
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
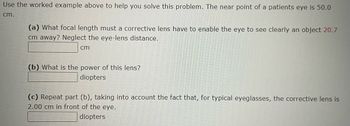
Transcribed Image Text:Use the worked example above to help you solve this problem. The near point of a patients eye is 50.0
cm.
(a) What focal length must a corrective lens have to enable the eye to see clearly an object 20.7
cm away? Neglect the eye-lens distance.
cm
(b) What is the power of this lens?
diopters
(c) Repeat part (b), taking into account the fact that, for typical eyeglasses, the corrective lens is
2.00 cm in front of the eye.
diopters
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Your camera’s zoom lens has an adjustable focal length ranging from 55 to 150 mm. Part (a) What is the maximum power of the lens, Pmax, in diopters? Part (b) What is the minimum power of the lens, Pmin, in diopters?arrow_forwardUse the worked example above to help you solve this problem. The near point of a patients eye is 50.0 cm. (a) What focal length must a corrective lens have to enable the eye to see clearly an object 29.9 cm away? Neglect the eye-lens distance. 69.0 x cm (b) What is the power of this lens? +1.45 X diopters (c) Repeat part (b), taking into account the fact that, for typical eyeglasses, the corrective lens is 2.00 cm in front of the eye. +2.21 X dioptersarrow_forwardAn individual is nearsighted; his near point is 17.0 cm and his far point is 49.0 cm. (a) What lens power is needed to correct his nearsightedness? diopters(b) When the lenses are in use, what is this person's near point?arrow_forward
- An optometrist needs to prescribe corrective lenses for a person whose near point is q = 58.8 cm. If the patient is to see objects clearly at a distance of p = 25.0 cm, calculate the following. (Neglect the distance from the lens to the eye.) (a) focal length (in cm) of the appropriate corrective lens cm (b) power (in diopters) of the appropriate corrective lens dioptersarrow_forwardAn object is placed 30 cm from the center of a 50-cm-focal-length converging lens. (a) Draw a ray diagram and show where the image is located. (Your diagram MUST be legible and correct to earn points). (b) Find the location of the image analytically using the thin lens equation. (c) What is the magnification? (Pay attention to the signs).arrow_forwardPeople who do very detailed work close up, such as jewellers, often can see objects clearly at much closer distance than the normal 25 cm. (a) What is the power in D of the eyes of a woman who can see an object clearly at a distance of only 7.30 cm? (Assume the lens-to-retina distance is 2.00 cm.) ____D (b) What is the size in mm of an image of a 6.00 mm object, such as lettering inside a ring, held at this distance? (Include the sign of the value in your answer.) ______mm (c) What would the size of the image be in mm if the object were held at the normal 25.0 cm distance? (Include the sign of the value in your answer.) _____mmarrow_forward
- Lenses with given radii. Object O stands in front of a thin lens, on the central axis. For this situation, each problem in the table (below) gives object distance p, index of refractionnof the lens, radius r of the nearer lens surface, and radius rɔ of the farther lens surface. (All distances are in centimeters.) Find (a) the image distance i and (b) the lateral magnification m of the object, including signs. Also, determine whether the image is (c) real or virtual, (d) inverted from object O or noninverted, and (e) on the same side of the lens as object O or on the opposite side. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) m R/V I/NI Side r1 r2 +78 1.56 +33 -48 (a) Number i Units i Units (b) Number MacBook Proarrow_forwardUse the worked example above to help you solve this problem. The near point of a patients eye is 50.0 cm. (a) What focal length must a corrective lens have to enable the eye to see clearly an object 28.5 cm away? Neglect the eye-lens distance. 50 x cm (b) What is the power of this lens? 2 diopters (c) Repeat part (b), taking into account the fact that, for typical eyeglasses, the corrective lens is 2.00 cm in front of the eye. 2.26 X dioptersarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON