
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:(c) Use the F test to test for a significant relationship. Use a = 0.05.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Ho: B1 + 0
Ha: B1 = 0
Ho: Bo # 0
Ha: Po
= 0
Ho: Bo = 0
Ha: Po + 0
Ho: B1 = 0
Ha: B1 + 0
Ho: B1 2 0
Ha: B1 < 0
Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
3.87
Find the p-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
p-value
%D
What is your conclusion?
Reject Ho. We cannot conclude that the relationship between x and y is significant.
Do not reject Ho: We conclude that the relationship between x and y is significant.
0'
Do not reject Ho. We cannot conclude that the relationship between x and y is significant.
Reject Ho.
We conclude that the relationship between x and y is significant.
129 Tutorial
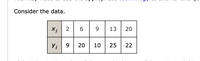
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the data.
X;
2
6
9
13
20
Y; 9 2
10
25
22
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following hypotheses are given. H0: ρ ≤ 0 H1: ρ > 0 A random sample of 12 paired observations indicated a correlation of 0.32. State the decision rule for 0.05 significance level. (Round your answer to 3 decimal places.) Compute the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Can we conclude that the correlation in the population is greater than zero? Use the 0.05 significance level.arrow_forwardYou are conducting a hypothesis test where the null hypothesis is that true population mean is less than or equal to 180. Your test will be at the 0.10 significance level. You take a sample of size n=60, and find that the sample average is 185, and the STANDARD ERROR is 15. What is the value of your test statistic? (Please answer to two decimal places. ex: 5.43)arrow_forwardtrue or false If the p-value is 0.13 and the level of significance , αα , is 0.05 in a hypothesis test for a mean, then we accept the null hypothesis.arrow_forward
- Test the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is smaller than the proportion of women who own cats at the .05 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho: HM = HF H,:PM = PF Ho: HM = PF Ho:HM = Pr Ho:PM = Pr Ho:PM PF H1: HM PF H1:HM > HF H1:HM # HF H1:PM + PF H1:PM < Pf The test is: right-tailed two-tailed left-tailed Based on a sample of 40 men, 40% owned cats Based on a sample of 40 women, 65% owned cats The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals) The p-value is: (to 4 decimals) Based on this we: O Reject the null hypothesis OFail to reject the null hypothesis Check Answerarrow_forwardre-help with this one Q3arrow_forwardYou wish to determine if there is a linear correlation between the two variables at a significance level of α=0.01. You have the following bivariate data set. x y 39.3 36.4 52.7 73 50.3 79.8 51.3 71 42 50.8 44.7 74.9 59.2 39.5 54.1 31.6 43.5 90.5 What is the critival value for this hypothesis test?rc.v. = What is the correlation coefficient for this data set?r = Your final conclusion is that... There is insufficient sample evidence to support the claim the there is a correlation between the two variables. There is sufficient sample evidence to support the claim that there is a statistically significant correlation between the two variables. Note: Round to three decimal places when necessary.arrow_forward
- Q: Using the data (provided below this question) test the hypotheses that the mean difference in writing and reading scores is zero and that the mean difference in math and science scores is zero. Use the paired-sample procedure. Use a 5% significance level if the problem doesn’t give an alpha. Note: Please only provide the t stat, p(T<=t) value and critical value. No need to explain the steps. School District Writing Reading Math Citizenship Science All Indian Hill 95 98 89 95 91 83 Wyoming 98 96 86 93 87 81 Mason City 96 92 85 94 86 72 Madiera 94 95 88 82 88 69 Mariemont 99 92 74 89 88 68 Sycamore 85 88 80 87 84 68 Forest Hills 93 91 73 85 88 67 Kings Local 92 86 78 82 78 64 Lakota 90 88 73 85 81 64 Loveland 85 93 72 86 86 61 Southwest 92 82 73 78 73 58 Fairf ield 90 86 71 83 77 57 Oak Hills 88 86 75 77 79 57 Three Rivers 87 85 66 84 77 56 Milford 82 86 72 82 76 53 Ross 84 85 66 75 78 52 West Clermont 88 83 63 73 70 48 Reading 88 80 58 76 75…arrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is significantly different than the proportion of women who own cats at the 0.02 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho: M = μF Ho: PM = PF H₁ μM μF H₁:PM > PF The test is: left-tailed right-tailed two-tailed Based on a sample of 60 men, 30% owned cats Based on a sample of 40 women, 45% owned cats The test statistic is: Ho: PM = PF H₁: PM μF (to 2 decimals) (to 2 decimals) Ho: PM = PF Ho: M = μF H₁:PM ‡ PF H₁: μM < MFarrow_forward%3D Suppose IQ scores were obtained for 20 randomly selected sets of siblings. The 20 pairs of measurements yield x = 99.21, y = 101.2, r= 0.698, P-value = 0.000, and y = 21.92 + 0.8x, where x represents the IQ score of the older child. Find the best predicted value of y given that the older child has an IQ of 92? Use a significance level of 0.05. Click the icon to view the critical values of the Pearson correlation coefficient r. The best predicted value of y is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Consider this study and identify the null hypothesis. (Remember: the null hypothesis is what Noel Hypothesis believes- that whatever interesting features you might think your data has are just coincidences.) An Uber driver's average customer rating is a 4.3. She decides to change how she greets passengers to a new greeting and see whether it changes how customers rate her. After the change, on her first 50 customers she sees an average rating of 4.47. Use u for her average rating from all customers using her new greeting. Ο Ημ 4.3 Hou > 4.3 Hoiu #4.3 Hou = 4.47 O Hou < 4.47 HoH+4.47arrow_forwardPls help I need in 1 hourarrow_forwardConsumer Reports did a survey of 1100 adults and found that 565 were unhappy that their food did not look like the picture in the menu. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the majority of adults are annoyed by food that does not look like the picture in the menu. Identify the null and alternate hypotheses. TTTArial 3 (12pt) v T- = - E·Varrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman