
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
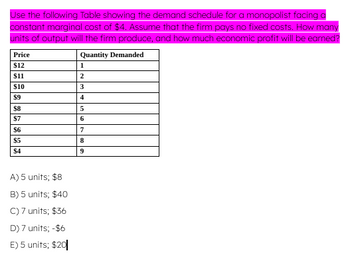
Transcribed Image Text:Use the following Table showing the demand schedule for a monopolist facing a
constant marginal cost of $4. Assume that the firm pays no fixed costs. How many
units of output will the firm produce, and how much economic profit will be earned?
Quantity Demanded
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Price
$12
$11
$10
$9
$8
$7
$6
$5
$4
A) 5 units; $8
B) 5 units; $40
C) 7 units; $36
D) 7 units; -$6
E) 5 units; $20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a monopolist with the following demand curve. Price: 24, 22 , 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6 Quantity Demanded: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 [All answers are integers with no units.] 1.If this firm has a marginal cost of $12 per unit, how many will they produce? 2.What will their profit be? 3.What will consumer surplus be? (Rectangle method!) 4.What is the efficient quantity?arrow_forwardIn the following table, enter the price and quantity that would arise in a competitive market; then enter the profit-maximizing price and quantity that would be chosen if a monopolist controlled this market. Market Structure Price Quantity (Dollars) (Hot dogs) Competitive Monopolyarrow_forwardSuppose that a monopolist faces inverse demand given by P = 100 - 10Q and marginal cost given by MC = 20. 1. What is the profit function? 2. What is the marginal revenue function? 3. What is the equilibrium quantity? 4. What is the equilibrium markup?arrow_forward
- The government of a small developing country has granted exclusive rights to Linden Enterprises for the production of plastic syringes. The table below shows the cost and demand data for this government-protected monopolist. Quantity per Day (cases) 1 2 3 $49.0 $42.0 $47.0 $34.5 5 6 7 8 10 Price per Case $16 15 14 13 12 11 10 7 What is the amount of profit that the firm earns? Total Cost $7.00 9.50 11.00 12.00 14.50 17.00 21.00 25.00 30.00 35.50arrow_forwardRefer to the accompanying graph to answer the next six questions. Price D MR D and H B and F A and H Which price and quantity combination is most desirable from the monopolist firm's point of view? A and E G H C and G D ATC MC Quantityarrow_forwardThe accompanying figure depicts a generalized downward-sloping market demand (D) curve for a product. It also shows the firm's relevant marginal revenue (MR) curve and marginal cost (MC) curve. Use this figure to answer the questions that follow. Price $10 $8 $6 $4 $2 10 20 MR 30 40 D MC → 50 60 Quantity What is the change in total welfare if the firm moves from a monopolist model that charges a single price to a perfect competition model? There would be a loss of $160 in total welfare. O There would be a loss of $80 in total welfare. There would be a gain of $40 in total welfare. O There would be a gain of $120 in total welfare. O There would be no change in total welfare.arrow_forward
- Please refer to the figure provided. Imagine that this market could be perfectly competitive, controlled by a monopolist who charges a single price or a monopolist who charges each customer a different price 1. How much is producer surplus if the market is controlled by a single-price monopolist? $ 2. Suppose now the monopolist is able to charge all customers the maximum price they are willing to pay, how much is the producer surplus?arrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusion A monopolist has a demand curve given by P = 88 − Q and a total cost curve given by TC = 34 + Q2. The associated marginal cost curve is MC = 2Q. Suppose the monopolist also has access to a foreign market in which he can sell whatever quantity he chooses at a constant price of 60. How much will he sell in the foreign market? What will his new quantity and price be in the original market?arrow_forwardSuppose the accompanying table describes the demand for a good produced by monopolist. Price Quantity $ 20 1 19 2 18 3 17 4 16 5 15 6 14 7 13 8 12 9 11 10 10 11 9 12 The monopolist’s total revenue from selling three units is ______, and the monopolist’s marginal revenue from selling the third unit is ______. Multiple Choice $57; $18 $57; $16 $54; $16 $6; $6arrow_forward
- 1. A firm faces the following inverse demand curve: P = 500 - 0.25Q Where: Q is the monthly production P is price, measured in dollars per unit. The firm also has a total cost (TC) function of: TC = 200Q. Assuming the firm maximizes profits, answer the following: a) Assuming the firm operates as a monopolist, calculate the following: price, quantity, and profit. Graph and show the equilibrium price and quantity. b) Assuming perfect competition, what are price, quantity and profit? Show on the graph from above.arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows a monopolist's marginal cost schedule and the demand curve. Find and depict the following items within the diagram and briefly explain how you found them: Price Monopoly Price Demand Marginal Revenue Total Surplus Quantity Maximising Quantity b) Draw a possible marginal cost curve for the monopolist into the diagram that is consistent with all the other curves that are already given. c) Based on the marginal cost curve that you constructed in part (b), find and highlight the monopolist's total costs at the monopoly price in the diagram. d) Briefly explain the shape of the marginal revenue curve as compared to the demand curve in the diagram.arrow_forwardA perfectly competitive firm is expected to make a $0 economic profit in the long-run. What type(s) of profit would you expect a monopolist to earn in the long-run? Why the difference? Use the editor to format your answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education