
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
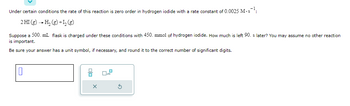
Transcribed Image Text:Under certain conditions the rate of this reaction is zero order in hydrogen iodide with a rate constant of 0.0025 M.s¹:
2 HI(g) → H₂(g) +1₂ (8)
Suppose a 500. mL flask is charged under these conditions with 450. mmol of hydrogen iodide. How much is left 90. s later? You may assume no other reaction
is important.
Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to the correct number of significant digits.
0
X
x10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider this reaction: 2H,PO, (aq) → P,O; (aq)+ 3H,0 (aq) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate = (0.0362 s)[H,PO,] Suppose a vessel contains H,PO, at a concentration of 0.190M. Calculate the concentration of H,PO, in the vessel 22.0 seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. ?arrow_forwardYou have a reaction: A + B --> C The reaction is first order with respect to A and 2nd order with respect to B. If 1.2 mol of A is mixed with 2.5 mol of B to make a 1.000 L solution and the rate of the reaction is 1.9 M/s, what is the rate constant (k)? Your answer should have no units.arrow_forwardUnder certain conditions the rate of this reaction is zero order in dinitrogen monoxide with a rate constant of 0.0051 M.s 1: 2N₂O(g) →2N2(g) +0₂ (g) Suppose a 5.0 L flask is charged under these conditions with 250. mmol of dinitrogen monoxide. After how much time is there only 125. mmol left? You may assume no other reaction is important. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits. = X x10arrow_forward
- Under certain conditions the rate of this reaction is zero order in hydrogen iodide with a rate constant of ·0.0040Ms−1:2HI(g)→H2(g)+I2(g) Suppose a 300.mL flask is charged under these conditions with 500.mmol of hydrogen iodide. After how much time is there only 250.mmol left? You may assume no other reaction is important. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardConsider this reaction: 2H,PO, (aq)→ P,0, (aq) + 3H,0 (aq) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate = (14,5 M)[H,PO.] Suppose a vessel contains H,PO at a concentration of 1.17 M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of H,PO to decrease by 84.0%. You may 4 assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardDeducing a rate law from the change in concentration over time A chem raduate student is studying the rate of this reaction: 2N,05 (g) → 2N,0,(g)+O, (g) He fills a reaction vessel with N,O, and measures its concentration as the reaction proceeds: time (seconds) N,0s] 0.0300 M 1.0 0.0114 M 2.0 0.00707 M 3.0 0.00511 M 4.0 0.00401 M Use this data to answer the following questions. Write the rate law for this reaction. rate = k I %3D x10 Calculate the value of the rate constant k. k = 0 Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure vour answer has the correct unit svmbol. Explanation Check 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. IIarrow_forward
- Consider the following balanced chemical equation: H2O2 (aq) + 3 l"(aq) + 2 H* (aq) → l3 (aq) + 2 H2O (1) In the first 32.7 seconds of the reaction, the concentration of H2O2 decreased from 1.5 M to 0.72 M. What is the average reaction rate over this time interval (in mol L-1 s-1)? Remember: if you want to express an answer in scientific notation, use the letter "E". For example "4.32 x 104" should be entered as "4.32E4". Answer:arrow_forwardThe rate of the reaction NO2+ CO - NO + CO2 depends only on the concentration of nitrogen dioxide, NO2. The following data were collected. time (s) [NO] (M) 0.500 1.20 x 10 0.444 3.00 x 10 0.381 4.50 x 10 0.340 9.00 x 10 0.257 1.80 x 10 0.174 When entering values in scientific notation follow this format: 6.022 x 1023 would be 6.022e23 (no spaces) 1. Using graphical analysis (Google Sheet et) determine the overall reaction order. (0.1.2) Be sure to upload a screenshot copy of the the Google sheet for question 2 in the next question box. 2 Determine the value of the rate constant for the reaction (do not round answer). 3. Calculate the [NO2l, at 2:40 x 10 s. (show answer to 3 places after the decimal) 182 4. Determine the t, for the reaction. (round answer to the whole number)arrow_forwardConsider this reaction: H,CO, (ag) – H,0 (aq) + CO, (ag) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate = (9.70 x 10-4s)H,co,] Suppose a vessel contains H,CO, at a concentration of 0.470 M. Calculate the concentration of H,CO, in the vessel 680. seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. x10arrow_forward
- Under certain conditions the rate of this reaction is zero order in hydrogen lodide with a rate constant of 0.0038 M's ': 2 HI(g) H,(g)+1,(g) Suppose a 4.0L flask is charged under these conditions with 100, mmol of hydrogen lodide. After how much time is there only 50.0 mmol left? You may assume no other reaction Is important. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardConsider this reaction: 2HI (g) → H₂ (g) + 1₂ (g) At a certain temperature it obeys this rate law. rate = (0.00315 M¹-s¯¹) [HI] ² S olo Suppose a vessel contains HI at a concentration of 1.16M. Calculate the concentration of HI in the vessel 970. seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Ar Round your answer to 2 significant digits. M x10 X Ś ?arrow_forwardUnder certain conditions the rate of this reaction is zero order in ammonia with a rate constant of 0.0032 M's : 2 NH, (g) → N2 (g) +3 H, (g) Suppose a 3.0 L flask is charged under these conditions with 400. mmol of ammonia. How much is left 10. s later? You may assume no other reaction is important. olo Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 2 significant digits. Ararrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY