
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
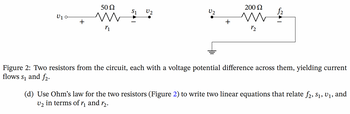
Transcribed Image Text:**Figure 2: Two resistors from the circuit, each with a voltage potential difference across them, yielding current flows \( s_1 \) and \( f_2 \).**
Diagram Explanation:
- The left section shows a resistor labeled \( r_1 \) with a resistance of 50 Ω, which is connected between voltage points \( v_1 \) and \( v_2 \). The current flowing through this resistor is denoted as \( s_1 \).
- The right section shows another resistor labeled \( r_2 \) with a resistance of 200 Ω, which is connected between voltage \( v_2 \) and the ground (earth), with the current through this resistor denoted as \( f_2 \).
**(d) Use Ohm’s law for the two resistors (Figure 2) to write two linear equations that relate \( f_2, s_1, v_1, \) and \( v_2 \) in terms of \( r_1 \) and \( r_2 \).**
![(e) Rewrite your system of equations as a single matrix equation of the form
\[
B \begin{bmatrix} f \\ s \\ v \end{bmatrix} = 0.
\]
Keep in mind that \( f, s, v \in \mathbb{R}^2 \).
Give an expression for the matrix \( B \). What are the dimensions of matrix \( B \)?
(f) Are the columns of \( B \) linearly independent? Justify.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/1da88d38-e18c-40f1-9bb8-69bad3269ec7/bc92d4d1-8d7b-41de-96ac-156839bf21be/m4roztd_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:(e) Rewrite your system of equations as a single matrix equation of the form
\[
B \begin{bmatrix} f \\ s \\ v \end{bmatrix} = 0.
\]
Keep in mind that \( f, s, v \in \mathbb{R}^2 \).
Give an expression for the matrix \( B \). What are the dimensions of matrix \( B \)?
(f) Are the columns of \( B \) linearly independent? Justify.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Summarize the details given:
Given Data:
Two DC resistive circuits with,
- Voltages
- Currents
- Resistors
To Find:
d. The linear equations relating in terms of
.
e. The expression and the dimension of B which in the form of .
f. Are the columns of the matrix B linearly independent or not?
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 18 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Initially a 10 V battery is in series with a 100 ohm resistor and a 2 mH inductor. After a long time, a switch is thrown to remove the battery from the circuit, and replacing it with another 100 ohm resistor (and so the inductor ends up with two 100 ohm resistors In series). What is the current at t=0 s (immediately after the switch is thrown)?What is the current at t=5 ms later?arrow_forwardUsing Kirchhoff’s rules, analyze the circuit below where R1 = 3.00 kΩ, R2 = 7.00 kΩ, R3 = 2.00 kΩ and ε1 = 60.0 V, ε2 = 40.0 V, ε3 = 50.0 V (g) find the potential difference between points c and f.arrow_forwardGive an independent set of linear that can ve solved for the current shown. Use the Junction Rulearrow_forward
- Assume right most resistance is 12.5 ohm..arrow_forwardAfter the jumper wire is connected across D1 in step 4, what is the new potential of the low side of D1, relative to ground ?arrow_forwardP1 Is P2 Vs = P3 VA Value Powers Value Sources PRI Pr2 1250.000 mw Vs 10 V 1250.000 mw Is 0.500 A PR3 1250.000 mw Find V4arrow_forward
- Consider the circuit shown below. R1 = 100 N R2 = 100 N C1 10 mF V = 12 V R3 3 100 N C, = 4.7 mF %3D %3D a. After the switch has been closed for a very long time, what are the voltages across the capacitors C1 and C2? Hint for (a) Voltage across C1 is V, and voltage across C2 is V. b. After the switch has been closed for a very long time, what is the energy stored in each capacitor? Hint for (b) Energy stored on C, is J, and energy stored on C, is J.arrow_forwardFind i1 i2 , and i3 in the figurearrow_forwardR148 R149 R150 If R148 is 18 Ohms, R149 is 13 Ohms, R150 is 25 Ohms, and there is 4 Amps flowing through R150, what is the current through R148? Please show 3 decimal places and don't include units in your answer (i.e. don't include A in your answer).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,