
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:30
8 01:12:27
Mc
Graw
Hill
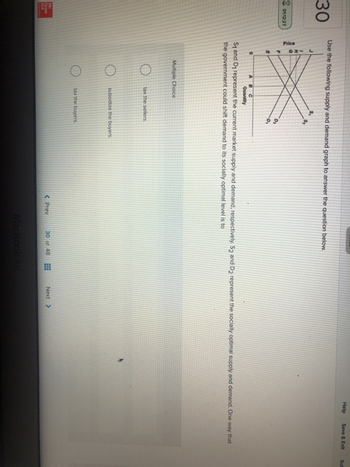
Use the following supply and demand graph to answer the question below.
Price
0
ABC
D₂
Multiple Choice
Quantity
S₁ and D₁ represent the current market supply and demand, respectively. S2 and D2 represent the socially optimal supply and demand. One way that
the government could shift demand to its socially optimal level is to
tax the sellers
subsidize the buyers.
tax the buyers
< Prev
30 of 48
MacBook Air
Help Save & Exit
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A negative externality means the quantity in the market is _____ the allocatively efficient quanitity and can be corrected by a _____. A positive externality means the quantity in the market is _____ the allocatively efficient quantity and can be corrected by a ______. Word Bank: Larger than, tax, smaller than, subsidy, smaller than, equal to, subsidy, larger than, equal to, tax.arrow_forwardSome economists claim that early child care generates an external benefit to society. a. What is the market equilibrium? What is the socially optimal outcome? How do they differ? b. The government is planning to provide a per-unit subsidy for child care to achieve the socially optimal outcome. How large should this subsidy be? c. How much is the total government subsidy each month to reach a socially optimal outcome?arrow_forwardanswer to this q?arrow_forward
- Costs and Revenue MR MC D Quantity Based on the graph, you can answers. MR curve is defined as 20-2Q, MC curve is defined as 2Q, and Demand curve is definded as 20 - Q. What is the quantities that maximize a social benefit? Your answer should be 1 decimal points such as 2.1 or 3.1. Do not write ratio such as 10/3. Do not include $. Answer should be 200 instead of $200arrow_forwardThe graph depicts the market for a good that creates a negative externality. Move the triangle labeled "DWL" to illustrate the deadweight loss associated with the market equilibrium quantity. Supply (social) DWL Supply (internal) Demand Quantity Pricearrow_forwardFigure 1. The graph depicts the market for plastic containers. Price 16- 14- 12- 10 8- 6 200 500 650 Social Cost Private Cost Demand Quantity Refer to Figure 1. In order to reach the social optimum, the government could O offer a subsidy of $8 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O impose a tax of $8 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O offer a subsidy of $4 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O impose a tax of $4 per unit on the production of plastic containers.arrow_forward
- 12arrow_forwardThe production of fabric generates toxic effluents related to the dyes used. This is typically disposed of with wastewater, which generates pollution. If the government does not intervene, the market for fabric has an equilibrium price of $250 per roll and an equilibrium quantity of 10,000 rolls. a.How would the socially optimal quantity of fabric compare to the free market equilibrium quantity of 10,000 rolls? Why? b. Using a supply and demand graph show the effect on social welfare of allowing the market for fabric to operate without government intervention. Label all the curves and relevant points on your graph. c. Would a government subsidy or tax help the market achieve the social optimum? Explain. Show the necessary subsidy/tax on your graph. d. Explain how this intervention helps achieve the social optimum and what information would be necessary to implement it.arrow_forwardSuppose the hot sauce firm cannot reduce the externality without reducing costs. What is a possible next step the government could take to reduce it? Select all that apply. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. Tax the firm for each bottle of hot sauce produced. a b C d e Create a limit on the maximum number of bottles the firm can make. Subsidizing each bottle of hot sauce made. Not allowing consumers to buy hot sauce. Forcing the firm to install equipment to reduce the amount of pollution generated. Answered Incorrect 1 attempt left Resubmitarrow_forward
- Use appropriate figures to show the deadweight losses associated with a) positive externalities b) negative externalities (in a perfectly competitive goods market)arrow_forwardMarginal Social Cost: P = 1 + 2 Q Graph the market. Be sure to fully and clearly label the graph, including: the Demand (D), the Marginal Private Cost (MPC), the Marginal Social Cost (MSC), the Private Equilibrium Quantity (Qpe), Private Equilibrium Price as (Ppe), the Socially Optimal Price (Ps), the Socially Optimal Quantity (Qs), and the Deadweight Loss (DWL).arrow_forwardK P % 5 My Child, My Choice If all U.S. children were vaccinated many lives would be saved, infections would be down, and medical costs would be lower. Vaccinations protect not only the kids that receive the shots but also those who can't receive them. Source: Time, June 2, 2008 Draw a graph to illustrate the private market for vaccinations and show the deadweight loss. t Draw a demand and marginal benefit curve. Label it D = MB. Draw a supply and marginal cost curve. Label it S= MC. As the quantity of vaccinations increases, the marginal external benefit from each vaccination decreases. Draw a marginal social benefit curve. Label it MSB. Draw a point at the market equilibrium. Label it 1. Draw a point at the efficient equilibrium. Label it 2. Draw a triangle that shows the deadweight loss. Label it DWL. 6 y g h & 7 O * 8 70 O k ( 9 $ O 12- 10- 8- 0- 0 Price (dollars per flu shot) 8 10 Quantity (millions of flu shots per season) >>> Draw only the objects specified in the question. 0 р…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education