
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
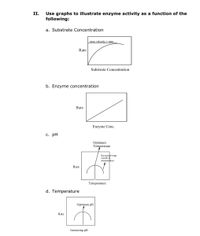
Transcribed Image Text:## Illustrating Enzyme Activity with Graphs
**II. Use graphs to illustrate enzyme activity as a function of the following:**
### a. Substrate Concentration
- **Graph Description:** The graph shows the relationship between substrate concentration and the rate of reaction. It starts with a steep increase in rate as substrate concentration increases, eventually leveling off at a point labeled "max velocity or Vmax." This indicates that the enzyme activity reaches a maximum rate and does not increase further with additional substrate.
### b. Enzyme Concentration
- **Graph Description:** This graph illustrates a linear relationship between enzyme concentration and the rate of reaction. As enzyme concentration increases, the rate of reaction increases proportionally, showing a direct correlation.
### c. pH
- **Graph Description:** The graph depicts enzyme activity as a function of pH. It indicates an optimum pH where the rate of reaction is highest. The curve shows enzyme activity dropping off at pH levels above or below this optimum due to denaturation or reduced efficacy.
### d. Temperature
- **Graph Description:** This graph illustrates enzyme activity as it varies with temperature. It has a peak indicating the optimum temperature for activity. Beyond this peak, particularly at higher temperatures, enzyme activity decreases due to denaturation.
These graphs highlight how various factors such as substrate concentration, enzyme concentration, pH, and temperature affect enzyme activity, providing insights into the optimal conditions for enzyme functionality.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nonearrow_forward15) The graph at right shows the results of reaction rate vs. substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menten type enzyme 16) Th a. True b. False* reaction rate substrate concentrationarrow_forwardV 23. The graph below is a graph of Vmax (a) Label the graph clearly with both the Vmax and the Km. Estimate the Km from this graph giving the correct units. v/Vmax 1.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 vs [S] for an enzyme. Enzyme Activity vs [Substrate] :0.2 0.4 Substrate (HM): 0.6 (b) If the Vmax = 25 mmoles per minute per µmole of enzyme calculate the Keat and the specificity constant."arrow_forward
- The following data were collected in the study of a new enzyme and an inhibitor of the new enzyme: Vo (nmol/sec) [S] (µM). 1.3 - Inhibitor + Inhibitor 2.50 0.62 2.6 4.00 1.42 6.5 6.30 2.65 13.0 7.60 3.12 26.0 9.00 3.58 What is the Vmax of the inhibited enzyme reaction?arrow_forwardThe enzymatic activity of an enzyme with Kg = 2 mM that converts substrate S into product P is measured at an initial substrate concentration S, of 10 µM. After 5 min, the substrate concentration is halved. What is the rate constant k, the maximal velocity vmax and the concentration of product after 12 min?arrow_forward1. The concentration of substrate X is high. What happens to the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction if the concentration of substrate X is reduced? Explain. 2. An enzyme has an optimum pH of 7.2. What is most likely to happen to the activity of the enzyme if the pH drops to 6.2? Explainarrow_forward
- Explain how running a reaction with the enzyme aldolase at a pH of 14 affects its activity Enzyme Activity e Activity 765432TO Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity 0 6543 2 6 Solution pH 8 a) It significantly diminishes activity because enzyme is denatured b) It significantly diminishes activity because the enzyme becomes too reactive Oc) It will quadruple its activity because enzyme is denatured and free Question 9 (5 points) Estimate the optimum pH required for maximum enzyme activity 10 d) It will double its activity because enzyme now has more active sites 12 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activityarrow_forwardYou measure the kinetics of an enzyme as a function of substrate concentration using the Lineweaver-Burke equation. The enzyme concentration is maintained constant at a level of 1 μM. From these data, determine the equation of the line, Vmax, KM, and kcat for the enzyme. [S], μM Velocity, μM/min 2 2.9 3 3.8 4 4.4 5 5.0 6 5.4 7 5.8 8 6.2 9 6.4 10 6.7 The Lineweaver-Burke equation is 1V=1V= ____________(1[S])(1[S]) + ___________. Therefore, the Vmax is ____________ μM/min, KM is ____________ μM, and kcat is ____________ /min. Round-off all answers to four (4) decimal places.arrow_forwardDetermine the Vo as a function of Vmax when the substrate concentration is equal to 10 KM or 20 KM. What does this tell you about an enzyme ability to reach Vmax?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON