
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Using the attached infrared spectroscopy spectrum for the compound Heptanoic Acid, identify the
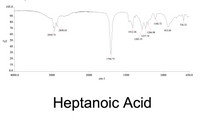
Transcribed Image Text:### Heptanoic Acid Infrared Spectrum Analysis
The infrared (IR) spectrum for heptanoic acid is presented in the graph above, which displays transmittance (%T) on the y-axis against wavenumber (cm<sup>-1</sup>) on the x-axis, ranging from 4000 to 650 cm<sup>-1</sup>.
#### Key Peaks and Their Assignments
- **2930.75 cm<sup>-1</sup> and 2858.03 cm<sup>-1</sup>**: These peaks are associated with C-H stretching vibrations common in alkyl chains.
- **1704.75 cm<sup>-1</sup>**: A notable peak signifying C=O stretching vibration, characteristic of carboxylic acids.
- **1412.26 cm<sup>-1</sup> and 1283.53 cm<sup>-1</sup>**: These are likely associated with bending vibrations in aliphatic chains.
- **1206.98 cm<sup>-1</sup> and 1237.74 cm<sup>-1</sup>**: These peaks may correspond to carboxyl group vibrations, indicating C-O stretching.
- **1106.72 cm<sup>-1</sup>**: Often associated with C-O stretching in carboxylic acids.
- **933.85 cm<sup>-1</sup> and 726.32 cm<sup>-1</sup>**: These lower wavenumber peaks could indicate various bending vibrations, potentially linking to alkyl chain motions or other molecular interactions.
This spectrum analysis provides insight into the molecular structure and functional groups present in heptanoic acid, confirming the presence of the carboxylic acid group and aliphatic chains.

Transcribed Image Text:### Infrared Spectroscopy Guide
#### I. Identifying Carbonyl Groups (C=O)
1. **Check for Carbonyl Absorption**:
- Look for strong absorption between 1750 to 1650 cm<sup>-1</sup>.
2. **Carbonyl Functional Group Identification**:
- **Carboxylic Acids**: Broad, strong absorption (3300-2500 cm<sup>-1</sup>) due to O-H stretch.
- **Aldehydes**: Two medium peaks around 2780 and 2670 cm<sup>-1</sup> (may include aliphatic C-H stretch).
- **Amides**: Absorption around 1670 cm<sup>-1</sup>, possibly accompanied by N-H stretch (3050-3550 cm<sup>-1</sup>).
3. **Carbonyl Position Determination** (if I.A options are ruled out):
- **Anhydrides**: Two peaks in the carbonyl range.
- **Ketones and Esters**: Stretching band usually at frequencies higher than 1725 cm<sup>-1</sup>.
#### II. Absence of Carbonyl Absorption
1. **Check for N-H Stretching Bands** (higher than 3100 cm<sup>-1</sup>):
- **Primary Amines**: Two peaks.
- **Secondary Amines**: One peak.
- **Tertiary Amines**: No absorption here.
2. **O-H Stretching in Alcohols**:
- "Free" O-H: Around 3600 cm<sup>-1</sup> (broad, strong).
- "Hydrogen-bonded" O-H: Around 3400 cm<sup>-1</sup> (broad, strong).
#### III. Triple Bonds
- **Acetylenes**: C≡C stretch at about 2100-2260 cm<sup>-1</sup>.
- **Nitriles**: Similar band at about 2200-2300 cm<sup>-1</sup>.
#### IV. C-H Stretching
1. **Aliphatic C-H Stretch**: Intense absorption slightly less than 3030 cm<sup>-1</sup>.
2. **Aromatic & Alkene C-H Stretch**: Weaker absorption slightly
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 9 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- values : Experimental values of IR Peaks compared to literature values for Benzoic Acid (ATR method) Bond Stretch Functional group Experimental Peak(cm-1) Literature Peak(cm-1) O-H Carboxylic acid 2800 3200-2200 C=O Carboxylic Acid 1674.9 1677.5 C=C (ring) Aromatic stretch 1579.5 1581-1418.5 C-H Aromatic Sp2 3100 C-O stretch 1285.5 O-H Alcohol 929.89 table 3: Experimental values of IR peaks compared to literature values for 2-Naphthol Bond Stretch Functional group Experimental Peak(cm-1) Literature Peak(cm-1) O-H Alcohol 3219.1 3400-3080 C-C Aromatic (ring) stretch 1507.6 C=C Aromatic stretch 1597.7 1627.3-1377.8 C-H Aromatic Sp2 3050 C-O Secondary alcohol stretch 1168.9 IR results used to prove that the compounds are effectively separated. Discuss on bothdiagnostic peaks and fingerprint region.arrow_forwardThe functional groups in an organic compound can frequently be deduced from its infrared absorption spectrum. A compound exhibits strong, broad absorption between 3300 and 3500 and at 1050 cm-1. Relative absorption intensity: (s)=strong, (m)=medium, (w)=weak. What functional class(es) does the compound belong to? List only classes for which evidence is given here. Attach no significance to evidence not cited explicitly. Do not over-interpret exact absorption band positions. None of your inferences should depend on small differences like 10 to 20 cm-1. The functional class(es) of this compound is(are) -(Enter letters from the table below, in any order, with no spaces or commas.) a. alkane (List only if no other functional class applies.) b. alkene c. terminal alkyne d. internal alkyne h. amine i. aldehyde or ketone j. carboxylic acid k. ester I. nitrile e. arene f. alcohol g. etherarrow_forwardGiven the H-NMR spectra, identify the peaks that can be represented for 2-Naphthyl-Butylether.arrow_forward
- I need help with making an ir spectrum Analysis for Cyclohexanol that includes in a table: Ir absorbtion bands cm^- and functional group in the fuctional group i have to connecet it to a specific compung group I thinkarrow_forwardBy examining the carbon NMR spectra of 1,1-dichlorocyclohexane and cis-1,2- dichlorocyclohexane, what TWO things would you look for to distinguish between the spectra. Use structures to explain your answer.arrow_forwardDetermine which of the following belongs to this ir spectra then complete the nmr analysismethyl butanoate benzaldehyde 1-chlorobutane 1-chloro-2-methylpropane butan-2-one propan-2-ol propanalarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY