
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Convert the strength of selected materials given in the accompanying table from MPa to ksi, where 1000 lbf ⁄in2 = 1 ksi .
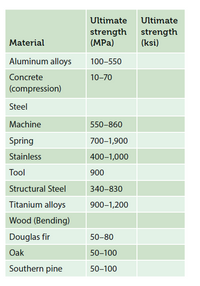
Transcribed Image Text:Ultimate
Ultimate
strength
(MPa)
strength
(ksi)
Material
Aluminum alloys
100–550
Concrete
10-70
(compression)
Steel
Machine
550-860
Spring
700-1,900
Stainless
400–1,000
Tool
900
Structural Steel
340-830
Titanium alloys
900–1,200
Wood (Bending)
Douglas fir
50-80
Oak
50–100
Southern pine
50–100
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The stress in a steel bar is given as 25,0000 kN/m² and length of the bar is 50 m. Calculate the shortening of the bar if E = 2.14 × 108 N/mm²arrow_forward2. A cube made of an alloy with dimensions of 50mmx50mm×50mm is placed into a pressure chamber and subjected to a pressure of 80 MPa. If the modulus of elasticity of the alloy is 200 GPa and Poisson's ratio is 0.30, what will be the length of each side of the cube, assuming that the material remains within the elastic region?arrow_forwardThe assembly shown in the figure consists of an aluminum tube AB and a steel rod BC. The rod is attached to the tube through the rigid collar at B and passes through the tube. The cross-sectional area of the rod is 75 mm2 and the cross-sectional area of the tube is 400 + UV in mm2, where UV is 99. A tensile load of 80 kN is applied to the rod. Take Est = 200 GPa for the steel rod, Eal = 70 GPa for the aluminum tube. Determine: (a) the displacement of end C with respect to end B (i.e., the elongation of the steel rod), (b) the displacement of end B with respect to the fixed end A (i.e., the shrink of the aluminum tube), (c) the displacement of the end C of the rod (i.e., (a) + (b)).arrow_forward
- For the state of stress (MPa) shown in the figure below. The ratio of Major principal stress to minor principal stress will be (up to two decimal places) 10 5 15+ + 15 5 10 LOarrow_forwardA brass alloy rod having a cross sectional area of 0.24 in.2and a modulus of 16 * 106 psi is subjected to a tensile load. Plastic deformation was observed to begin at a load of 8,944 lb.a. Determine the maximum stress that can be applied without plastic deformation.b. If the maximum length to which a specimen may be stretched without causing plastic deformation is 3.28 in., what is the original specimen length?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning