
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
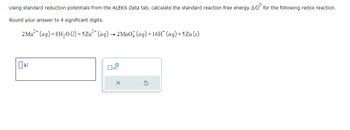
Transcribed Image Text:Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG for the following redox reaction.
Round your answer to 4 significant digits.
2 Mn²+ (aq) +8H₂O (1) +5Zn²+ (aq) → 2MnO4 (aq) + 16H* (aq) +5Zn (s)
☐ kJ
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. ■ 10Fe²+ (aq) +2103 (aq) +12H* (aq) → 10Fe³ KJ 10Fe³+ (aq) + ¹₂ (s) + 6H₂O (1) x10 X Ś AGO for the ? olo 18 Ararrow_forwardUsing standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AGO for the following redox reaction. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 2C1 (aq) + 2HNO₂ (aq) + 2H* (aq) → Cl₂ (g) + x10 +2NO(g) + 2H₂O (1) Xarrow_forwardUsing standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG for the following redox reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 2Cr(OH)3 (s) +100H¯ (aq) +3Zn²+ (aq) → 2CrO²¯ (aq) +8H₂O (1) + 3 Zn (s) 0 x10 Xarrow_forward
- Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy for the following redox reaction. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. The final units should be in kjarrow_forwardUsing standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG for the following redox reaction. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 4Br (aq) +N2 (g)+4H₂O (1) → 2Bг2 (1)+N₂H4 (aq) +40H (aq) OkJ T x10 ×arrow_forwardUsing standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3+ 4Fe²+ (aq) + O₂(g) + 4H* (aq) → 4Fe³+ (aq) + 2H₂O (1) KJ x10 X Ś AGO for the following redox reaction.arrow_forward
- Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 6CI (aq)+2Cr0 (aq)+8H,0 (1) → 3Cl, (g)+2Cr(OH), (s) + 10OH (aq)arrow_forwardCalculate the standard free‑energy change for this reaction at 25 °C. A list of standard reduction potentials can be found in this table. 2Au3+(aq)+3Ni(s)↽−−⇀2Au(s)+3Ni2+(aq) Δ?∘= kJ/molarrow_forwardConsider these two entries from a fictional table of standard reduction potentials. X+ (aq) + e¯ Y+ (aq) + e- →Y(s) E = 2.01 V →X(s) O X and Y O X+ and Y+ O X and Y+ O X+ and Y E = 2.62 V Which pair of species will react under standard conditions at 25 °C?arrow_forward
- Balance the redox reaction in acidic solution:Cu(s)+NO−3(aq)→Cu2+(aq)+NO2(g) Express your answer as a chemical equation including phases.arrow_forwardUsing standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. H₂(g) + 2OH¯(aq) + 2Fe³+ (aq) → 2H₂O (1) + 2Fe²+ (aq) kJ x10 X Ś AGO for thearrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 2H+ (aq) + Hg(1)→ H₂(g) + Hg²+ (aq) 2H+ (aq) + 2e¯ → H₂(g) Fº red 2+ Hg2 (aq) + 2e¯ → Hg(1) AGO = || kJ K for this reaction would be Eº red = 0.000 V = = 0.855 V than one.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY