
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
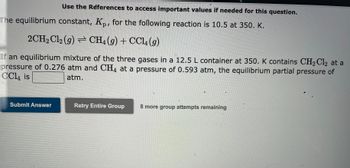
Transcribed Image Text:Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
The equilibrium constant, Kp, for the following reaction is 10.5 at 350. K.
2CH₂Cl2 (g) CH4 (9) + CCl4 (9)
If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 12.5 L container at 350. K contains CH₂Cl2 at a
pressure of 0.276 atm and CH4 at a pressure of 0.593 atm, the equilibrium partial pressure of
CCl4 is
atm.
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
1
8 more group attempts remaining
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction given the following information. CO (g) + 2 H2S (g) CS2 (g) + H2O (g) + H2 (g) K =? = 5.49 · 102 CH. (g) + H20 (g) → CO (g) + 3 H2 (g) K CHA g) + 2 H2S (g) CS2 (g) + 4 H2 (g) K = 2.70 . 105 2.03 10-3 4.92 102 3.03 103 O 1.48 · 10° « Previous MacBook Air 80 888 DII F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 23 $ & 3 4 6. 7 8. E R Y U LIarrow_forwardFor the reaction H₂(g) + CO₂(g) → H₂O(g) + CO(g) at 700 °C, K=0.534. Calculate the number of moles of H₂ that are present at equilibrium if a mixture of 0.660 mole of CO and 0.660 mole of H₂O is heated to 700 °C in a 30.0 L container. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mol x10 Xarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forward
- Methanol liquid burns readily in air. One way to represent this equilibrium is: 2 CH3ОН(1) + 3 02(9)+ 2 CO2(g) + 4 H20(g) We could also write this reaction three other ways, listed below. The equilibrium constants for all of the reactions are related. Write the equilibrium constant for each new reaction in terms of K, the equilibrium constant for the reaction above. 1) CНH3ОН(1) + 3/2 02(9)+ =cO2(g) + 2 H20(g) K1 = %D 2) 2 CO2(9) + 4 H20(g) 2 CH3ОН (1) + 3 02(9) K2 = 3) СO2(g) + 2 H20(g) еснзон (1) + 3/2 02(g) K3 : %3D Drag and drop your selection from the following list to complete the answer: к1/2 1/K (1/K)!/2arrow_forwardSulfur dioxide and oxygen react to form sulfur trioxide during one of the key steps in sulfuric acid synthesis. An industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 500. mL flask with 1.2 atm of sulfur dioxide gas and 4.7 atm of oxygen gas, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of sulfur trioxide gas to be 0.60 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the reaction of sulfur dioxide and oxygen at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K, -0 x10 5arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.20 mol of NO, and 1.3 mol of NO. This reaction becomes possible: 2NO,(g) = 2NO(g)+0,(g) Complete the table below, so that it lists the initial molarity of each compound, the change in molarity of each compound due to the reaction, and the equilibrium molarity of each compound after the reaction has come to equilibrium. Use x to stand for the unknown change in the molarity of O,. You can leave out the M symbol for molarity. NO, NO 0, initial ? change equilibriumarrow_forward
- 12) If 1.34 moles each of Br2 and Cl2 are introduced into an 11.0 liter flask and allowed to come to equilibrium, what should the equilibrium concentrations of Br2, Cl2, and BrCl be? 2 BrCl (g) « Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g)Kc = 0.143arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.70 mol of Br,, 1.8 mol of BrOCl and 1.1 mol of BrCl. The following reaction becomes possible: Br, (g) + OCl,(g) =BROC1 (g)+BrCl (g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.244 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of BrOCI. Round your answer to two decimal places. ?arrow_forward3. If the equilibrium constant K, for the reaction 2 NO (g) + O2(g) = 2 NO2 (g) is 5.0 x 1012 at a given temperature, what is the value of the equilibrium constant K, for each of the following reactions at the same temperature? a) NO (g) + ½ O2 (g) → NO2 (g) b) 2 NO2 (g) = 2 NO (g) + 02 (g) c) NO2(g) = NO (g) + ½ 02 (g)arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction: 2NOBr(g) 2NO(g) + Br₂ (9) for this question. If 0.340 moles of NOBr(g), 0.327 moles of NO, and 0.499 moles of Br₂ are at equilibrium in a 12.3 L container at 445 K, the value of the equilibrium constant, Ke, isarrow_forwardThoroughly explain and answerarrow_forwardCalculating an equilibrium constant from a partial equilibrium composition Steam reforming of methane ( CH4 ) produces "synthesis gas," a mixture of carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas, which is the starting point for many important industrial chemical syntheses. An industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 1.5 L flask with 4.3 atm of methane gas and 1.8 atm of water vapor, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of hydrogen gas to be 3.2 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the steam reforming of methane at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K p 11] ☐ x10 ☑ ⑤arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY