotopes entering the chamber. The region shown is immersed
in a constant magnetic field of 0.352 T pointing out of the
В
-AV
plane of the schematic. Motion of the positively-charged
isotopes toward the right was initiated by a potential
difference of 2876 V on the two plates shown.
Detector
F
Using the data shown in the table, calculate the path radius of
the Ca ion.
Cat path radius:
Charge
Mass
Isotope
(x10-19 C
(x10-25 kg)
Ca
0.666
+1.602
Ca2+
0.666
+3.204
Ba*
2.28
+1.602
Ba2+
2.28
+3.204
Rat
3.75
+1.602
Ra2+
3.75
+3.204
Ra3+
3.75
+4.806
Using the same data table, match the particles to their
Path A
Answer Bank
path label.
Path B
Ba
Ba2+
Ra34
Path C
Ra+
Rat
Ca
Path D
Path E
Ca
Path F
Path G
DE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q 4 pleasearrow_forwardUse the following constants if necessary. Coulomb constant, k = 8.987 x 10° N m2 /C. Vacuum permitivity, eo = 8.854 x 10 12 F/m. Magnitude of the Charge of one electron, e =-1.60217662 x 10-19 C. Mass of one electron, m, = 9.10938356 x 10-31 kg. Unless specified otherwise, each symbol carries their usual meaning. For example, uC means micro coulomb. Y R. Suppose you have 5 point charges q to q, distributed along a semi-circle maintaining equal distance. The charge q6 is on the center of the circle which is also the origin of given coordinate system. The radius of the semi-circle is R = 34 cm and the magnitude of the charges are as follows : 91 = = 19 µC, q2 = q4 = 32 µC and q = q6 = -25 µC. a) Find the vector that points from q to g6 and call it F1,6- b) Calculate the coulomb force on g6 due to q in unit vector notation and call it F16 c) Find the vector that points from q3 to g6 and call it F3,6- d) Calculate the coulomb force on q6 due to g in unit vector notation and call it F36. e)…arrow_forwardCoulomb’s law tells us that the electrostatic force between two charged objects can be calculated by: ?= ??1?2/?^2Where k is a constant with a value of 8.99x109 Nm2/C2; ?1 and ?2 are the charges of the two particles (1.602x10-19 C), and r is the distance between the two particles. The force is attractive if the charges of the two particles is opposite (one’s positive and one’s negative) and repulsive if the charges have the same charge (both positive or both negative). Calculate the electrostatic force on proton #1 from the other two protons.Will the gravitational force between the protons be attractive or repulsive? What about the electrostatic force? Which has the larger magnitude, the electrostatic force or the gravitational force? Can the electrostatic and gravitational forces alone create a stable Lithium nucleus?arrow_forward
- Plz correct solutionarrow_forwardThe ratio of the electrostatic force to the gravitational force is different between two electrons and two protons. Why? I. The magnitude of the fundamental charge of an electron is different from a proton. II. Electrons and protons have different masses. III. False. The ratio is the same A. III only B. Both I and II only C. II only D. I onlyarrow_forwardQ 4 pleasearrow_forward
- Q 5 pleasearrow_forwardWhat is the total electrostatic potential energy of a hydrogen atom (which consists of an electron orbiting a proton at a distance of 5.3 Å)? Note that this will be a negative number given the formula you're using... Note: for this question, there may be more than one correct answer! -4.34 x 10-18 J -13.7 eV -27.1 eV -8.19 x 10-8 Jarrow_forwardQ 1 pleasearrow_forward
- Q 6 pleasearrow_forwardensitivity Editor Reuse 保存到 A Select v Files 百度网盘 Styles Editing Voice Sensitivity Editor Reuse Files 保存 12. How much work is required to assemble 4 identical charged particles, each of magnitude q=5 nC (red balls) at the corners of a cube of side a=10 cm ?(Fig 2) Fig.2 O cm and bh 1>arrow_forward8) The nucleus of a silver atom has a charge +47 e and is fixed at the origin of a cartesian coordinate system. An alpha particle of mass 6.68 × 10^−27 kg and charge +4 e is fired along the x-axis from infinity with an initial kinetic energy of 7.00 × 10^−13 J. At what distance from the silver nucleus will the alpha particle come (momentarily) to rest?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON