
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Using data from Table A-25, calculate the equilibrium constant expressed as log₁0K, for the water-gas shift reaction
CO + H₂O (g) ↔ CO₂ + H₂
at 298 K and then at 1000K.
Also, determine the equilibrium constant at 298 K and then at 1000K using Table A-27.
Table A-25:
T(K)
298
1000
log10K
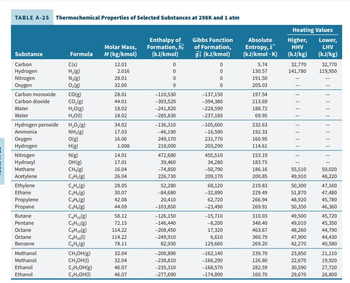
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE A-25 Thermochemical Properties of Selected Substances at 298K and 1 atm
Substance
Carbon
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Carbon monoxide
Carbon dioxide
Water
Water
Hydrogen peroxide
Ammonia
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Hydroxyl
Methane
Acetylene
Ethylene
Ethane
Propylene
Propane
Butane
Pentane
Octane
Octane
Benzene
Methanol
Methanol
Ethanol
Ethanol
Formula
C(s)
H₂(g)
N₂(g)
O₂(g)
CO(g)
CO₂(g)
H₂O(g)
H₂O(l)
H₂O₂(g)
NH,(g)
O(g)
H(g)
N(g)
OH(g)
CH₂(g)
C₂H₂(g)
C₂H₂(g)
C₂Hs(g)
C3Hs(g)
C₂H₂(g)
C₂H₂(g)
C3H₁2(g)
CgH18(g)
C8H18(1)
CH(g)
CH₂OH(g)
CH₂OH(1)
C₂H₂OH(g)
C₂H₂OH(1)
Molar Mass,
M (kg/kmol)
12.01
2.016
28.01
32.00
28.01
44.01
18.02
18.02
34.02
17.03
16.00
1.008
14.01
17.01
16.04
26.04
28.05
30.07
42.08
44.09
58.12
72.15
114.22
114.22
78.11
32.04
32.04
46.07
46.07
Enthalpy of
Formation, h
(kJ/kmol)
0
0
0
0
-110,530
-393,520
-241,820
-285,830
-136,310
-46,190
249,170
218,000
472,680
39,460
-74,850
226,730
52,280
-84,680
20,410
-103,850
-126,150
-146,440
-208,450
-249,910
82,930
-200,890
-238,810
-235,310
-277,690
Gibbs Function
of Formation,
gi (kJ/kmol)
0000
0
-137,150
-394,380
-228,590
-237,180
-105,600
-16,590
231,770
203,290
455,510
34,280
-50,790
209,170
68,120
-32,890
62,720
-23,490
-15,710
-8,200
17,320
6,610
129,660
-162,140
-166,290
-168,570
-174,890
Absolute
Entropy, sº
(kJ/kmol. K)
5.74
130.57
191.50
205.03
197.54
213.69
188.72
69.95
232.63
192.33
160.95
114.61
153.19
183.75
186.16
200.85
219.83
229.49
266.94
269.91
310.03
348.40
463.67
360.79
269.20
239.70
126.80
282.59
160.70
Heating Values
Higher, Lower,
HHV
LHV
(kJ/kg)
(kJ/kg)
32,770
141,780
55,510
49,910
50,300
51,870
48,920
50,350
49,500
49,010
48,260
47,900
42,270
23,850
22,670
30,590
29,670
32,770
119,950
|||||||||||||
50,020
48,220
47,160
47,480
45,780
46,360
45,720
45,350
44,790
44,430
40,580
21,110
19,920
27,720
26,800
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- QUESTION 8 Regarding the following reaction CO2 (g)+H2 (g)→→CO(g)+H₂O (g) ArH=-41.2kJ/mol Using Le Chatelier's principle to predict (a) to which direction the equilibrium shifts when pressure is decreased. Enter R for reactants, P for products and N for Neither: Direction= ; (b) to which direction the equilibrium shifts when temperature is reduced. Enter R for reactants, P for products and N for Neither: Direction=arrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to be at equilibrium: 4 A(e) + 3 B(e) + heat 5 Ce) + 3 D(e) In which direction will the reaction shift if more D is added? O It will not shift O It will shift toward the products. O It will shift toward the reactants.arrow_forwardUsing enthalpies of formation, calculate AHrxn for the reaction: C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(()arrow_forward
- How many electrons are transferred in the following process, given the unbalanced reaction? PbO2 (s) + H* (aq) + Fe (s) → Fe3+(aq) + Pb2+ (aq) + H20 (1) Group of answer choices A-1 В-2 C-6 D-4 Е-3arrow_forwardCalculate the ΔG^O (in kJ/mol) for the following reaction at 25.0℃.3Co^+2(aq)+2Al(s)→3Co(s)+2Al^+3(aq)arrow_forwardPlease help me with this one as soon as you can and show all the work for the enthalpy table. I provided the problem statement and the enthalpy table I need filled out please show the work for it.arrow_forward
- 24. Study the reaction.CH44 + 2O22 → CO22 + 2H22OIf 7.4 moles of carbon dioxide (CO22) form at the end of the reaction, how many moles of methane (CH44) and oxygen gas (O22) entered the reaction? ___moles of methane ___moles of oxygen gasarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardPlease answer correctly b/c last time it was wrong When zinc metal reacts with oxygen gas, 2Zn(s) + O2(g) → 2ZnO(g), large amounts of light and heat are released. A student states that this reaction is a combustion reaction but not a redox reaction. Do you agree? Defend your answer by explaining whether or not it meets the requirements of each type of reaction.arrow_forward
- Write out the gibbs phase rule equation & calculate the degrees of freedom. Air (02 & N2) w/ water vapor, in equilibrium w/ a container that holds liquid water and solid water (Ice) & no reactions Ethanol & acetic acid to form ethyl acetate & water. Reaction occurs in the liquid phase, but both liquid & vapor are present.arrow_forwardUsing the information provided, determine the enthalpy (in kJ/mol) for the reaction 2 K(s) + 2 H₂O(l) → 2 KOH (aq) + H₂(g) K (s) = 0 kJ/mol H2O(l) = -285.8 kJ/mol KOH(aq) = -482.4 kJ/mol H2(g)= 0 kJ/molarrow_forwardRedox/ oxidation. Someone please help!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The