
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Use the information provided in the position-time graph to describe Diane's velocity in words.
Which runner is going faster during the first 5 seconds? How do you know? Please explain.
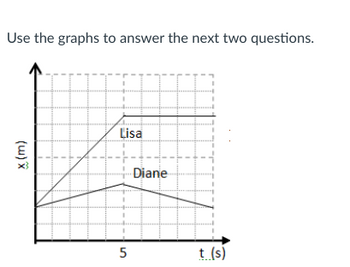
Transcribed Image Text:Use the graphs to answer the next two questions.
(w) x
Lisa
5
Diane
t (s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I know the answer is c but can you please explain whyarrow_forwardHow do you calculate the displacement of a moving object? Also, how do you determine the two positions in a time and position graph?arrow_forwardNumber 84 how do you find the average velocity ? Is this reasonable time ? Explainarrow_forward
- Conclusion: Write a single paragraph describing the how the velocity of the car changes as time passes. Be sure to include your equation and the acceleration in your description.arrow_forwardThis distance vs time graph does not represent velocity. Why? Explain in your own words.arrow_forwardPlease view the pictures below to answer the following questions. Match the following descriptions of an objects motion with the graph of the object's position vs time graph shown in the pictures. Question 1: An object has a postive initial velocity and a negative accelertion, but never comes to a stop. Question 2: An object has an initial negative velocity and a positive acceleration which slows it to a stop before speeding it up in the positive direction. Question 3. An object is initially at rest and then accelerates in the negative direction. Question 4: An object has a postive constant velocity Please answer questions 1-4arrow_forward
- B. The graph at the right shows the journey of a car over a 50-second time interval. Find the car’s displacement after 50 seconds.arrow_forwardIn understanding motion lab, one of your velocity vs. time graph produced a line with positive slope. Which one of the following options exactly describes the slope? The slope represents average velocity. O The slope represents acceleration that is constant. The slope represents instantaneous velocity. The slope represents the displacement.arrow_forwardImage shows the velocity-versustime graphs for two objects A and B. Students Zach and Victoria are asked to tell stories that correspond to the motion of the objects. Zach says, “The graph could represent two cars traveling in opposite directions that pass each other.” Victoria says, “No, I think they could be two rocks thrown vertically from a bridge; rock A is thrown upward and rock B is thrown downward.” Which student, if either, is correct? Explain.arrow_forward
- Karen bikes at 8 mph for 0.3 hours from home to the park. At soon as she arrives, Karen remembers she has a study session with Marie. So, Karen turns around and bikes to Marie's house at 12 mph for 0.1 hours. They study for 0.5 hours. Then, Karen bikes home for 0.4 hours. Note: Marie's house is in between Karen's house and the park. 1. Plot a velocity vs. time graph. 2. Calculate Karen's speed when she bikes from Marie's to her house. 3. Calculate the distance of each segment. 4. Plot a position vs. time graph.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardA basketball dropped from the roof of a three-story building falls to the ground. Ignoring air resistance, sketch the motion diagram for this motion, including approximate representations of the position versus time, velocity versus time, and acceleration versus time graphs for this motion. Include axes labels, appropriate numbers, and units for each graph. Upload an image of the sketches and explain your sketches in words in the panels below.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON