
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
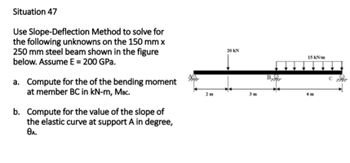
Transcribed Image Text:Situation 47
Use Slope-Deflection Method to solve for
the following unknowns on the 150 mm x
250 mm steel beam shown in the figure
below. Assume E = 200 GPa.
a. Compute for the of the bending moment
at member BC in kN-m, MBc.
b. Compute for the value of the slope of
the elastic curve at support A in degree,
ӨА.
20 KN
15 kN/m
4m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A beam is subjected to equal bending moments of M₂ = 3300 N-m. The cross-sectional dimensions are b = 190 mm, c = 26 mm, d = 75 mm, and t = 5 mm. Determine: (a) the centroid location, the moment of inertia about the z axis, and the controlling section modulus about the z axis. (b) the bending stress at point H. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (c) the bending stress at point K. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (d) the maximum bending stress produced in the cross section. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. M₂ N y| M₂ (typ) Z- b H K darrow_forwardA simply supported beam is subject to a downwards uniform distributed load, w, as shown below. B A uniform distributed load, w L1 L2 The cross-section of the beam is constant with second moment of area I = 3750 mm², and Young's elastic modulus is E = 200 GPa. The distributed load has magnitude w = 220 N/m. If Point B is distance L₁ (Point C), calculate: the downwards vertical deflection at Point B: C C 435 mm from the left end (Point A) and distance L2 = 385 mm from the right end Round your answer to 3 significant figures. X [Units: mm]arrow_forwardThe figure shows a soil profile with a silty sand (y = 17 kN/m²; ysat = 19.2 kN/m3) underlain by high plasticity clay (ysat =18.8 kN/m³) and a peat layer (Ysat =15 kN/m³), followed by dense sand. To expedite consolidation and minimize future settlement, an additional 1.75-m thick fill material, compacted to a unit weight of 20.1 kN/m³, will be placed on top of the silty sand layer. The fill load will be left in place for 18 months, after which construction will begin over the compacted fill. Fill load (kN/m3) 1.5 m Silty sand GWT 1.5 m 3.2 m 4 m Clay V •A NPiezometer 1.8 m Peat Dense sand Undisturbed samples collected from the clay and organic Peat layers had the following properties: Layer C. C. c, (cm³/sec) Clay 0.31 0.048 0.006 1.08 Peat 7.2 0.273 0.029 6.4 Are the layers singly or doubly drained? Explain. Estimate the time for 99% primary consolidation in each layer. Estimate the total consolidation settlement under the action of the fill load. Consider both the clay and peat…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning