
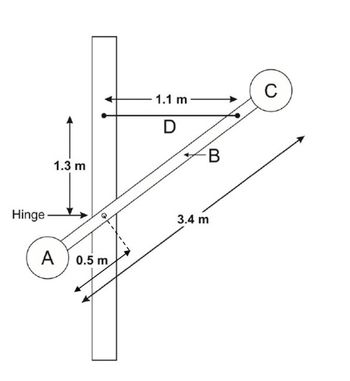
Two weights, A and C, are fixed to a bar, B. Their masses are: A = 60 kg, B = 230 kg,
C = 45 kg. B is, in turn, connected to a fixed vertical post by a hinge and a support cable
D. The geometry of the system is shown at right. Treat weights A and C as point masses
a)What is the tension in support cable D? Be sure to include a detailed free
body diagram to accompany your analysis.
b) What is the magnitude of the force provided by the hinge?
c) What is the moment of inertia of the A + B + C as a rigid system, for rotation
about the hinge?
For analysis, break the beam into a short piece to the left of the
hinge, and a separate longer piece to the right of the hinge.
If the support cable D on should break,
d) what is the angular acceleration of the beam and weights at the moment the cable breaks?
e) what is the magnitude of the linear acceleration experienced by each of the weights, A and C, at moment the cable breaks?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- The truss shown below has a hinge support at point A, a horizontal roller at point B, and is subjected to two point loads (P1 and P2). If P1- 30 kN and P2 - 55 kN, what is the force, in kN, in member AE? NOTE: Enter a positive value if the member is in Tension and a negative value if the member is in Compression. PI (KN) 60 A 4 m 4 m P2 (kN)arrow_forwardA horizontal L=1.2 m long mb=14 kg uniform bar is hinged on the left end and pulled at the right end by a cable. The cable makes 23° angle with horizontal. A 24 kg store sign is suspended below the bar at d=0.18 m from the right end. Find the magnitude of horizontal hinge force.arrow_forwardВ A Ь 30° 2b E a- 130⁰ K Н сarrow_forward
- The structure shown in the figure carries a 5000 kg platform. Considering that the structure has also singular forces at joints C and D:a) Determine the reactions at the supports, b) Also determine the forces in members AB, AC, AD, and BD. State whether each member is in tension or compression. Note 1: Take the gravitational acceleration as 10 m/s2.Note 2: Assume that all connections between members are pin joints.arrow_forwardThe structure ABCD (shown below) is designed to support a finite mass hanging from a cable, DF, attached to the structure at point D. x=8m, y=6 m, and z-15 m. The structure is mounted to the ground by a hinge at B and a roller at C and is also supported by a horizontal cable, AE, attached to the wall. The mass of the object hanging from cable DF is 500 kg. The tension in the support cable AE is 1.000 × 10³ N. Determine the force in each member and the reaction forces. E Darrow_forwardA 1,400-N uniform boom at o = 58.5° to the horizontal is supported by a cable at an angle 0 = 31.5° to the horizontal as shown in the figure below. The boom is pivoted at the bottom, and an object of weight w = 1,850 N hangs from its top. w Pivot (a) Find the tension in the support cable. kN (b) Find the components of the reaction force exerted by the pivot on the boom. (Assume the positive x-direction is to the right and the positive y-direction is upward. Include the sign of the value in your answer.) horizontal component kN vertical component kNarrow_forward
- A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in the figure below, with AC = BC = { = 4.40 m. A painter of mass m = 73.0 kg stands on the ladder d = 3.00 m from the bottom. E d B Assuming the floor is frictionless, find the following. (Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately.) (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder (b) the normal forces at A and B at A at B (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half rightward component N upward component N Need Help? Master It Additional Materials еBookarrow_forwardThe lid shown has a mass, m = 60 kg, and is held in position by rod AB. The rod is held in place by rounded surfaces at A and B, where B is right at the edge of the lid. The hinges at C and D rotate smoothly and only the hinge at C provides a reaction force along its axis (the x-direction). a = 950 mm, b = 300 mm, c = 55 degrees Determine A) Reactions at hinge C and D B) Reaction force in rod AB C) The minimum coefficient of friction that is needed between the rod and the lid to maintain this positionarrow_forward2. In the figure below, the cable BCD passes over a smooth pulley and is attached to a ring at B and a ring at D. Cables AB and DE are attached to the rings at B and D and to the ceiling at A and E. If the maximum tension in any cable cannot exceed 10 kN, what are the maximum weights W1 and W2? Smooth Pulley E 60° в 45 60° 65° W, W2arrow_forward
- Problem 1.6-4 The inclined ladder AB supports a house painter (82 kg) at C and the self weight (q = 36 N/m) of the ladder itself. Each ladder rail (1, = 4 mm) is supported by a shoe (f, = 5 mm) which is attached to the ladder rail by a bolt of diameter d, = 8 mm. B B, (a) Find support reactions at A and B. (b) Find the resultant force in the shoe bolt at A. (c) Find maximum average shear (7) and bearing (o,) stresses in the shoe bolt at A. Typical rung H =7 m -Ladder rail (1, = 4 mm) Shoe bolt at A Shoe bolt (d, = 8 mm) Ladder shoe (1, = 5 mm) A a = 1.8 m b = 0.7 m Ay Assume no slip at A Section at base E==============: = 36 N/marrow_forwardThe linkage shown is used in a vehicle suspension system. Find the forces indicated below when a static force of F = 1000 lb is applied to the tire at point C at an angle of 0 = 17° as shown. Assume the connection of the wheel to member AB is rigid. 1 h₁ K: LOFF 0 W₁ h₂ h3 h4 h5 B W₁₂ AXHIMAL W4 hs: h₂ cc i❀O BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom W3 - W₁ Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value Variable Value h₁ 6.6 in W1 7.5 in 16.6 in W2 4.6 in 14.6 in W3 8.3 in 10.2 in W4 6.2 in 5.2 in W5 9.7 inarrow_forwardSITUATION 1: As shown in the figure, a weight W = 50 kN hangs from two wires. Given that θ = 30° and α = 45°. Calculate the tension (kN) in AC. (Answer: 36.60) Calculate the tension (kN) in BC. (Answer: 44.83)arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





