
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
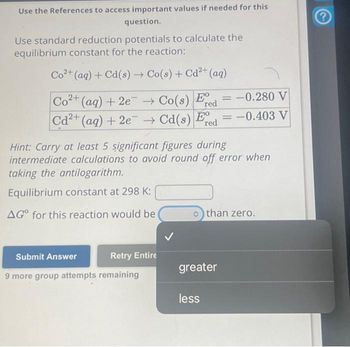
Transcribed Image Text:Use the References to access important values if needed for this
question.
Use standard reduction potentials to calculate the
equilibrium constant for the reaction:
Co2+(aq) +Cd(s) → Co(s) +Cd2+ (aq)
Co2+ (aq) +2e → Co(s) Ed=-0.280 V
red
Cd2+ (aq) + 2e → Cd(s) Ed = -0.403 V
red
Hint: Carry at least 5 significant figures during
intermediate calculations to avoid round off error when
taking the antilogarithm.
Equilibrium constant at 298 K:
AGO for this reaction would be
Retry Entire
Submit Answer
9 more group attempts remaining
>than zero.
greater
less
?
![A voltaic cell is constructed in which the cathode is a
standard hydrogen electrode and the anode is a
hydrogen electrode (
PH₂)= 1 atm) immersed in a solution of unknown [H*]. If
the cell potential is 0.189 V, what is the pH of the
unknown solution at 298 K?
pH =](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/6d3ead86-d738-4554-929a-5127414f39f2/647a7c9b-9d9f-4c43-808b-ff29fde3afcd/z58e7fn_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:A voltaic cell is constructed in which the cathode is a
standard hydrogen electrode and the anode is a
hydrogen electrode (
PH₂)= 1 atm) immersed in a solution of unknown [H*]. If
the cell potential is 0.189 V, what is the pH of the
unknown solution at 298 K?
pH =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use standard reduction potentials to calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction: I₂ (s) + 2Fe²+ (aq). → 21¯ (s) + 2Fe³+ (aq) 0.535 V, E³+ /Fe²+ From the table of standard reduction potentials: E Hint: Carry at least 5 significant figures during intermediate calculations to avoid round off error when taking the antilogarithm. Equilibrium constant at 298 K: AGO for this reaction would be + than zero. 0.771 Varrow_forwardUsing the standard reduction potentials listed in Appendix E in the textbook, calculate the equilibrium constant for each of the following reactions at 298 K. Fe(s)+Ni2+(aq)→Fe2+(aq)+Ni(s)arrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 31₂ (s) + 2Cr(s) → 61¯(s) + 2Cr³+ (aq) I₂ (s) + 2e¯ → 21¯ (s) Cr³+ r³+ (aq) + 3e¯ → Cr(s) E red kJ AGO = Eº = = 0.535 V red = -0.740 Varrow_forward
- What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 25 oC for the reaction between the pair: Ag(s) and Mn2+(aq) to give Ag+(aq) and Mn(s) Use the reduction potential values for Ag+(aq) of +0.80 V and for Mn2+(aq) of -1.18 Varrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 2+ Cd²+ (aq) + Zn(s) → Cd(s) + Zn²+ (aq) AG⁰ = Cd2+ (aq) +2e → Cd(s) E red Zn²+ (aq) +2e → Zn(s) E red K for this reaction would be greater less = -0.403 V -0.763 V kJ than one.arrow_forwardRank the following in increasing ability as oxidizing agents. The reduction potentials of all species are shown below. Cl, (g) + 2e → 2C1 (aq) E° = 1.3583 V Ag*(aq) + le Cu²+ (aq) + 2e¯ → Ag(s) E° = 0.7996 V → Cu(s) E° = 0.342 V Sn²+ (aq) + 2e → Sn(s) E° = - 0.136 V к"(ад) + 1е — → K(s) E° - 2.95 V 1st attemptarrow_forward
- What is the equilibrium constant for the dissolution of copper (II) hydroxide: Cu(OH)₂ (s) Given the standard reduction potentials Cu(OH)₂ (aq) + e- → Cu (s) + OH¯ (aq) Cu²+ (aq) + e¯ →→ Cu (s) O 5.16 x 10^-9 O 1.63 x 10^3 O 1.93 x 10^8 O 6.12 x 10^-4 Cu²+ (aq) + OH¯ (aq) O 2.20 x 10^-20 EO = -0.15 V Eº = +0.34 Varrow_forwardBalance the following skeletal reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include “1” in the blank if the coefficient is 1. Ag+(aq) +PbO(s) → PbO2(s) + Ag(s)arrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 2+ Co²+ (aq) + Zn(s) → Co(s) + Zn²+ (aq) red Co²+ (aq) + 2e → Co(s) Ee Zn²+ (aq) + 2e¯ → Zn(s) Ee red AGO K for this reaction would be kJ = -0.280 V -0.763 V than one.arrow_forward
- Using standard reduction electrode potentials, calculate standard free-energy change at 25°C for the following reaction:3Cu(s) + 2NO3-(aq) + 8H+(aq) → 3Cu2+(aq) + 2NO(g) + 4H2O(l).arrow_forwardJust the last one. And use table if neededarrow_forwardUse the standard reduction potentials given below to predict if a reaction will occur when Fe metal is put into a 1 M aqueous Cd²+ solution. Cd²+ red (aq) + 2e¯ → Cd(s) Ee Fe²+ (aq) + 2e → Fe(s) E red If a reaction will occur, write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction. If no reaction will occur, leave all boxes blank. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) -0.403 V -0.440 V + +arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY